The "eight queens puzzle" is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×88\times 88×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other. Thus, a solution requires that no two queens share the same row, column, or diagonal. The eight queens puzzle is an example of the more general NNN queens problem of placing NNN non-attacking queens on an N×NN\times NN×N chessboard. (From Wikipedia - "Eight queens puzzle".)
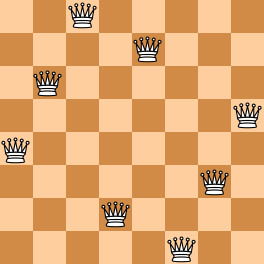
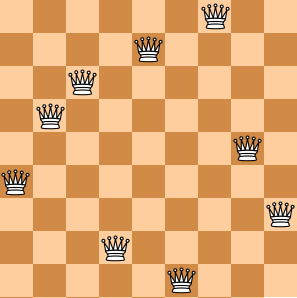
Here you are NOT asked to solve the puzzles. Instead, you are supposed to judge whether or not a given configuration of the chessboard is a solution. To simplify the representation of a chessboard, let us assume that no two queens will be placed in the same column. Then a configuration can be represented by a simple integer sequence (Q1,Q2,⋯,QN)(Q_1, Q_2, \cdots , Q_N)(Q1,Q2,⋯,QN), where QiQ_iQi is the row number of the queen in the iii-th column. For example, Figure 1 can be represented by (4, 6, 8, 2, 7, 1, 3, 5) and it is indeed a solution to the 8 queens puzzle; while Figure 2 can be represented by (4, 6, 7, 2, 8, 1, 9, 5, 3) and is NOT a 9 queens' solution.
 |
 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 |
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives an integer KKK (1<K≤2001<K\le 2001<K≤200). Then KKK lines follow, each gives a configuration in the format "NNN Q1Q_1Q1 Q2Q_2Q2 ... QNQ_NQN", where 4≤N≤10004\le N\le 10004≤N≤1000 and it is guaranteed that 1≤Qi≤N1\le Q_i\le N1≤Qi≤N for all i=1,⋯,Ni=1, \cdots , Ni=1,⋯,N. The numbers are separated by spaces.
Output Specification:
For each configuration, if it is a solution to the NNN queens problem, print YES in a line; or NO if not.
Sample Input:
4
8 4 6 8 2 7 1 3 5
9 4 6 7 2 8 1 9 5 3
6 1 5 2 6 4 3
5 1 3 5 2 4
Sample Output:
YES
NO
NO
YES
题意:给出n个k皇后的解决方案 ,问你该方案是否可行。
思路:假设棋盘为k*k,则这些皇后必须分布在不同行不同列不同对角线上,才是一个正确的解决方案,由于给出的数据是不同列的数据,因此列一定不同,检查行是否相同,是否在同一对角线上,即可。
参考代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int n,num,a[1010],vis[1010];
bool judge(int a[],int num){
bool flag=true;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++){
if(vis[a[i]])
return false;
vis[a[i]]=1;
for(int j=i+1;j<=num;j++){
if(a[j]-a[i]==j-i) //如果y1-y2==x2-x2,则在同一对角线
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&num);
for(int j=1;j<=num;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[j]);
if(judge(a,num)) printf("YES\n");
else printf("NO\n");
}
return 0;
}