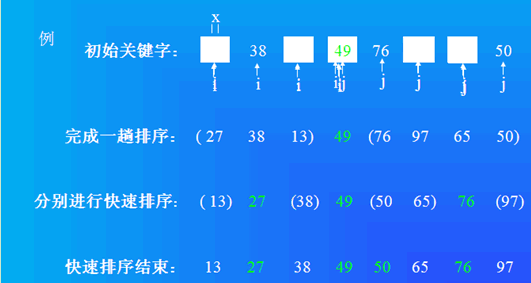
快速排序
1.快速排序的描述
通过一躺排序将要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分的所有数据都比另外一部分的所有数据都要小,基准数据排在这两个子序列的中间;
然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,以此达到整个数据变成有序序列。
采用分治思想,对一个输入的子数组A[p…r],按以下三个步骤进行排序:
分解:以数组A[p]为基准元素将A[p…r ]划分成三段A[p…q-1] 、A[q]和 A[q+1…r ],使A[p…q-1]中任何一个元素小于等于A[q],而A[q+1…r ]中任何一个元素大于等于A[q]。下标q在划分过程中确定。
递归求解:通过递归调用快速排序算法分别对A[p…q-1]和A[q+1…r]进行排序。
合并:由于A[p…q-1]和A[q+1…r]的排序是就地进行的,所以在A[p…q-1]和A[q+1…r]都已排好的序后,不需要执行任何计算,A[p…r]就已排好序。
2、伪代码
QuickSort(A,p,r) 1 if p<r 2 tmp=Partition(A,p,r) 3 QuickSort(A,p, tmp-1) 4 QuickSort(A, tmp+1, r)
Partition(A,p,r) 1 tmp=A[p] //当做轴 2 while p<r 3 while p<r and A[r]>=tmp 4 r-- 5 exchange A[p] with A[r] 6 while p<r and A[p]<=tmp 7 p++ 8 exchange A[p] with A[r] 9 return p
3、具体实现
/*快速排序*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//打印数组
void printQuickSort(int *arr, int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//元素互换
void SwapQuickSort(int *arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = 0;
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
//分治思想(第一个元素当轴,分成两个有序子序列)
int Partition(int *arr, int low, int high)
{
int temp = arr[low];
while (low < high)
{
while ((low<high) && (arr[high]>=temp))
{
high--;// 比基准大,本来就在右边,所以high后移动
}
SwapQuickSort(arr, low, high);
while ((low < high) && (arr[low] <= temp))
{
low++;//比基准小,本来就在左边,所以low向前移动
}
SwapQuickSort(arr, low, high);
}
//返回轴的位置
return low;
}
//快速排序
void QuickSort(int *arr, int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
int tmp = Partition(arr, low, high);
QuickSort(arr, low, tmp - 1);//对左半段排序
QuickSort(arr, tmp + 1, high);//对右半段排序
}
}
int main()
{
int len = 0;
int array[] = { 2, 8, 7, 1, 3, 5, 6, 4 };
//数组长度
len = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
//快速排序前
cout << "Before QuickSort:" << endl;
printQuickSort(array, len);
//快速排序
QuickSort(array, 0, len-1);
//快速排序后
cout << "After QuickSort:" << endl;
printQuickSort(array, len);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4、快速排序的性能
快速排序的运行时间依赖于划分是否平衡,而平衡与否又依赖于用于划分的元素。如果划分是平衡的,那么快速排序算法性能与归并排序一样。如果划分是不平衡的,那么快速排序的性能就接近于插入排序。
最坏情况划分
当划分产生的两个字问题分别包含了n-1个元素和0个元素时,T(n)=T(n-1)+O(n),快速排序的时间复杂度是O(n2)
最好情况划分
划分得到的两个子问题的规模都不大于n/2,T(n)=T(n/2)+O(n),快速排序的时间复杂度是O(nlgn)。