1.3.3. 接收机
1.3.3. Receivers
第1.3.1节指出,雷达信号通常是窄带、带通的相位调制或频率调制信号。
It was shown in Sec. 1.3.1that radar signals are usually narrowband, bandpass, phase- orfrequency-modulated functions.
这意味着单散射点的雷达回波表达式r(t)为:
This means that the echo waveform r(t)received from a single scatterer is of the form
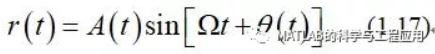
其中幅度调制A(t)表示脉冲包络。
where the amplitude modulation A(t)represents only the pulse envelope.
接收机处理的主要功能是将雷达信号的承载信息解调到基带,其目的之一是测量θ(t)。
The major function of the receiverprocessing is demodulation of the information bearing part of the radar signalto baseband, with the goal of measuring θ(t).
图1.9描述了大多数经典雷达中使用的接收机设计的传统方法。
Figure 1.9 illustrates the conventionalapproach to receiver design used in most classical radars.
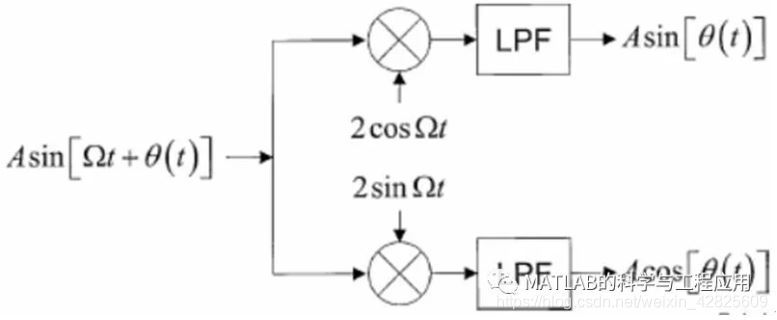
图1.9 传统的正交通道接收机模型,图中的下通道为同相I通道,上通道为正交相位Q通道Conventional quadrature channelreceiver model. In this illustration, the lower channel is the in-phase(“I”) channel, and the upper is the quadrature phase (“Q”)channel
正交接收机中的信号被分离为两个通道。
The received signal is split into twochannels.
在雷达工作频率上,称为同相I通道的信号与本振LO进行混频。
One channel, called the in-phase or"I" channel of the receiver (the lower branch in Fig. 1.9) mixes thereceived signal with an oscillator, called the local oscillator (LO), at theradar frequency.
混频产生和频、差频:
This generates both sum and differencefrequency components:
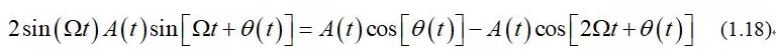
采用低通滤波器可以滤除掉和频,从而只保留差频调制项A(t)cos[θ(t)]。
The sum term is then removed by the lowpassfilter, leaving only the modulation term A(t)cos[θ(t)].
正交相位Q通道经过混频后具有与I通道相同的信号频率,但会产生90度的相移。
The other channel, called the quadraturephase or “Q” channel, mixes the signal with an oscillator having thesame frequency but a 90° phase shift from the I channel oscillator.
Q通道混频器输出为:
The Q channelmixer output is
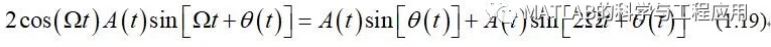
Q通道经过低通滤波后,得到的调制项为A(t)sin[θ(t)]。
which, after filtering, leaves themodulation term A(t)sin[θ(t)].
如果输入信号r(t)为A(t)cos[Ωt + θ(t)],则图1.9中的上通道成为同相I通道,下通道成为正交Q通道,低通滤波后的输出分别为A(t)cos[θ(t)]和–A(t)sin[θ(t)]。
If the input r(t) is written as A(t)cos[Ωt+ θ(t)] instead, the upper channel of Fig. 1.9 becomes the I channel and thelower the Q channel, with outputs A(t)cos[θ(t)] and –A(t)sin[θ(t)],respectively.
I通道是指本振信号与输入信号相同的通道。
In general, the I channel is the one wherethe oscillator function (sine or cosine) is the same as that used in modelingthe signal.
采用I通道和Q通道解调的原因在于,单独一个通道不能提供足够的信息来明确地确定相位调制θ(t)。
The reason that both the I and Q channelsare needed is that either one alone does not provide sufficient information todetermine the phase modulation θ(t) unambiguously.
——本文译自Mark A. Richards所著的《Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing(Second edition)》
更多精彩文章请关注微信号: