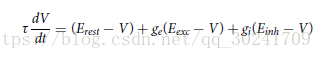该代码Github地址:
https://github.com/peter-u-diehl/stdp-mnist/blob/master/Diehl%26Cook_spiking_MNIST.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.cm as cmap
import time
import os.path
import scipy
import cPickle as pickle
import brian_no_units #import it to deactivate unit checking --> This should NOT be done for testing/debugging
import brian as b
from struct import unpack
from brian import *
# specify the location of the MNIST data
MNIST_data_path = ''首先导入模块,定义数据集的路径变量。
def get_labeled_data(picklename, bTrain = True):
"""Read input-vector (image) and target class (label, 0-9) and return
it as list of tuples.
"""
if os.path.isfile('%s.pickle' % picklename):
data = pickle.load(open('%s.pickle' % picklename))
else:
# Open the images with gzip in read binary mode
if bTrain:
images = open(MNIST_data_path + 'train-images.idx3-ubyte','rb')
labels = open(MNIST_data_path + 'train-labels.idx1-ubyte','rb')
else:
images = open(MNIST_data_path + 't10k-images.idx3-ubyte','rb')
labels = open(MNIST_data_path + 't10k-labels.idx1-ubyte','rb')
# Get metadata for images
images.read(4) # skip the magic_number
number_of_images = unpack('>I', images.read(4))[0]
rows = unpack('>I', images.read(4))[0]
cols = unpack('>I', images.read(4))[0]
# Get metadata for labels
labels.read(4) # skip the magic_number
N = unpack('>I', labels.read(4))[0]
if number_of_images != N:
raise Exception('number of labels did not match the number of images')
# Get the data
x = np.zeros((N, rows, cols), dtype=np.uint8) # Initialize numpy array
y = np.zeros((N, 1), dtype=np.uint8) # Initialize numpy array
for i in xrange(N):
if i % 1000 == 0:
print("i: %i" % i)
x[i] = [[unpack('>B', images.read(1))[0] for unused_col in xrange(cols)] for unused_row in xrange(rows) ]
y[i] = unpack('>B', labels.read(1))[0]
data = {'x': x, 'y': y, 'rows': rows, 'cols': cols}
pickle.dump(data, open("%s.pickle" % picklename, "wb"))
return data函数功能:获得带标签的数据
输入:图片矩阵及其目标类(0-9的标签)、是否为训练数据
输出:元组列表
注:官方MNIS数据集有60000个训练集和10000个测试集,为IDX格式,IDX格式形式如下:
magic number
size in dimension 0
size in dimension 1
size in dimension 2
.....
size in dimension N
data魔法数字是个整数,前两个字节总是0,第三个字节表示数据的类型:
0x08: unsigned byte
0x09: signed byte
0x0B: short (2 bytes)
0x0C: int (4 bytes)
0x0D: float (4 bytes)
0x0E: double (8 bytes)第四个字节表示矩阵的维度。
接着便是每个维度的尺寸,用四字节的整数表示。
images.read(4)跳过了MNIST数据集的魔法数字的四个字节。
unpack是struct模块中的函数,用法是unpack(fmt, string),代码中的'>'说明了改变对齐方式的方法,为大端对齐;'I'表示将C类型的unsigned int 转换为Python类型的integer。
获取到MNIST数据集中的数据后转换为numpy类型数组。
pickle提供了一个简单的持久化功能,可以将对象以文件的形式存放在磁盘上,dump方法:
pickle.dump(obj, file[, protocol])
def get_matrix_from_file(fileName):
offset = len(ending) + 4
if fileName[-4-offset] == 'X':
n_src = n_input
else:
if fileName[-3-offset]=='e':
n_src = n_e
else:
n_src = n_i
if fileName[-1-offset]=='e':
n_tgt = n_e
else:
n_tgt = n_i
readout = np.load(fileName)
print readout.shape, fileName
value_arr = np.zeros((n_src, n_tgt))
if not readout.shape == (0,):
value_arr[np.int32(readout[:,0]), np.int32(readout[:,1])] = readout[:,2]
return value_arr函数功能:从文件中获得矩阵
输入:文件名
输出:数值数列
def save_connections(ending = ''):
print 'save connections'
for connName in save_conns:
connMatrix = connections[connName][:]
# connListSparse = ([(i,j[0],j[1]) for i in xrange(connMatrix.shape[0]) for j in zip(connMatrix.rowj[i],connMatrix.rowdata[i])])
connListSparse = ([(i,j,connMatrix[i,j]) for i in xrange(connMatrix.shape[0]) for j in xrange(connMatrix.shape[1]) ])
np.save(data_path + 'weights/' + connName + ending, connListSparse)函数功能:存储连接
def save_theta(ending = ''):
print 'save theta'
for pop_name in population_names:
np.save(data_path + 'weights/theta_' + pop_name + ending, neuron_groups[pop_name + 'e'].theta)函数功能:存储theta值
def normalize_weights():
for connName in connections:
if connName[1] == 'e' and connName[3] == 'e':
connection = connections[connName][:]
temp_conn = np.copy(connection)
colSums = np.sum(temp_conn, axis = 0)
colFactors = weight['ee_input']/colSums
for j in xrange(n_e):#
connection[:,j] *= colFactors[j]函数功能:正则化权重
只有连接名的第1和第3个字符为'e'时(兴奋层连接),才会读取连接权重。
但个人感觉应该写成以下形式(未经验证):
def normalize_weights():
for connName in connections:
if connName[1] == 'e' and connName[3] == 'e':
connection = connections[connName][:]
temp_conn = np.copy(connection)
colSums = np.sum(temp_conn, axis = 0)
colFactors = weight['ee_input']/colSums
for j in xrange(n_e):#
connection[:,j] *= colFactors[j]def get_2d_input_weights():
name = 'XeAe'
weight_matrix = np.zeros((n_input, n_e))
n_e_sqrt = int(np.sqrt(n_e))
n_in_sqrt = int(np.sqrt(n_input))
num_values_col = n_e_sqrt*n_in_sqrt
num_values_row = num_values_col
rearranged_weights = np.zeros((num_values_col, num_values_row))
connMatrix = connections[name][:]
weight_matrix = np.copy(connMatrix)
for i in xrange(n_e_sqrt):
for j in xrange(n_e_sqrt):
rearranged_weights[i*n_in_sqrt : (i+1)*n_in_sqrt, j*n_in_sqrt : (j+1)*n_in_sqrt] = \
weight_matrix[:, i + j*n_e_sqrt].reshape((n_in_sqrt, n_in_sqrt))
return rearranged_weights函数功能:获取二维输入权重
def plot_2d_input_weights():
name = 'XeAe'
weights = get_2d_input_weights()
fig = b.figure(fig_num, figsize = (18, 18))
im2 = b.imshow(weights, interpolation = "nearest", vmin = 0, vmax = wmax_ee, cmap = cmap.get_cmap('hot_r'))
b.colorbar(im2)
b.title('weights of connection' + name)
fig.canvas.draw()
return im2, fig函数功能:绘制二维输入权重
输出:权重矩阵图
def update_2d_input_weights(im, fig):
weights = get_2d_input_weights()
im.set_array(weights)
fig.canvas.draw()
return im函数功能:更新二维输入权重
def get_current_performance(performance, current_example_num):
current_evaluation = int(current_example_num/update_interval)
start_num = current_example_num - update_interval
end_num = current_example_num
difference = outputNumbers[start_num:end_num, 0] - input_numbers[start_num:end_num]
correct = len(np.where(difference == 0)[0])
performance[current_evaluation] = correct / float(update_interval) * 100
return performance函数功能:获取当前表现
def plot_performance(fig_num):
num_evaluations = int(num_examples/update_interval)
time_steps = range(0, num_evaluations)
performance = np.zeros(num_evaluations)
fig = b.figure(fig_num, figsize = (5, 5))
fig_num += 1
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
im2, = ax.plot(time_steps, performance) #my_cmap
b.ylim(ymax = 100)
b.title('Classification performance')
fig.canvas.draw()
return im2, performance, fig_num, fig函数功能:绘制表现
def update_performance_plot(im, performance, current_example_num, fig):
performance = get_current_performance(performance, current_example_num)
im.set_ydata(performance)
fig.canvas.draw()
return im, performance函数功能:更新绘制表现
def get_recognized_number_ranking(assignments, spike_rates):
summed_rates = [0] * 10
num_assignments = [0] * 10
for i in xrange(10):
num_assignments[i] = len(np.where(assignments == i)[0])
if num_assignments[i] > 0:
summed_rates[i] = np.sum(spike_rates[assignments == i]) / num_assignments[i]
return np.argsort(summed_rates)[::-1]函数功能:获取已识别数字的范围
np.argsort(summed_rates)返回的是从小到大排序的summed_rates
np.argsort(summed_rates)[::-1]返回的则是从大到小的summed_rates
def get_new_assignments(result_monitor, input_numbers):
assignments = np.zeros(n_e)
input_nums = np.asarray(input_numbers)
maximum_rate = [0] * n_e
for j in xrange(10):
num_assignments = len(np.where(input_nums == j)[0])
if num_assignments > 0:
rate = np.sum(result_monitor[input_nums == j], axis = 0) / num_assignments
for i in xrange(n_e):
if rate[i] > maximum_rate[i]:
maximum_rate[i] = rate[i]
assignments[i] = j
return assignments函数功能:获得新的分配
np.array和np.asarray的区别:
array和asarray都可以将结构数据转化为ndarray,但是主要区别就是当数据源是ndarray时,array仍然会copy出一个副本,占用新的内存,但asarray不会。
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# load MNIST
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
start = time.time()
training = get_labeled_data(MNIST_data_path + 'training')
end = time.time()
print 'time needed to load training set:', end - start
start = time.time()
testing = get_labeled_data(MNIST_data_path + 'testing', bTrain = False)
end = time.time()
print 'time needed to load test set:', end - start加载训练集和测试集,同时计算两者的加载时间。
test_mode = True
b.set_global_preferences(
defaultclock = b.Clock(dt=0.5*b.ms), # The default clock to use if none is provided or defined in any enclosing scope.
useweave = True, # Defines whether or not functions should use inlined compiled C code where defined.
gcc_options = ['-ffast-math -march=native'], # Defines the compiler switches passed to the gcc compiler.
#For gcc versions 4.2+ we recommend using -march=native. By default, the -ffast-math optimizations are turned on
usecodegen = True, # Whether or not to use experimental code generation support.
usecodegenweave = True, # Whether or not to use C with experimental code generation support.
usecodegenstateupdate = True, # Whether or not to use experimental code generation support on state updaters.
usecodegenthreshold = False, # Whether or not to use experimental code generation support on thresholds.
usenewpropagate = True, # Whether or not to use experimental new C propagation functions.
usecstdp = True, # Whether or not to use experimental new C STDP.
) 设置Brian的默认全局偏好。
defaultclock说明了在未定义默认时钟时所使用的默认时钟
useweave = True说明使用内联的C代码
gcc_options说明了gcc编译器选项
usecodegen = True表示使用实验性的代码生成支持
usecodegenweave = True表示使用实验性的代码支持的C
usecodegenstateupdate = True表示对状态更新器使用实验性的代码生成
usecodegenthreshold = False表示不对阈值使用实验性的代码生成
usenewpropgate = True表示使用新的实验性的C传播函数
usestdp = True表示使用新的实验性的C STSP
np.random.seed(0)
data_path = './'
if test_mode:
weight_path = data_path + 'weights/'
num_examples = 10000 * 1
use_testing_set = True
do_plot_performance = False
record_spikes = True
ee_STDP_on = False
update_interval = num_examples
else:
weight_path = data_path + 'random/'
num_examples = 60000 * 3
use_testing_set = False
do_plot_performance = True
if num_examples <= 60000:
record_spikes = True
else:
record_spikes = True
ee_STDP_on = Truenp.random.seed(0)的作用:
使得随机数据可预测。
如:
np.random.seed(0)
np.random.rand(4)
每次输出的随机数都是相同的,而只执行:
np.random.rand(4)
每次输出的随机数是不同的。
ending = ''
n_input = 784
n_e = 400
n_i = n_e
single_example_time = 0.35 * b.second #
resting_time = 0.15 * b.second
runtime = num_examples * (single_example_time + resting_time)
if num_examples <= 10000:
update_interval = num_examples
weight_update_interval = 20
else:
update_interval = 10000
weight_update_interval = 100
if num_examples <= 60000:
save_connections_interval = 10000
else:
save_connections_interval = 10000
update_interval = 10000该SNN网络为三层网络,网络神经元数目为:
输入层:784个神经元,即MNIST数据集每个字符数据的28*28
兴奋层:400个神经元
抑制层:400个神经元
单样本时间0.35s,复位时间0.15s
总的运行时间:样本数量*(0.35s+0.15s)
v_rest_e = -65. * b.mV
v_rest_i = -60. * b.mV
v_reset_e = -65. * b.mV
v_reset_i = -45. * b.mV
v_thresh_e = -52. * b.mV
v_thresh_i = -40. * b.mV
refrac_e = 5. * b.ms
refrac_i = 2. * b.ms
conn_structure = 'dense'
weight = {}
delay = {}
input_population_names = ['X']
population_names = ['A']
input_connection_names = ['XA']
save_conns = ['XeAe']
input_conn_names = ['ee_input']
recurrent_conn_names = ['ei', 'ie']
weight['ee_input'] = 78.
delay['ee_input'] = (0*b.ms,10*b.ms)
delay['ei_input'] = (0*b.ms,5*b.ms)
input_intensity = 2.
start_input_intensity = input_intensity
tc_pre_ee = 20*b.ms
tc_post_1_ee = 20*b.ms
tc_post_2_ee = 40*b.ms
nu_ee_pre = 0.0001 # learning rate
nu_ee_post = 0.01 # learning rate
wmax_ee = 1.0
exp_ee_pre = 0.2
exp_ee_post = exp_ee_pre
STDP_offset = 0.4一些常量的设定。
兴奋层:
静态电位 -65mV 复位电位 -65mV 静默电位 -52mV 静默期 5ms
抑制层:
静态电位 -60mV 复位电位 -45mV 静默电位 -40mV 静默期 2ms
if test_mode:
scr_e = 'v = v_reset_e; timer = 0*ms'
else:
tc_theta = 1e7 * b.ms
theta_plus_e = 0.05 * b.mV
scr_e = 'v = v_reset_e; theta += theta_plus_e; timer = 0*ms'
offset = 20.0*b.mV
v_thresh_e = '(v>(theta - offset + ' + str(v_thresh_e) + ')) * (timer>refrac_e)'scr_e表示的是复位操作方程
neuron_eqs_e = '''
dv/dt = ((v_rest_e - v) + (I_synE+I_synI) / nS) / (100*ms) : volt
I_synE = ge * nS * -v : amp
I_synI = gi * nS * (-100.*mV-v) : amp
dge/dt = -ge/(1.0*ms) : 1
dgi/dt = -gi/(2.0*ms) : 1
'''
if test_mode:
neuron_eqs_e += '\n theta :volt'
else:
neuron_eqs_e += '\n dtheta/dt = -theta / (tc_theta) : volt'
neuron_eqs_e += '\n dtimer/dt = 100.0 : ms'兴奋层神经元方程。
方程遵循以下公式:
个人认为 I_synE = ge * nS * -v : amp 有误,应该是
I_synE = ge * nS * ( E_exc -v) : amp
neuron_eqs_i = '''
dv/dt = ((v_rest_i - v) + (I_synE+I_synI) / nS) / (10*ms) : volt
I_synE = ge * nS * -v : amp
I_synI = gi * nS * (-85.*mV-v) : amp
dge/dt = -ge/(1.0*ms) : 1
dgi/dt = -gi/(2.0*ms) : 1抑制层神经元方程。
eqs_stdp_ee = '''
post2before : 1.0
dpre/dt = -pre/(tc_pre_ee) : 1.0
dpost1/dt = -post1/(tc_post_1_ee) : 1.0
dpost2/dt = -post2/(tc_post_2_ee) : 1.0
'''
eqs_stdp_pre_ee = 'pre = 1.; w -= nu_ee_pre * post1'
eqs_stdp_post_ee = 'post2before = post2; w += nu_ee_post * pre * post2before; post1 = 1.; post2 = 1.'突触连接处的STDP算法方程。
有点疑惑的是为什么不管突触前还是突触后神经元产生脉冲时都不会对突触前后的神经元电位产生影响?
b.ion()
fig_num = 1
neuron_groups = {}
input_groups = {}
connections = {}
stdp_methods = {}
rate_monitors = {}
spike_monitors = {}
spike_counters = {}
result_monitor = np.zeros((update_interval,n_e))
neuron_groups['e'] = b.NeuronGroup(n_e*len(population_names), neuron_eqs_e, threshold= v_thresh_e, refractory= refrac_e, reset= scr_e,
compile = True, freeze = True)
neuron_groups['i'] = b.NeuronGroup(n_i*len(population_names), neuron_eqs_i, threshold= v_thresh_i, refractory= refrac_i, reset= v_reset_i,
compile = True, freeze = True)构建兴奋层和抑制层神经元组。
ion()用于激活Pylab的交互绘图模式,Brian1中存在,Brian2中不再存在。
for name in population_names:
print 'create neuron group', name
neuron_groups[name+'e'] = neuron_groups['e'].subgroup(n_e)
neuron_groups[name+'i'] = neuron_groups['i'].subgroup(n_i)
neuron_groups[name+'e'].v = v_rest_e - 40. * b.mV
neuron_groups[name+'i'].v = v_rest_i - 40. * b.mV
if test_mode or weight_path[-8:] == 'weights/':
neuron_groups['e'].theta = np.load(weight_path + 'theta_' + name + ending + '.npy')
else:
neuron_groups['e'].theta = np.ones((n_e)) * 20.0*b.mV
print 'create recurrent connections'
for conn_type in recurrent_conn_names:
connName = name+conn_type[0]+name+conn_type[1]
weightMatrix = get_matrix_from_file(weight_path + '../random/' + connName + ending + '.npy')
connections[connName] = b.Connection(neuron_groups[connName[0:2]], neuron_groups[connName[2:4]], structure= conn_structure,
state = 'g'+conn_type[0])
connections[connName].connect(neuron_groups[connName[0:2]], neuron_groups[connName[2:4]], weightMatrix)
if ee_STDP_on:
if 'ee' in recurrent_conn_names:
stdp_methods[name+'e'+name+'e'] = b.STDP(connections[name+'e'+name+'e'], eqs=eqs_stdp_ee, pre = eqs_stdp_pre_ee,
post = eqs_stdp_post_ee, wmin=0., wmax= wmax_ee)
print 'create monitors for', name
rate_monitors[name+'e'] = b.PopulationRateMonitor(neuron_groups[name+'e'], bin = (single_example_time+resting_time)/b.second)
rate_monitors[name+'i'] = b.PopulationRateMonitor(neuron_groups[name+'i'], bin = (single_example_time+resting_time)/b.second)
spike_counters[name+'e'] = b.SpikeCounter(neuron_groups[name+'e'])
if record_spikes:
spike_monitors[name+'e'] = b.SpikeMonitor(neuron_groups[name+'e'])
spike_monitors[name+'i'] = b.SpikeMonitor(neuron_groups[name+'i'])
if record_spikes:
b.figure(fig_num)
fig_num += 1
b.ion()
b.subplot(211)
b.raster_plot(spike_monitors['Ae'], refresh=1000*b.ms, showlast=1000*b.ms)
b.subplot(212)
b.raster_plot(spike_monitors['Ai'], refresh=1000*b.ms, showlast=1000*b.ms)创建网络群体和循环连接。
Brian1和Brian2在创建突触连接时有较大的不同,在Brian2中,突触连接的写法应该是:
connections[connName]=b.Synapses(neuron_groups[conn_name[0:2],
neuron_groups[conn_name[2:4]],
structure = 'sparse', state='g' + conn_type[0])
connections[connName].connect(neuron_groups[connName[0:2]], neuron_groups[connName[2:4]])
在Brian2中不再使用raster_plot来绘制光栅图,直接使用plot
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# create input population and connections from input populations
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
pop_values = [0,0,0]
for i,name in enumerate(input_population_names):
input_groups[name+'e'] = b.PoissonGroup(n_input, 0)
rate_monitors[name+'e'] = b.PopulationRateMonitor(input_groups[name+'e'], bin = (single_example_time+resting_time)/b.second)
for name in input_connection_names:
print 'create connections between', name[0], 'and', name[1]
for connType in input_conn_names:
connName = name[0] + connType[0] + name[1] + connType[1]
weightMatrix = get_matrix_from_file(weight_path + connName + ending + '.npy')
connections[connName] = b.Connection(input_groups['Xe'], neuron_groups[name[1] + conn_type[1]], structure= conn_structure,
state = 'g'+connType[0], delay=True, max_delay=delay[connType][1])
connections[connName].connect(input_groups[connName[0:2]], neuron_groups[connName[2:4]], weightMatrix, delay=delay[connType])
if ee_STDP_on:
print 'create STDP for connection', name[0]+'e'+name[1]+'e'
stdp_methods[name[0]+'e'+name[1]+'e'] = b.STDP(connections[name[0]+'e'+name[1]+'e'], eqs=eqs_stdp_ee, pre = eqs_stdp_pre_ee,
post = eqs_stdp_post_ee, wmin=0., wmax= wmax_ee)从输入群组创建
同样这里的突触连接写法在Brian2中不适用。
输入层与兴奋层之间的连接是全连接,兴奋层与抑制层之间为一对一连接。
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# run the simulation and set inputs
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
previous_spike_count = np.zeros(n_e)
assignments = np.zeros(n_e)
input_numbers = [0] * num_examples
outputNumbers = np.zeros((num_examples, 10))
if not test_mode:
input_weight_monitor, fig_weights = plot_2d_input_weights()
fig_num += 1
if do_plot_performance:
performance_monitor, performance, fig_num, fig_performance = plot_performance(fig_num)
for i,name in enumerate(input_population_names):
input_groups[name+'e'].rate = 0
b.run(0)
j = 0
while j < (int(num_examples)):
if test_mode:
if use_testing_set:
rates = testing['x'][j%10000,:,:].reshape((n_input)) / 8. * input_intensity
else:
rates = training['x'][j%60000,:,:].reshape((n_input)) / 8. * input_intensity
else:
normalize_weights()
rates = training['x'][j%60000,:,:].reshape((n_input)) / 8. * input_intensity
input_groups['Xe'].rate = rates
# print 'run number:', j+1, 'of', int(num_examples)
b.run(single_example_time, report='text')
if j % update_interval == 0 and j > 0:
assignments = get_new_assignments(result_monitor[:], input_numbers[j-update_interval : j])
if j % weight_update_interval == 0 and not test_mode:
update_2d_input_weights(input_weight_monitor, fig_weights)
if j % save_connections_interval == 0 and j > 0 and not test_mode:
save_connections(str(j))
save_theta(str(j))
current_spike_count = np.asarray(spike_counters['Ae'].count[:]) - previous_spike_count
previous_spike_count = np.copy(spike_counters['Ae'].count[:])
if np.sum(current_spike_count) < 5:
input_intensity += 1
for i,name in enumerate(input_population_names):
input_groups[name+'e'].rate = 0
b.run(resting_time)
else:
result_monitor[j%update_interval,:] = current_spike_count
if test_mode and use_testing_set:
input_numbers[j] = testing['y'][j%10000][0]
else:
input_numbers[j] = training['y'][j%60000][0]
outputNumbers[j,:] = get_recognized_number_ranking(assignments, result_monitor[j%update_interval,:])
if j % 100 == 0 and j > 0:
print 'runs done:', j, 'of', int(num_examples)
if j % update_interval == 0 and j > 0:
if do_plot_performance:
unused, performance = update_performance_plot(performance_monitor, performance, j, fig_performance)
print 'Classification performance', performance[:(j/float(update_interval))+1]
for i,name in enumerate(input_population_names):
input_groups[name+'e'].rate = 0
b.run(resting_time)
input_intensity = start_input_intensity
j += 1使用MNIST样本的每个像素点的灰度值/8*输入强度,作为泊松组的脉冲激发频率。
print 'save results'
if not test_mode:
save_theta()
if not test_mode:
save_connections()
else:
np.save(data_path + 'activity/resultPopVecs' + str(num_examples), result_monitor)
np.save(data_path + 'activity/inputNumbers' + str(num_examples), input_numbers)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# plot results
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
if rate_monitors:
b.figure(fig_num)
fig_num += 1
for i, name in enumerate(rate_monitors):
b.subplot(len(rate_monitors), 1, i)
b.plot(rate_monitors[name].times/b.second, rate_monitors[name].rate, '.')
b.title('Rates of population ' + name)
if spike_monitors:
b.figure(fig_num)
fig_num += 1
for i, name in enumerate(spike_monitors):
b.subplot(len(spike_monitors), 1, i)
b.raster_plot(spike_monitors[name])
b.title('Spikes of population ' + name)
if spike_counters:
b.figure(fig_num)
fig_num += 1
for i, name in enumerate(spike_counters):
b.subplot(len(spike_counters), 1, i)
b.plot(spike_counters['Ae'].count[:])
b.title('Spike count of population ' + name)
plot_2d_input_weights()
b.ioff()
b.show()最后进行结果的保存和显示。
东南大学FutureX实验室
Email: [email protected]