在三维空间中,给定一固定旋转轴,任意初始向量绕旋转轴旋转任意角度,可表示为 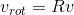 ,其中,v 表示旋转前向量,
,其中,v 表示旋转前向量, 表示旋转后向量,R 表示旋转矩阵,该矩阵参数与固定旋转轴坐标,旋转角度有关。下面使用图示推导旋转矩阵 R:
表示旋转后向量,R 表示旋转矩阵,该矩阵参数与固定旋转轴坐标,旋转角度有关。下面使用图示推导旋转矩阵 R:
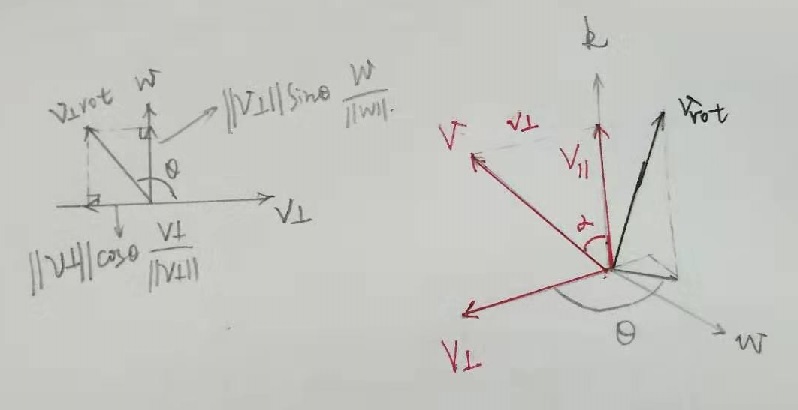
如上图所示,单位向量  为固定旋转轴,原向量 v 旋转
为固定旋转轴,原向量 v 旋转  后为
后为  ;
;
分解原向量 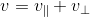 ,向量 v 与向量 k(或者
,向量 v 与向量 k(或者  ) 的夹角为
) 的夹角为 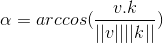 ,该值已知;
,该值已知;
向量  构成直角三角形,则有:
构成直角三角形,则有:  ,
, ;
;
向量叉乘 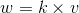 ,其方向垂直于
,其方向垂直于 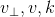 构成的平面,w 的模长为
构成的平面,w 的模长为  ,则有
,则有 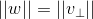 ,且两向量正交;
,且两向量正交;
以上向量 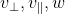 构成三维空间已知正交向量基,
构成三维空间已知正交向量基, 可表示:
可表示: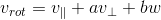 ,在
,在  向量构成平面上,
向量构成平面上,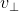 旋转
旋转 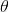 后为:
后为:
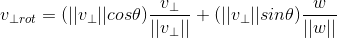 ,
, 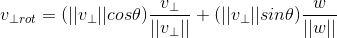 ,由于
,由于 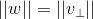 ,进一步化简为:
,进一步化简为:
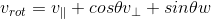 ;
;
定义向量 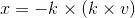 ,其方向与
,其方向与  平行,其模长为
平行,其模长为 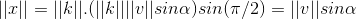 ,则
,则 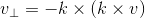 ;
;
引入向量 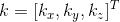 的叉积矩阵
的叉积矩阵  ,叉积运算可转换为矩阵运算
,叉积运算可转换为矩阵运算  ;
;
改写 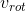 线性组合
线性组合 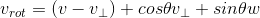 ,引入叉积矩阵 K得:
,引入叉积矩阵 K得:
 ,
,
则旋转矩阵 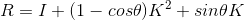 。
。
以下给出代码实现:
1 void GetRotateMatrix(Matrix<float>& Q, Vector<float>& axis, float theta) 2 { 3 // 使用罗德里格斯公式(Rodriguez formula) 4 5 // 构造单位向量 6 float len = sqrt(axis.data[0] * axis.data[0] + 7 axis.data[1] * axis.data[1] + axis.data[2] * axis.data[2]); 8 axis.data[0] = axis.data[0] / len; 9 axis.data[1] = axis.data[1] / len; 10 axis.data[2] = axis.data[2] / len; 11 12 // 构造叉积矩阵K 13 Matrix<float> K(3, 3); 14 *(K.data + 0) = 0.; 15 *(K.data + 1) = -axis.data[2]; 16 *(K.data + 2) = axis.data[1]; 17 *(K.data + K.step * 1 + 0) = axis.data[2]; 18 *(K.data + K.step * 1 + 1) = 0.; 19 *(K.data + K.step * 1 + 2) = -axis.data[0]; 20 *(K.data + K.step * 2 + 0) = -axis.data[1]; 21 *(K.data + K.step * 2 + 1) = axis.data[0]; 22 *(K.data + K.step * 2 + 2) = 0.; 23 24 // 求K^2 25 Matrix<float> K_Temp; K_Temp = K; 26 Matrix<float> K_2; K_2 = K; 27 K_2.Multiply(K, K_Temp); 28 29 // 求变换矩阵Q(Q = I + (1 - cos(theta))K^2 + sin(theta)K) 30 K.ScalarMultiply(sin(theta)); 31 K_2.ScalarMultiply(1. - cos(theta)); 32 K_Temp.SetIdentity(); 33 34 Q.SetZero(); 35 Q.Add(K); 36 Q.Add(K_2); 37 Q.Add(K_Temp); 38 39 // 得到旋转矩阵后,使用旋转矩阵Q将任意点沿axis轴旋转theta幅度 40 }
1 template<typename TYPE> struct Matrix 2 { 3 int rows; 4 int cols; 5 int step; 6 7 TYPE* data; 8 9 Matrix() 10 { 11 rows = cols = step = 0; 12 data = 0; 13 } 14 15 Matrix(int _rows, int _cols) 16 { 17 rows = _rows; 18 cols = _cols; 19 step = _cols; 20 data = (TYPE*)malloc(sizeof(TYPE) * rows * cols); 21 memset(data, 0, sizeof(TYPE) * rows * cols); 22 } 23 24 ~Matrix() 25 { 26 if(!data) free(data); 27 } 28 29 void operator = (Matrix<TYPE>& _mat) 30 { 31 rows = _mat.rows; 32 cols = _mat.cols; 33 step = _mat.step; 34 35 if(data) free(data); 36 data = (TYPE*)malloc(sizeof(TYPE) * rows * cols); 37 memcpy(data, _mat.data, sizeof(TYPE) * rows * cols); 38 } 39 40 bool Add(Matrix<TYPE>& src1) 41 { 42 if (src1.rows != rows || src1.cols != cols) 43 return false; 44 45 for (int r = 0; r < rows; ++r) 46 for (int c = 0; c < cols; ++c) 47 { 48 *(data + r * step + c) += *(src1.data + r * src1.step + c); 49 } 50 } 51 52 void ScalarMultiply(double scalar) 53 { 54 for (int r = 0; r < rows; ++r) 55 for (int c = 0; c < cols; ++c) 56 { 57 *(data + r * step + c) = *(data + r * step + c) * scalar; 58 } 59 } 60 61 void SetZero() 62 { 63 memset(data, 0, sizeof(TYPE) * rows * cols); 64 } 65 66 void SetIdentity() 67 { 68 memset(data, 0, sizeof(TYPE) * rows * cols); 69 70 int m = cols < rows ? cols : rows; 71 for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) 72 *(data + i * step + i) = 1; 73 } 74 75 void ExchangeRows(int i, int j) 76 { 77 if(i < rows && j < rows) 78 { 79 TYPE* temp = (TYPE*)malloc(sizeof(TYPE) * rows); 80 memcpy(temp, data + i * step, sizeof(TYPE) * rows); 81 memcpy(data + i * step , data + j * step, sizeof(TYPE) * rows); 82 memcpy(data + j * step, temp, sizeof(TYPE) * rows); 83 free(temp); 84 } 85 } 86 87 bool Transpose(Matrix<TYPE>& dst) 88 { 89 if(rows != dst.cols || cols != dst.rows || !data || !dst.data) 90 return false; 91 92 for(int r = 0; r < rows; ++r) 93 { 94 TYPE* src_data = data + r * step; 95 TYPE* dst_data = dst.data + r; 96 97 for(int c = 0; c < cols; ++c) 98 { 99 *dst_data = *src_data; 100 101 ++src_data; 102 dst_data += dst.step; 103 } 104 } 105 106 return true; 107 } 108 109 110 bool Multiply(Matrix<TYPE>& src1, Matrix<TYPE>& src2) 111 { 112 if(src1.cols != src2.rows || rows != src1.rows || cols != src2.cols) 113 return false; 114 115 for(int r = 0; r < rows; ++r) 116 { 117 for(int c = 0; c < cols; ++c) 118 { 119 double value = 0.; 120 for (int i = 0; i < src1.cols; ++i) 121 { 122 value += (*(src1.data + r * src1.step + i)) * (*(src2.data + i * src2.step + c)); 123 } 124 *(data + r * step + c) = value; 125 } 126 } 127 128 return true; 129 130 } 131 132 };