分享一下我老师大神的人工智能教程。零基础!通俗易懂!风趣幽默!还带黄段子!希望你也加入到我们人工智能的队伍中来!https://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow
本文实现了两幅图像的颜色转换(based on Opencv2.3.1 + vs )
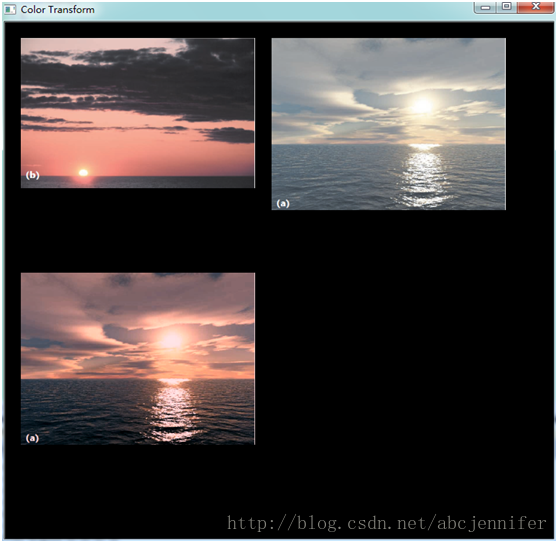
效果:
上图左的颜色空间给上图右得下图。
Algorithm:
Paper <color transfer between Images>.
Code:
// // colortransfer.cpp// ColorTransfer// // Created by Rachel on 13-12-2.// Copyright (c) 2013年 ZJU. All rights reserved.// Email: [email protected]// // // ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Input: image src (想用src的颜色分布) , dst(要转换的图像).// Output: 结果放在res中.// // #include "iostream" #include "showhelper.h" #include "cv.h" #include "highgui.h" using namespace std; #pragma comment (lib, "cv.lib") #pragma comment (lib,"cxcore.lib") #pragma comment (lib,"highgui.lib") IplImage* Transform(IplImage* A,CvScalar avg_src, CvScalar avg_dst,CvScalar std_src, CvScalar std_dst) { for(int i=0;i<3;i++) { for(int x=0;x<A->height;x++) { uchar *ptr=(uchar*)(A->imageData+x*A->widthStep); for(int y=0;y<A->width;y++) { double tmp=ptr[3*y+i]; int t=(int)((tmp-avg_dst.val[i])*(std_src.val[i]/std_dst.val[i])+avg_src.val[i]); t = t<0?0:t; t = t>255?255:t; ptr[3*y+i]=t; } } } return A; } void main() { //load IplImage* source = cvLoadImage("..\\ColorTransfer\\Images\\2.jpg",CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); IplImage* dst = cvLoadImage("..\\ColorTransfer\\Images\\1.jpg",CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); IplImage* dstlab = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst),dst->depth,dst->nChannels); IplImage* res = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(dst),dst->depth,dst->nChannels); dstlab = cvCloneImage(dst); //calculate average and standard derivation CvScalar avg_src,avg_dst,std_src, std_dst; cvAvgSdv(source,&avg_src,&std_src); cvAvgSdv(dstlab, &avg_dst, &std_dst); //transform dstlab = Transform(dstlab,avg_src,avg_dst,std_src, std_dst); res = cvCloneImage(dstlab); cvShowManyImages("Color Transform",3, source, dst, res); cvWaitKey(); cvReleaseImage(&source); cvReleaseImage(&dst); cvReleaseImage(&dstlab); cvReleaseImage(&res); }另外还有个显示多幅图像的showhelper.h,当时是从stackoverflow上搞下来的,但是已经不知道原作者是哪位大牛啦。。。
// showManyImage.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.//#include <cv.h>#include <highgui.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdarg.h>#include <time.h>#include <iostream>void cvShowManyImages(char* title, int nArgs, ...) { // img - Used for getting the arguments IplImage *img; // DispImage - the image in which input images are to be copied IplImage *DispImage; int size; int i; int m, n; int x, y; // w - Maximum number of images in a row // h - Maximum number of images in a column int w, h; // scale - How much we have to resize the image float scale; int max; // If the number of arguments is lesser than 0 or greater than 12 // return without displaying if(nArgs <= 0) { printf("Number of arguments too small....\n"); return; } else if(nArgs > 12) { printf("Number of arguments too large....\n"); return; } // Determine the size of the image, and the number of rows/cols from number of arguments else if (nArgs == 1) { w = h = 1; size = 300; } else if (nArgs == 2) { w = 2; h = 1; size = 300; } else if (nArgs == 3 || nArgs == 4) { w = 2; h = 2; size = 300; } else if (nArgs == 5 || nArgs == 6) { w = 3; h = 2; size = 200; } else if (nArgs == 7 || nArgs == 8) { w = 4; h = 2; size = 200; } else { w = 4; h = 3; size = 150; } // Create a new 3 channel image0 DispImage = cvCreateImage( cvSize( 100+ size*w, 60 + size*h), 8, 3 ); // Used to get the arguments passed va_list args; va_start(args, nArgs); // Loop for nArgs number of arguments for (i = 0, m = 20, n = 20; i < nArgs; i++, m += (20 + size)) { // Get the Pointer to the IplImage img = va_arg(args, IplImage*); // Check whether it is NULL or not // If it is NULL, release the image, and return if(img == 0) { printf("Invalid arguments"); cvReleaseImage(&DispImage); return; } // Find the width and height of the image x = img->width; y = img->height; // Find whether height or width is greater in order to resize the image max = (x > y)? x: y; // Find the scaling factor to resize the image scale = (float) ( (float) max / size ); // Used to Align the images if( i % w == 0 && m!= 20) { m = 20; n+= 0 + size; } // Set the image ROI to display the current image //cvSetImageROI(DispImage, cvRect(m, n, (int)( x/scale ), (int)( y/scale ))); cvSetImageROI(DispImage, cvRect(m, n, (int)( x/scale ), (int)( y/scale ))); // cout<<"x="<<m<<"y="<<n<<endl; // Resize the input image and copy the it to the Single Big Image cvResize(img, DispImage); // Reset the ROI in order to display the next image cvResetImageROI(DispImage); } // Create a new window, and show the Single Big Image //cvNamedWindow( title, 1 ); cvShowImage( title, DispImage); /*cvWaitKey(0);*/ //cvDestroyWindow(title); // End the number of arguments va_end(args); // Release the Image Memory cvReleaseImage(&DispImage);}关于Computer Vision更多的学习资料将继续更新,敬请关注本博客和新浪微博Rachel____Zhang。
分享一下我老师大神的人工智能教程。零基础!通俗易懂!风趣幽默!还带黄段子!希望你也加入到我们人工智能的队伍中来!https://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow