一、外极几何
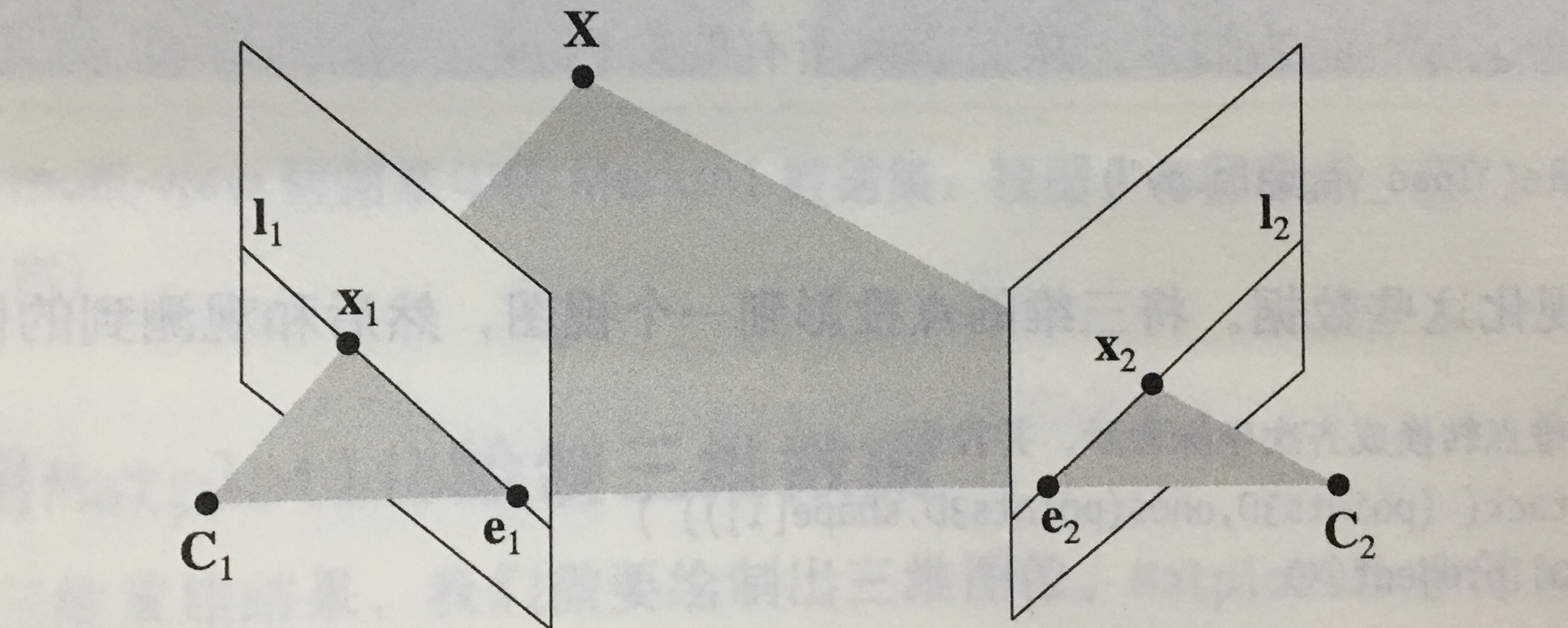
图一:外极几何示意图:
在这两个视图中,分别将三维点X投影为x1和x2.两个相机中心之间的基线C1和C2与图像平面相交于外极点e1和e2,线I1和I2成为外极线。
如果已经知道相机的参数,那么在重建过程中遇到的问题就是两幅图像之间的关系,外极线约束的主要作用就是限制对应特征点的搜索范围,将对应特征点的搜索限制在极线上。
二、基础矩阵
1.基础矩阵概述:
1)两幅图像之间的约束关系使用代数的方式表示出来即为基本矩阵。
2)基础矩阵F满足:![]()
3)基础矩阵可以用于简化匹配和去除错配特征
2.八点算法估算基础矩阵F
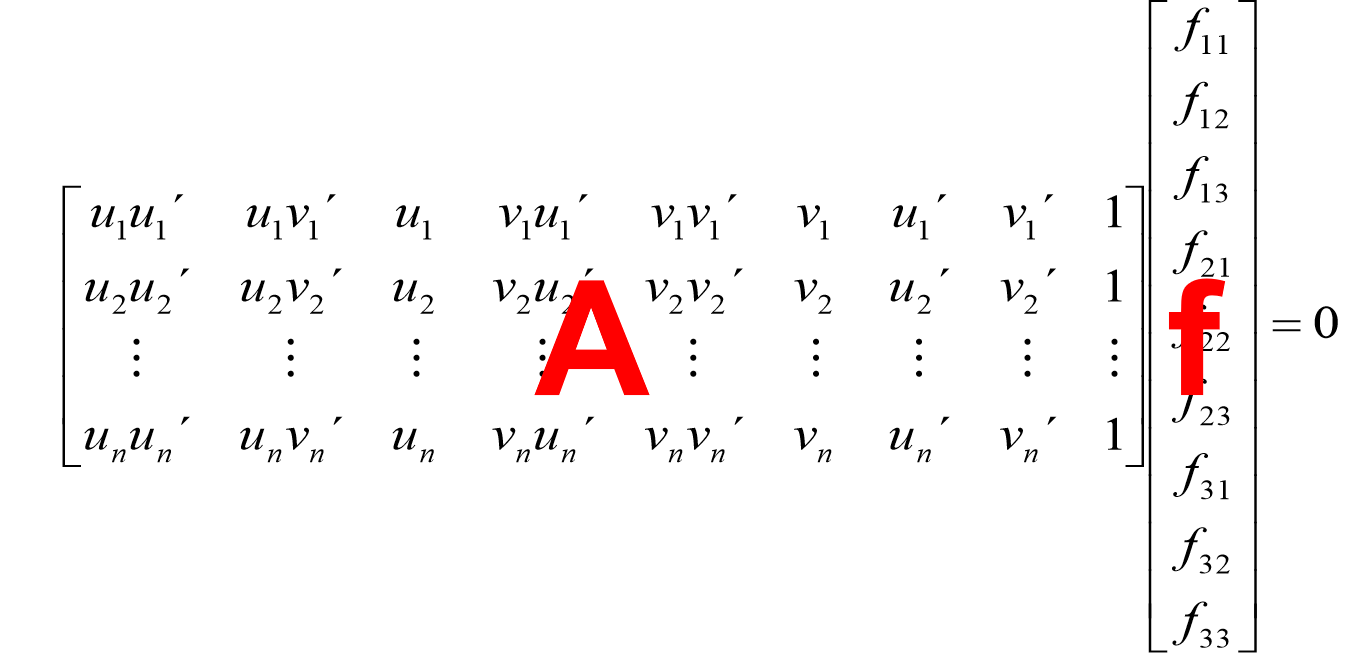
1)原理:任给两幅图像中的匹配点 x 与 x’ ,令 x=(u,v,1)^T ,x’=(u’,v’,1)^T
基础矩阵F是一个3×3的秩为2的矩阵,一般记基础矩阵F为:
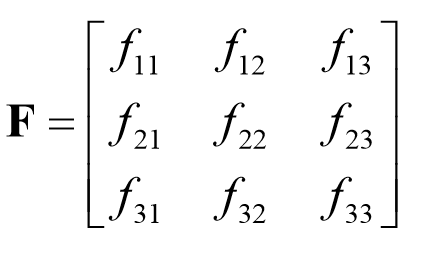
有相应方程:
![]()
由矩阵乘法可知有:
2)优点: 线性求解,容易实现,运行速度快 。
缺点:对噪声敏感。
三、照相机和三维结构的计算
1.三角剖分
给定照相机参数模型,图像点可以通过三角剖分来恢复出这些点的三维位置。

得到基础矩阵:

通过三角剖分得到的特征点:估计点和实际图像点很接近,可以很好地匹配。

三角剖分后有36个特征匹配的点:

照相机矩阵
1)数据集:

2)实验结果
a.sift特征匹配结果:

b.处理过后:
z1.jpg和z2.jpg:

z1.jpg和z6.jpg:

c.由三维点得到照相机矩阵
图z1的照相机矩阵
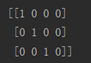
图z2的照相机矩阵
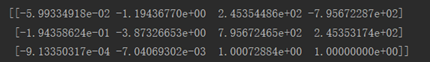
图z6的照相机矩阵
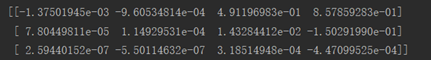
(二)室内
1.数据集:

2.s1与s2进行sift特征匹配:有180个特征匹配点

2.s1与s2通过三角剖分得到的特征点:估计点和实际图像点很接近,可以很好地匹配。
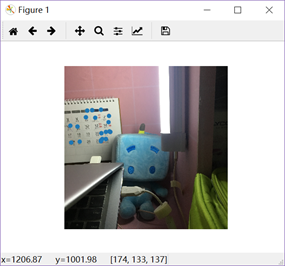
3.三角剖分后有29个特征匹配的点:

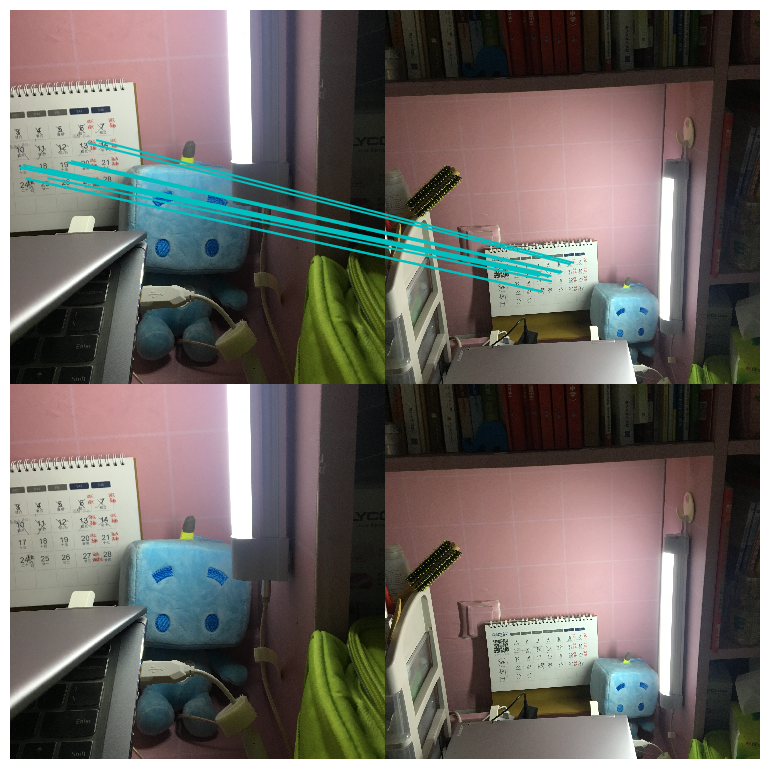
4.s1和拍摄距离较远的图片s3进行特征匹配
.
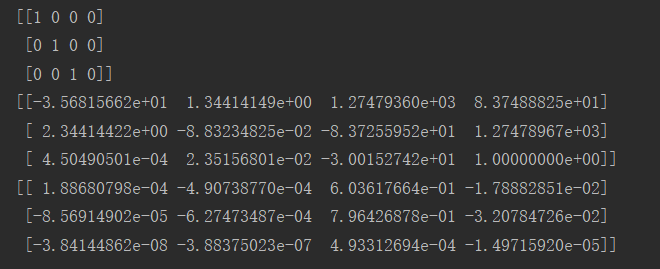
5.由三维点得到三张图的照相机矩阵(顺序:s1,s2,s3)
四、实验中遇到的问题
头文件问题:将头文件改为

1 # In[1]: 2 from PIL import Image 3 from numpy import * 4 from pylab import * 5 import numpy as np 6 from imp import reload 7 # In[2]: 8 9 from PCV.geometry import camera 10 from PCV.geometry import homography 11 from PCV.geometry import sfm 12 from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
五、参考文献
三角剖分算法(delaunay) https://blog.csdn.net/aaronmorgan/article/details/80389142
三维重建(一)外极几何,基础矩阵及求解https://blog.csdn.net/lhanchao/article/details/51834223
六、附代码

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # coding: utf-8 3 4 # In[1]: 5 from PIL import Image 6 from numpy import * 7 from pylab import * 8 import numpy as np 9 from imp import reload 10 # In[2]: 11 12 from PCV.geometry import camera 13 from PCV.geometry import homography 14 from PCV.geometry import sfm 15 from PCV.localdescriptors import sift 16 17 camera = reload(camera) 18 homography = reload(homography) 19 sfm = reload(sfm) 20 sift = reload(sift) 21 22 23 # In[3]: 24 25 26 # Read features 27 im1 = array(Image.open('D:/there/pictures/s1.JPG')) 28 sift.process_image('D:/there/pictures/s1.JPG', 'im1.sift') 29 l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift') 30 31 im2 = array(Image.open('D:/there/pictures/s2.JPG')) 32 sift.process_image('D:/there/pictures/s2.JPG', 'im2.sift') 33 l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('im2.sift') 34 35 36 # In[9]: 37 38 39 matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2) 40 41 42 # In[10]: 43 44 45 ndx = matches.nonzero()[0] 46 x1 = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx, :2].T) 47 ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx] 48 x2 = homography.make_homog(l2[ndx2, :2].T) 49 50 x1n = x1.copy() 51 x2n = x2.copy() 52 53 54 # In[11]: 55 56 57 print(len(ndx)) 58 59 60 # In[12]: 61 62 63 figure(figsize=(16,16)) 64 sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, True) 65 show() 66 67 68 # In[13]: 69 70 71 # Chapter 5 Exercise 1 72 # Don't use K1, and K2 73 74 #def F_from_ransac(x1, x2, model, maxiter=5000, match_threshold=1e-6): 75 def F_from_ransac(x1, x2, model, maxiter=5000, match_threshold=1e-6): 76 """ Robust estimation of a fundamental matrix F from point 77 correspondences using RANSAC (ransac.py from 78 http://www.scipy.org/Cookbook/RANSAC). 79 80 input: x1, x2 (3*n arrays) points in hom. coordinates. """ 81 82 from PCV.tools import ransac 83 data = np.vstack((x1, x2)) 84 d = 20 # 20 is the original 85 # compute F and return with inlier index 86 F, ransac_data = ransac.ransac(data.T, model, 87 8, maxiter, match_threshold, d, return_all=True) 88 return F, ransac_data['inliers'] 89 90 91 # In[15]: 92 93 94 # find E through RANSAC 95 model = sfm.RansacModel() 96 F, inliers = F_from_ransac(x1n, x2n, model, maxiter=5000, match_threshold=1e-3) 97 98 99 # In[16]: 100 101 102 print (len(x1n[0])) 103 print (len(inliers)) 104 105 106 # In[17]: 107 108 109 P1 = array([[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0]]) 110 P2 = sfm.compute_P_from_fundamental(F) 111 112 113 # In[18]: 114 115 116 # triangulate inliers and remove points not in front of both cameras 117 X = sfm.triangulate(x1n[:, inliers], x2n[:, inliers], P1, P2) 118 119 120 # In[19]: 121 122 123 # plot the projection of X 124 cam1 = camera.Camera(P1) 125 cam2 = camera.Camera(P2) 126 x1p = cam1.project(X) 127 x2p = cam2.project(X) 128 129 130 # In[20]: 131 132 133 figure() 134 imshow(im1) 135 gray() 136 plot(x1p[0], x1p[1], 'o') 137 #plot(x1[0], x1[1], 'r.') 138 axis('off') 139 140 figure() 141 imshow(im2) 142 gray() 143 plot(x2p[0], x2p[1], 'o') 144 #plot(x2[0], x2[1], 'r.') 145 axis('off') 146 show() 147 148 149 # In[21]: 150 151 152 figure(figsize=(16, 16)) 153 im3 = sift.appendimages(im1, im2) 154 im3 = vstack((im3, im3)) 155 156 imshow(im3) 157 158 cols1 = im1.shape[1] 159 rows1 = im1.shape[0] 160 for i in range(len(x1p[0])): 161 if (0<= x1p[0][i]<cols1) and (0<= x2p[0][i]<cols1) and (0<=x1p[1][i]<rows1) and (0<=x2p[1][i]<rows1): 162 plot([x1p[0][i], x2p[0][i]+cols1],[x1p[1][i], x2p[1][i]],'c') 163 axis('off') 164 show() 165 166 167 # In[22]: 168 169 170 print (F) 171 172 173 # In[23]: 174 175 176 # Chapter 5 Exercise 2 177 178 x1e = [] 179 x2e = [] 180 ers = [] 181 for i,m in enumerate(matches): 182 if m>0: #plot([locs1[i][0],locs2[m][0]+cols1],[locs1[i][1],locs2[m][1]],'c') 183 p1 = array([l1[i][0], l1[i][1], 1]) 184 p2 = array([l2[m][0], l2[m][1], 1]) 185 # Use Sampson distance as error 186 Fx1 = dot(F, p1) 187 Fx2 = dot(F, p2) 188 denom = Fx1[0]**2 + Fx1[1]**2 + Fx2[0]**2 + Fx2[1]**2 189 e = (dot(p1.T, dot(F, p2)))**2 / denom 190 x1e.append([p1[0], p1[1]]) 191 x2e.append([p2[0], p2[1]]) 192 ers.append(e) 193 x1e = array(x1e) 194 x2e = array(x2e) 195 ers = array(ers) 196 197 198 # In[24]: 199 200 201 indices = np.argsort(ers) 202 x1s = x1e[indices] 203 x2s = x2e[indices] 204 ers = ers[indices] 205 x1s = x1s[:20] 206 x2s = x2s[:20] 207 208 209 # In[25]: 210 211 212 figure(figsize=(16, 16)) 213 im3 = sift.appendimages(im1, im2) 214 im3 = vstack((im3, im3)) 215 216 imshow(im3) 217 218 cols1 = im1.shape[1] 219 rows1 = im1.shape[0] 220 for i in range(len(x1s)): 221 if (0<= x1s[i][0]<cols1) and (0<= x2s[i][0]<cols1) and (0<=x1s[i][1]<rows1) and (0<=x2s[i][1]<rows1): 222 plot([x1s[i][0], x2s[i][0]+cols1],[x1s[i][1], x2s[i][1]],'c') 223 axis('off') 224 show() 225 226 227 # In[ ]:

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # coding: utf-8 3 4 # In[1]: 5 6 from PIL import Image 7 from numpy import * 8 from pylab import * 9 import numpy as np 10 from imp import reload 11 12 13 # In[2]: 14 15 16 from PCV.geometry import camera 17 from PCV.geometry import homography 18 from PCV.geometry import sfm 19 from PCV.localdescriptors import sift 20 21 camera = reload(camera) 22 homography = reload(homography) 23 sfm = reload(sfm) 24 sift = reload(sift) 25 26 27 # In[3]: 28 29 30 # Read features 31 im1 = array(Image.open('D:/there/pictures/s1.JPG')) 32 sift.process_image('D:/there/pictures/s1.JPG', 'im1.sift') 33 34 im2 = array(Image.open('D:/there/pictures/s2.JPG')) 35 sift.process_image('D:/there/pictures/s2.JPG', 'im2.sift') 36 37 38 # In[4]: 39 40 41 l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift') 42 l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('im2.sift') 43 44 45 # In[5]: 46 47 48 matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2) 49 50 51 # In[6]: 52 53 54 ndx = matches.nonzero()[0] 55 x1 = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx, :2].T) 56 ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx] 57 x2 = homography.make_homog(l2[ndx2, :2].T) 58 59 d1n = d1[ndx] 60 d2n = d2[ndx2] 61 x1n = x1.copy() 62 x2n = x2.copy() 63 64 65 # In[7]: 66 67 68 figure(figsize=(16,16)) 69 sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, True) 70 show() 71 72 73 # In[26]: 74 75 76 #def F_from_ransac(x1, x2, model, maxiter=5000, match_threshold=1e-6): 77 def F_from_ransac(x1, x2, model, maxiter=5000, match_threshold=1e-6): 78 """ Robust estimation of a fundamental matrix F from point 79 correspondences using RANSAC (ransac.py from 80 http://www.scipy.org/Cookbook/RANSAC). 81 82 input: x1, x2 (3*n arrays) points in hom. coordinates. """ 83 84 from PCV.tools import ransac 85 data = np.vstack((x1, x2)) 86 d = 10 # 20 is the original 87 # compute F and return with inlier index 88 F, ransac_data = ransac.ransac(data.T, model, 89 8, maxiter, match_threshold, d, return_all=True) 90 return F, ransac_data['inliers'] 91 92 93 # In[27]: 94 95 96 # find F through RANSAC 97 model = sfm.RansacModel() 98 F, inliers = F_from_ransac(x1n, x2n, model, maxiter=5000, match_threshold=1e-1) 99 print (F) 100 101 102 # In[28]: 103 104 105 P1 = array([[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0]]) 106 P2 = sfm.compute_P_from_fundamental(F) 107 108 109 # In[29]: 110 111 112 print (P2) 113 print (F) 114 115 116 # In[30]: 117 118 119 # P2, F (1e-4, d=20) 120 # [[ -1.48067422e+00 1.14802177e+01 5.62878044e+02 4.74418238e+03] 121 # [ 1.24802182e+01 -9.67640761e+01 -4.74418113e+03 5.62856097e+02] 122 # [ 2.16588305e-02 3.69220292e-03 -1.04831621e+02 1.00000000e+00]] 123 # [[ -1.14890281e-07 4.55171451e-06 -2.63063628e-03] 124 # [ -1.26569570e-06 6.28095242e-07 2.03963649e-02] 125 # [ 1.25746499e-03 -2.19476910e-02 1.00000000e+00]] 126 127 128 # In[31]: 129 130 131 # triangulate inliers and remove points not in front of both cameras 132 X = sfm.triangulate(x1n[:, inliers], x2n[:, inliers], P1, P2) 133 134 135 # In[32]: 136 137 138 # plot the projection of X 139 cam1 = camera.Camera(P1) 140 cam2 = camera.Camera(P2) 141 x1p = cam1.project(X) 142 x2p = cam2.project(X) 143 144 145 # In[33]: 146 147 148 figure(figsize=(16, 16)) 149 imj = sift.appendimages(im1, im2) 150 imj = vstack((imj, imj)) 151 152 imshow(imj) 153 154 cols1 = im1.shape[1] 155 rows1 = im1.shape[0] 156 for i in range(len(x1p[0])): 157 if (0<= x1p[0][i]<cols1) and (0<= x2p[0][i]<cols1) and (0<=x1p[1][i]<rows1) and (0<=x2p[1][i]<rows1): 158 plot([x1p[0][i], x2p[0][i]+cols1],[x1p[1][i], x2p[1][i]],'c') 159 axis('off') 160 show() 161 162 163 # In[34]: 164 165 166 d1p = d1n[inliers] 167 d2p = d2n[inliers] 168 169 170 # In[35]: 171 172 173 # Read features 174 im3 = array(Image.open('D:/there/pictures/s3.JPG')) 175 sift.process_image('D:/there/pictures/s3.JPG', 'im3.sift') 176 l3, d3 = sift.read_features_from_file('im3.sift') 177 178 179 # In[36]: 180 181 182 matches13 = sift.match_twosided(d1p, d3) 183 184 185 # In[37]: 186 187 188 ndx_13 = matches13.nonzero()[0] 189 x1_13 = homography.make_homog(x1p[:, ndx_13]) 190 ndx2_13 = [int(matches13[i]) for i in ndx_13] 191 x3_13 = homography.make_homog(l3[ndx2_13, :2].T) 192 193 194 # In[38]: 195 196 197 figure(figsize=(16, 16)) 198 imj = sift.appendimages(im1, im3) 199 imj = vstack((imj, imj)) 200 201 imshow(imj) 202 203 cols1 = im1.shape[1] 204 rows1 = im1.shape[0] 205 for i in range(len(x1_13[0])): 206 if (0<= x1_13[0][i]<cols1) and (0<= x3_13[0][i]<cols1) and (0<=x1_13[1][i]<rows1) and (0<=x3_13[1][i]<rows1): 207 plot([x1_13[0][i], x3_13[0][i]+cols1],[x1_13[1][i], x3_13[1][i]],'c') 208 axis('off') 209 show() 210 211 212 # In[39]: 213 214 215 P3 = sfm.compute_P(x3_13, X[:, ndx_13]) 216 217 218 # In[40]: 219 220 221 print (P3) 222 223 224 # In[41]: 225 226 227 print (P1) 228 print (P2) 229 print (P3) 230 231 232 # In[22]: 233 234 235 # Can't tell the camera position because there's no calibration matrix (K)
