先放个题目
Super_log
来源:计蒜客
https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/41299
In Complexity theory, some functions are nearly O(1)O(1), but it is greater then O(1)O(1). For example, the complexity of a typical disjoint set is O(nα(n))O(nα(n)). Here α(n)α(n) is Inverse Ackermann Function, which growth speed is very slow. So in practical application, we often assume α(n) \le 4α(n)≤4.
However O(α(n))O(α(n)) is greater than O(1)O(1), that means if nn is large enough, α(n)α(n) can greater than any constant value.
Now your task is let another slowly function log*log∗ xx reach a constant value bb. Here log*log∗ is iterated logarithm function, it means “the number of times the logarithm function iteratively applied on xx before the result is less than logarithm base aa”.
Formally, consider a iterated logarithm function log_{a}^*loga∗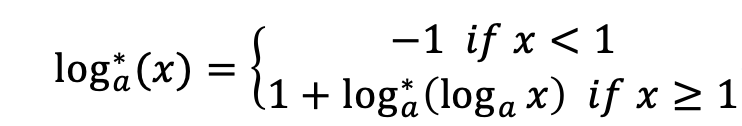
Find the minimum positive integer argument xx, let log_{a}^* (x) \ge bloga∗(x)≥b. The answer may be very large, so just print the result xx after mod mm.
Input
The first line of the input is a single integer T(T\le 300)T(T≤300) indicating the number of test cases.
Each of the following lines contains 33 integers aa , bb and mm.
1 \le a \le 10000001≤a≤1000000
0 \le b \le 10000000≤b≤1000000
1 \le m \le 10000001≤m≤1000000
Note that if a==1, we consider the minimum number x is 1.
Output
For each test case, output xx mod mm in a single line.
Hint
In the 4-th4−th query, a=3a=3 and b=2b=2. Then log_{3}^* (27) = 1+ log_{3}^* (3) = 2 + log_{3}^* (1)=3+(-1)=2 \ge blog3∗(27)=1+log3∗(3)=2+log3∗(1)=3+(−1)=2≥b, so the output is 2727 mod 16 = 1116=11.
样例输入
5 2 0 3 3 1 2 3 1 100 3 2 16 5 3 233
样例输出
1 1 3 11 223
这题就是简单的利用扩展欧拉定理来进行降幂,然后来一个递归的过程,把公式图贴上
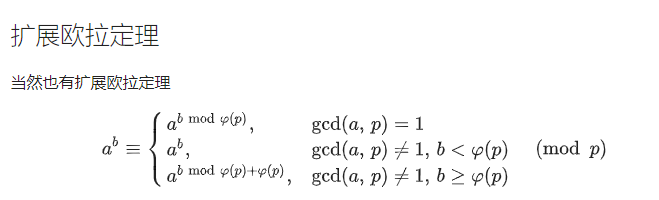
这一题主要运用的下面两个公式,一定一定一定要注意条件,比赛的时候没有看到b范围的条件,公式用错了,直接gg
这一题其实可以稍稍改一下,就可以变成好用的模板
想看证明过程的
https://oi-wiki.org/math/fermat/
ps:这个网站真的是学习知识点的好地方,全面,要求高的同学可以自行加深难度!
下面贴上我的代码:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int maxn=1e6+5; 4 typedef long long LL; 5 LL n,a,b,c,s; 6 7 LL phi(LL n) 8 { 9 LL rea = n; 10 LL t = (LL)sqrt(1.0*n); 11 for(int i=2; i<=t; i++) 12 { 13 if(n % i == 0) 14 { 15 rea = rea - rea / i; 16 while(n % i == 0) 17 n /= i; 18 } 19 } 20 if(n > 1) 21 rea = rea - rea / n; 22 return rea; 23 } 24 25 LL quick_pow(LL m,LL n,LL k) 26 { 27 LL ans=1; 28 while(n) 29 { 30 if(n&1) 31 ans=(ans*m)%k; 32 n=(n>>1); 33 m=(m*m)%k; 34 } 35 return ans; 36 } 37 38 LL solve(LL a,LL b,LL c) 39 { 40 if(b==0) 41 return 1; 42 if(c==1) 43 return 0; 44 LL kk=phi(c); 45 LL temp=solve(a,b-1,kk); 46 if(temp<kk&&temp) return quick_pow(a,temp,c); 47 else return quick_pow(a,temp+kk,c); 48 } 49 50 int main() 51 { 52 int t; 53 scanf("%d",&t); 54 while(t--) 55 { 56 scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&a,&b,&c); 57 LL ss=solve(a,b,c); 58 ss%=c; 59 printf("%lld\n",ss); 60 } 61 return 0; 62 }
继续努力,加油加油!