在第二章中,我们讨论了如何求一个函数的导函数问题,本章将讨论它的反问题,即要寻找一个可导函数,使它的导函数等于已知函数。——高等数学同济版
习题4-1 不定积分的概念与性质
本节主要介绍不定积分的基础定义与性质。
2.求下列不定积分:
(13)
∫(2ex+x3)dx;
解
∫(2ex+x3)dx=2∫exdx+3∫xdx=2ex+3ln∣x∣+C.
(这道题在积分时容易忘记加上绝对值)
习题4-2 换元积分法
本节把复合函数的微分法反过来用于求不定积分,利用中间变量的代换,得到复合函数的积分法,称为换元积分法,简称换元法。
本节主要介绍了两类换元积分法。
2.求下列不定积分(其中
a、
b、
ω、
φ均为常数)
(16)
∫xlnxlnlnxdx;
解
∫xlnxlnlnxdx=∫lnxlnlnxd(lnx)∫lnlnxd(lnlnx)=ln∣lnlnx∣+C.
(这道题表明在题目中包含
x>0这个条件时,
∫xdx=lnx)
(21)
∫(xlnx)21+lnxdx;
解
∫(xlnx)21+lnxdx=∫(xlnx)2d(xlnx)=−xlnx1+C.
(这道题主要利用
(1+lnx)dx=d(xlnx)求解)
(35)
∫x2−x−2xdx;
解
∫x2−x−2xdx=∫(x−2)(x+1)xdx=∫31(x−22+x+11)dx=32ln∣x−2∣+31ln∣x+1∣+C.
(这道题利用分解因式并进行凑整进行求导)
(36)
∫a2−x2
x2dx(a>0);
解 设
x=asinu(−2π<u<2π),则
a2−x2
=acosu,dx=acosudu,于是
∫a2−x2
x2dx=∫a2sin2udu=a2∫21−cos2udu=2a2(u−2sin2u)+C=2a2arcsinax−2xa2−x2
+C.
(这道题在进行换元时,为了保证只含根号的式子不小于0,对于
u进行了大小限制)
(37)
∫xx2−1
dx;
解 当
x>1时,
∫xx2−1
dxx=t1
−∫1−t2
dt=−arcsint+C=−arcsinx1+C.
当
x<−1时,
∫xx2−1
dxx=t1
∫1−t2
dt=arcsint+C=arcsinx1+C.
故在
(−∞,−1)或
(1,+∞)内,有
∫xx2−1
dx=−arcsin∣x∣1+C
(这道题表明对于不连续的不定积分可以进行分段求解)
(38)
∫(x2+1)3
dx;
解 设
x=tanu(−2π<u<2π),则
x2+1
=secu,dx=sec2udu,于是
∫(x2+1)3
dx=∫cosudu=sinu+C=1+x2
x+C.
(这道题说明对于可以取任意值的变量可以替换成
tanx求解)
(39)
∫xx2−9
dx;
解 当
x>3时,令
x=3secu(0⩽u<2π),
∫xx2−9
dx=∫3tan2udu=3∫(sec2u−1)du=3tanu−3u+C=x2−9
−3arccosx3+C.
当
x<−3时,令
x=3secu(2π<u⩽π),
∫xx2−9
dx=−∫3tan2udu=−3∫(sec2u−1)du=−3tanu+3u+C′=x2−9
+3arccosx3+C′=x2−9
−3arccos−x3+C+3π.
故可以统一写作
∫xx2−9
dx=x2−9
−3arccos∣x∣3+C(这道题表明对于
x>1的
x变量可以使用
secu来换元)
(41)
∫1+1−x2
dx;
解 令
x=sint(−2π<t<2π),则
1−x2
=cost,dx=costdt,于是
∫1+1−x2
dx=∫1+costcostdt=∫2cos22t2cos22t−1=t−tan2t+C=t−1+costsint+C=arcsinx−1+1−x2
x+C.
(这道题表明当
x∈(−1,1)时,可以用
sinx替换)
(42)
∫x+1−x2
dx;
解 设
x=sint(−4π<t<2π),则
1−x2
=cost,dx=costt,于是
∫x+1−x2
dx=∫sint+costcostdt.
记
I1=∫sint+costcostdt,I2=∫sint+costsintdt,利用
I1+I2I1−I2=∫dt=t+C,=∫sint+costcost−sintdt=∫sint+costd(cost+sint)=ln∣sint+cost∣+C.
求得
I1=∫sint+costcostdt=21(t+ln∣sint+cost∣)+C,
即求得在
(−22
,1)内,有
∫x+1−x2
dx=21(arcsinx+ln∣x+1−x2
∣)+C.
再设
x=sint(−2π<t<−4π),重复上面过程,可得在
(−1,−22
)内有与上面不定积分形式相同的结果。从而在
(−1,−22
)或
(−22
,1)内,有
∫x+1−x2
dx=21(arcsinx+ln∣x+1−x2
∣)+C.
(这道题主要是利用自变量的区间来进行分段确定不定积分的结果)
(43)
∫(x2+1)2x3+1dx;
解 设
x=tant(−2π<t<2π),则
x2+1=sec2t,dx=sec2tdt,于是
∫(x2+1)2x3+1dx=∫sec2ttan3t+1dt=∫costcos2t−1d(cost)+∫21+cos2tdt=21cos2t−lncost+2t+41sin2t+C=21cos2t−lncost+2t+21sintcost+C
按
tant=x作辅助三角形,便有
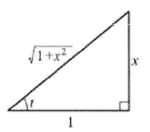
cost=1+x2
1,sint=1+x2
x.
于是
∫(x2+1)2x3+1dx=2(1+x2)1+x+21ln(1+x2)+21arctanx+C.
(这道题表明有时可以借助辅助三角形求解)
习题4-3 分部积分法
本节主要介绍了分部积分法。
求下列不定积分:
18.
∫x2ln3xdx
解
∫x2ln3xdx=∫−ln3xd(x1)=−xln3x−3∫ln2xd(x1)=−xln3x−3[xln2x+2∫lnxd(x1)]=−xln3x+3ln2x+6lnx+6+C.
(这道题说明可以采用不同的分部方式来进行计算)
习题4-4 有理函数的积分
本节主要介绍了有理函数的积分及可化为有理函数的积分。
求下列不定积分:
5.
∫x3+13dx.
解
∫x3+13dx=∫(1+x)(x2−x+1)3dx=∫(x+11+x2−x+12−x)dx=ln∣1+x∣−21∫x2−x+1(x2−x+1)′dx+23∫x2−x+11dx=ln∣1+x∣−21ln(x2−x+1)+3
∫(3
2x−1)2+11d(3
2x−1)=ln∣1+x∣−21ln(x2−x+1)+3
arctan3
2x−1+C.
(这道题先使用待定系数确定分解后的因式的分子上的系数,再对不可分解的因式进行拆分,分母化为平方和并进行积分)
12.
∫(x2+1)2(x+1)2dx.
解
∫(x2+1)2(x+1)2dx=∫(x+1)2x2+1dx+∫(x+1)22xdx=arctanx−x2+11+C.
(这道题需要把分子上的式子拆分成易于积分的几部分再进行运算)
13.
∫(x2+x+1)2−x2−2dx
解
∫(x2+x+1)2−x2−2dx=∫[−x2+x+11+(x2+x+1)2x−1]dx=−∫x2+x+11dx+21∫x2+x+1d(x2+x+1)−23∫(x2+x+1)21dx.
令
u=x+21,并记
a=23
,则
∫(x2+x+1)21dx=∫(u2+a2)21du=2a21[u2+a2u+∫u2+a21du]=2a2(u2+a2)u+2a21∫u2+a21du.
由此得
====∫x2+x+11dx+23∫(x2+x+1)21dx∫u2+a21du+23[2a2(u2+a2)u+2a21∫u2+a21du]4a2(u2+a2)3u+(4a23+1)∫u2+a21du4a2(u2+a2)3u+a1(4a23+1)arctanau+C12(x2+x+1)2x+1+3
4arctan3
2x+1+C1.
因此有
∫(x2+x+1)2−x2−2dx=−2(x2+x+1)1−2(x2+x+1)2x+1−3
4arctan3
2x+1+C.
(这道题通过逐步代换得到结果)
15.
∫3+cosxdx.
解 令
u=tan2x,则
∫3+cosxdx=∫3+1+u21−u21⋅1+u22du=∫2+u21du=2
1arctan2
u+C=2
1arctan2
tan2x+C.
(当式子中有三角函数时,可以用正切值代替)
习题4-5 积分表的使用
本节主要介绍了如何查阅积分表及其相关变形。(本节不在考纲中)
写在最后
总习题四难点比较多,综合性强,在下一篇《第四章 不定积分(二)》中详述。
如果觉得文章不错就点个赞吧。另外,如果有不同的观点,欢迎留言或私信。
欢迎非商业转载,转载请注明出处。
另,参考的积分表及公式见附录。

