softmax_axis_表示在那边切,当为1是,out_num_就表示batchsize,sum_multiplier表示通道数,scale相关的一般表示临时变量的存储,dim=C*W*H,spatial_dim=W*H,inner_num_如果fc层就为1,conv层就为H*W。
本文所举得例子是在mnist的基础上解说的,batchsize为128,类别为10。
首先看softmax求导公式:
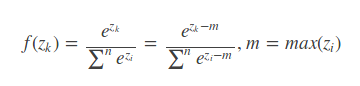

这里loss虽然由于标记形如(1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0),所以最终的loss只能由正确的那个1决定,其结果如上所示。
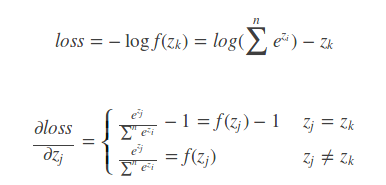
虽然loss只能由正确的那个1决定,但是在分母上还是包括除了1以外的其他项,这些项对loss也是有贡献的,所以求导的时候不能忘了。

caffe中softmax的计算:
template <typename Dtype>
void SoftmaxLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
softmax_axis_ =
bottom[0]->CanonicalAxisIndex(this->layer_param_.softmax_param().axis());
top[0]->ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]);
vector<int> mult_dims(1, bottom[0]->shape(softmax_axis_));
sum_multiplier_.Reshape(mult_dims);
Dtype* multiplier_data = sum_multiplier_.mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(sum_multiplier_.count(), Dtype(1), multiplier_data);
outer_num_ = bottom[0]->count(0, softmax_axis_);
inner_num_ = bottom[0]->count(softmax_axis_ + 1);
vector<int> scale_dims = bottom[0]->shape();
scale_dims[softmax_axis_] = 1;
scale_.Reshape(scale_dims);
}如上所示;在reshape阶段主要是进行相关参数维度的设定。softmax_axis主要是制定从哪个维度开始切,默认是1.后面主要是初始化了两个变量,sum_multiplier_和scale_局部变量的初始化。sum_multiplier_的形状是channel的大小,一般主要是通过矩阵乘法来实现每个feature map相对应的坐标数据进行相加或者相减或者其他的操作。scale通常情况下被用来当作临时的缓冲变量。这两个变量的使用在caffe中到处可见。接下来就是forward_cpu部分的代码。
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
Dtype* scale_data = scale_.mutable_cpu_data();
int channels = bottom[0]->shape(softmax_axis_);
int dim = bottom[0]->count() / outer_num_;
caffe_copy(bottom[0]->count(), bottom_data, top_data);首先还是获取top和bottom的data,把bottom的data中的数据拷贝给top,以后就直接在top中进行计算。另外在caffe中,dim变量表示的C*W*H,spatial_dim 标识的是W*H。
for (int i = 0; i < outer_num_; ++i) {
// initialize scale_data to the first plane
caffe_copy(inner_num_, bottom_data + i * dim, scale_data);
for (int j = 0; j < channels; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < inner_num_; k++) {
scale_data[k] = std::max(scale_data[k],
bottom_data[i * dim + j * inner_num_ + k]);
}
}
// subtraction
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, channels, inner_num_,
1, -1., sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), scale_data, 1., top_data);
// exponentiation
caffe_exp<Dtype>(dim, top_data, top_data);
// sum after exp
caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasTrans, channels, inner_num_, 1.,
top_data, sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., scale_data);
// division
for (int j = 0; j < channels; j++) {
caffe_div(inner_num_, top_data, scale_data, top_data);
top_data += inner_num_;
}
}在上面首先是outer_num_样本数据中输入softmax的数据进行一个‘归一化’操作,大红色方框是为了找出当前instance中输入softmax的特征中的那个最大的数值,然后再减去那个最大数值防止产生数值计算方面的问题(例如在mnist数据集中,outer_num_是128代表的是batch的大小,inner_num_是1,这里的softmax前面链接的是inner product层,所以spatial_dim和inner_num的大小均为1,dim的大小是10,scale_data中其实也只有一个数,虽然caffe_copy之后有两行循环,其实由于inner_num是1,也就一行循环). 计算出最大的数值,然后把那个最大是数值乘以sum_multiplier_,就从1个数变成了C个数。继而做exp,把结果存放到topdata,然后把全部channel的数据求和(求和caffe使用矩阵和向量的乘法进行计算)存放到scale_data,形状是inner_num_,也就是W*H(其实就是1*1),最后就是除以求和结果啦。这么多的语句也就描述了表达式(1). 最主要的是考虑到了数值计算中存在的问题。
先做减法subtraction,是预防计算方面的一些问题,比如最终预测出来的结果其中一个数值为120,那么e的120次方,似乎就有点大了,如果做了相应的减法(这时,一个batch中的10个类别中最大的数值为130),那么只需要做e的(120-130)次方即可。即便其中有一个类别的数值为0,计算e的(0-130)次方,这种应该是有逼近运算,那些计算库很有可能就直接取0。
其中gemm和gemv函数请参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/u013066730/article/details/86218269
下面就应该是softmaxWithLoss计算损失:
先看头文件
#ifndef CAFFE_SOFTMAX_WITH_LOSS_LAYER_HPP_
#define CAFFE_SOFTMAX_WITH_LOSS_LAYER_HPP_
#include <vector>
#include "caffe/blob.hpp"
#include "caffe/layer.hpp"
#include "caffe/proto/caffe.pb.h"
#include "caffe/layers/loss_layer.hpp"
#include "caffe/layers/softmax_layer.hpp"
namespace caffe {
template <typename Dtype>
class SoftmaxWithLossLayer : public LossLayer<Dtype> {
public:
// 构造函数
explicit SoftmaxWithLossLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
: LossLayer<Dtype>(param) {}
virtual void LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual void Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual inline const char* type() const { return "SoftmaxWithLoss"; }
virtual inline int ExactNumTopBlobs() const { return -1; }
virtual inline int MinTopBlobs() const { return 1; }
virtual inline int MaxTopBlobs() const { return 2; }
protected:
// 重载CPU和GPU正反向传导虚函数
virtual void Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual void Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual void Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
virtual void Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
/// Read the normalization mode parameter and compute the normalizer based
/// on the blob size. If normalization_mode is VALID, the count of valid
/// outputs will be read from valid_count, unless it is -1 in which case
/// all outputs are assumed to be valid.
// 返回归一化计数
virtual Dtype get_normalizer(
LossParameter_NormalizationMode normalization_mode, int valid_count);
/// The internal SoftmaxLayer used to map predictions to a distribution.
/// SoftmaxLayer类实例
shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> > softmax_layer_;
/// prob stores the output probability predictions from the SoftmaxLayer.
/// prob_作为SoftmaxLayer的输出blob
Blob<Dtype> prob_;
/// bottom vector holder used in call to the underlying SoftmaxLayer::Forward
/// 指针指向bottom[0],作为SoftmaxLayer的输入blob
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> softmax_bottom_vec_;
/// top vector holder used in call to the underlying SoftmaxLayer::Forward
/// 指针指向prob_
vector<Blob<Dtype>*> softmax_top_vec_;
/// Whether to ignore instances with a certain label.
/// 标识位,是否忽略标签
bool has_ignore_label_;
/// The label indicating that an instance should be ignored.
/// 被忽略的标签值
int ignore_label_;
/// How to normalize the output loss.
/// 标识如何归一化loss
LossParameter_NormalizationMode normalization_;
// 维数、输出样本数,inner_nume在最开始已经介绍过了
int softmax_axis_, outer_num_, inner_num_;
};
} // namespace caffe
#endif // CAFFE_SOFTMAX_WITH_LOSS_LAYER_HPP_再看源文件
template <typename Dtype>
void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
LossLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(bottom, top);
LayerParameter softmax_param(this->layer_param_);
softmax_param.set_type("Softmax");
softmax_layer_ = LayerRegistry<Dtype>::CreateLayer(softmax_param);
softmax_bottom_vec_.clear();
softmax_bottom_vec_.push_back(bottom[0]);
softmax_top_vec_.clear();
softmax_top_vec_.push_back(&prob_);
softmax_layer_->SetUp(softmax_bottom_vec_, softmax_top_vec_);
has_ignore_label_ =
this->layer_param_.loss_param().has_ignore_label();
if (has_ignore_label_) {
ignore_label_ = this->layer_param_.loss_param().ignore_label();
}
if (!this->layer_param_.loss_param().has_normalization() &&
this->layer_param_.loss_param().has_normalize()) {
normalization_ = this->layer_param_.loss_param().normalize() ?
LossParameter_NormalizationMode_VALID :
LossParameter_NormalizationMode_BATCH_SIZE;
} else {
normalization_ = this->layer_param_.loss_param().normalization();
}
}上面是softmaxWithLoss的set函数,可以和很清楚地看到在初始化完成softmax_param这个参数之后,直接把type设置成了softmax,然后又通过工厂函数创建softmaxlayer,继而进行Set_up函数。可以看出softmaxWithLoss是内部创建了一个softmaxlayer。继续后面主要就是检查当前layer是否设定不对某个label进行计算Loss,也就是说,在mnist中有10个class,但是我只想对12345678进行分类,那就设定ignore_label为9.这个时候遇到标签是9的就不计算Loss。注意protobuf中没有设定默认的数值,has_xxx就返回false,只有设定了数值,才会true。后面的norm是为ignore服务的。
template <typename Dtype>
void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
LossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(bottom, top);
softmax_layer_->Reshape(softmax_bottom_vec_, softmax_top_vec_);
softmax_axis_ =
bottom[0]->CanonicalAxisIndex(this->layer_param_.softmax_param().axis());
outer_num_ = bottom[0]->count(0, softmax_axis_);
inner_num_ = bottom[0]->count(softmax_axis_ + 1);
CHECK_EQ(outer_num_ * inner_num_, bottom[1]->count())
<< "Number of labels must match number of predictions; "
<< "e.g., if softmax axis == 1 and prediction shape is (N, C, H, W), "
<< "label count (number of labels) must be N*H*W, "
<< "with integer values in {0, 1, ..., C-1}.";
if (top.size() >= 2) {
// softmax output
top[1]->ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]);
}
}接下来的reshape函数也没啥用处,就是设定了三个变量。softmax_axis_=1,outer_num_=128,inner_num_=1.需要注意的是outer_num_ * inner_num_必须和bottom[1]->count()给定的lable数相同。也就是说当softmax前面接inner product的时候,每个lable对应的是instance对应的类别(一个数),但是当softmax前面是卷积层的时候,每个label就不是一个数,而是一个矩阵,对应着每个 feature map中每个像素值的分类。下面就是计算Loss:
template <typename Dtype>
void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
// The forward pass computes the softmax prob values.
softmax_layer_->Forward(softmax_bottom_vec_, softmax_top_vec_);
const Dtype* prob_data = prob_.cpu_data();
const Dtype* label = bottom[1]->cpu_data();
int dim = prob_.count() / outer_num_;
int count = 0;
Dtype loss = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < outer_num_; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < inner_num_; j++) {
const int label_value = static_cast<int>(label[i * inner_num_ + j]);
if (has_ignore_label_ && label_value == ignore_label_) {
continue;
}
DCHECK_GE(label_value, 0);
DCHECK_LT(label_value, prob_.shape(softmax_axis_));
loss -= log(std::max(prob_data[i * dim + label_value * inner_num_ + j],
Dtype(FLT_MIN)));
++count;
}
}
top[0]->mutable_cpu_data()[0] = loss / get_normalizer(normalization_, count);
if (top.size() == 2) {
top[1]->ShareData(prob_);
}
}这里寿面是计算softmax_layer_的forward函数,softmax_top_vec_其实是prob_的一个引用。prob_data的大小是N*C*1*1.static_cast<int>(label[i * inner_num_ + j])是从对应的instance中取出相对应的标签。如果当前的label和ignore label相同,那么就不计算Loss损失,这样就存在问题,假如128个instance中有10个不计算Loss,那么最终在计算Loss的平均的时候,是除以多少呢?这就用到了norm。count在这里统计我们计算了多少个instance的Loss数值。prob_data[i * dim + label_value * inner_num_ + j] dim是10,label_value是instance的标签来当作index来从prob中取数据(该instance的分类结果),j是0,因为W=H=1。 softmax_layer_->Forward(softmax_bottom_vec_, softmax_top_vec_);这句非常关键,通过forword就会调用softmax,这样就会计算出概率值。
get_normalizer在VAILD模式下会返回我们计算了多少个Loss的个数,也就是count。这个时候当前batch的Loss就已经放回到top[0]中去了。下一步要计算的就是Loss的反向传播。其实get_normalizer就是为了防止计数为0这种情况的出现。
// CPU反向传导
template <typename Dtype>
void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
if (propagate_down[1]) {
LOG(FATAL) << this->type()
<< " Layer cannot backpropagate to label inputs.";
}
if (propagate_down[0]) {
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
const Dtype* prob_data = prob_.cpu_data();
// 先将正向传导时计算的prob_数据(f(y_k))拷贝至偏导
caffe_copy(prob_.count(), prob_data, bottom_diff);
const Dtype* label = bottom[1]->cpu_data();
int dim = prob_.count() / outer_num_;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < outer_num_; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < inner_num_; ++j) {
const int label_value = static_cast<int>(label[i * inner_num_ + j]);
// 如果为忽略标签,则偏导为0
if (has_ignore_label_ && label_value == ignore_label_) {
for (int c = 0; c < bottom[0]->shape(softmax_axis_); ++c) {
bottom_diff[i * dim + c * inner_num_ + j] = 0;
}
} else {
// 计算偏导,预测正确的bottom_diff = f(y_k) - 1,其它不变
bottom_diff[i * dim + label_value * inner_num_ + j] -= 1;
++count;
}
}
}
// Scale gradient
// top[0]->cpu_diff()[0] = 1.0,已在SetLossWeights()函数中初始化
Dtype loss_weight = top[0]->cpu_diff()[0] /
get_normalizer(normalization_, count);
// 将bottom_diff归一化
caffe_scal(prob_.count(), loss_weight, bottom_diff);
}
}在反向传播时,根据求导结果,可以得到求导公式:

因此,通过caffe_copy(prob_.count(), prob_data, bottom_diff);来实现zj不等于zk的情况,通过bottom_diff[i * dim + label_value * inner_num_ + j] -= 1;来实现zj等于zk的情况。
参考