[深度学习入门]实战二·使用TensorFlow拟合直线
- 问题描述
拟合直线 y =(2x -1) + 0.1(-1到1的随机值)
给定x范围(0,3)
可以使用学习框架
建议使用
y = w * x + b 网络模型
- 生成数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_data(x,w,b):
c,r = x.shape
y = (x * w + b)+ (0.1*(2*np.random.rand(c,r)-1))
return(y)
xs = np.arange(0,3,0.01).reshape(-1,1)
ys = get_data(xs,2,-1)
plt.title("X-Y")
plt.plot(xs,ys)
plt.show()
生成图像:
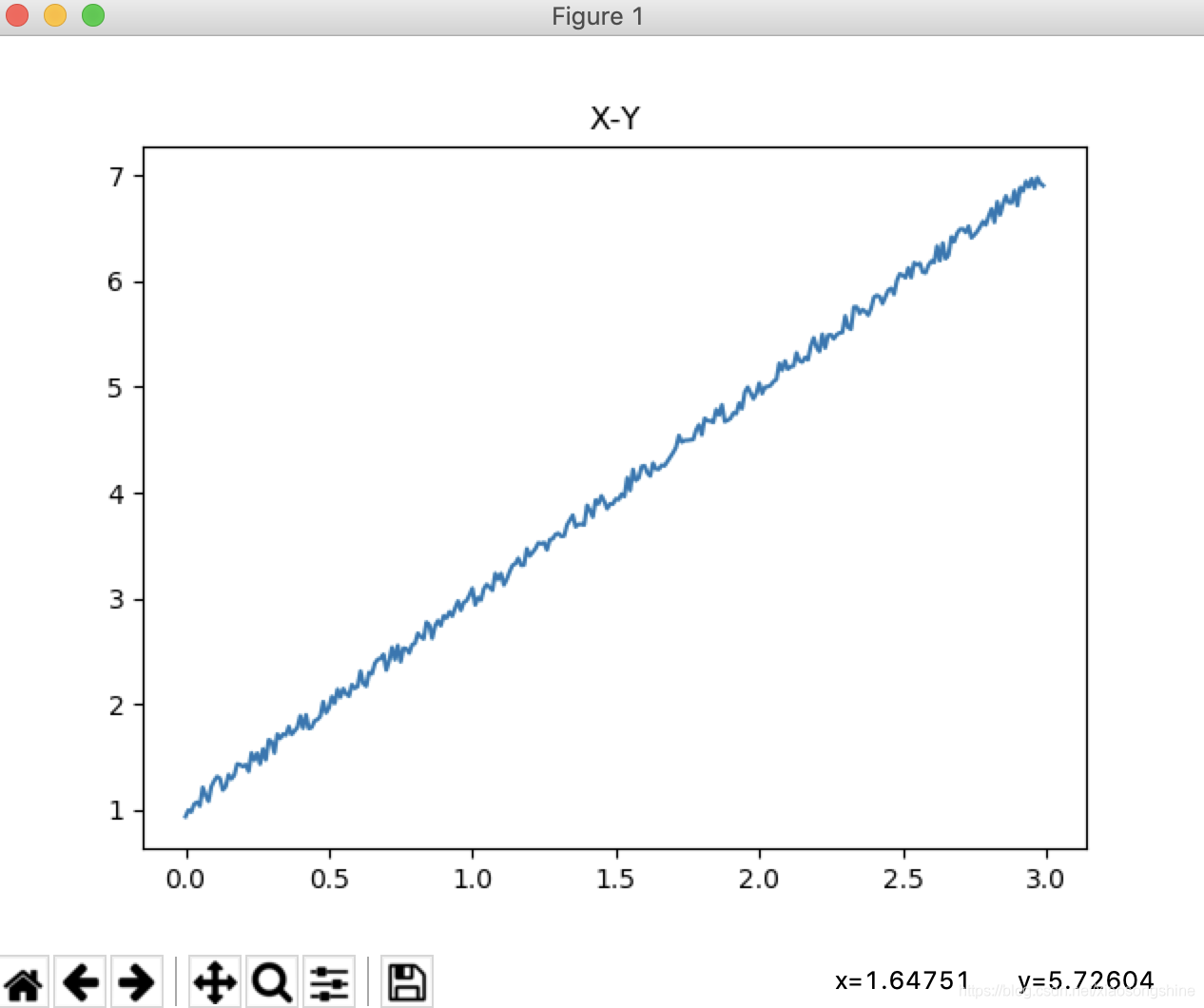
- 搭建网络结构
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])
w = tf.get_variable("w1",initializer=tf.random_normal([1,1]))
b = tf.get_variable("b1",initializer=tf.zeros([1,1]))
y = w*x + b
- 定义学习函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_))
opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.02).minimize(loss)
- 训练网络参数
with tf.Session() as sess:
srun = sess.run
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
srun(init)
print("w0 b0",srun([w,b]))
for e in range(500):
loss_val,_ = srun([loss,opt],{x:xs,y_:ys})
if(e%50 ==0):
print("%d steps loss is %f",e,loss_val)
print("w b",srun([w,b]))
w_pre,b_pre =srun(w)[0,0],srun(b)[0,0]
print(w_pre,b_pre)
- 显示预测结果
ys_pre = get_data(xs,w_pre,b_pre)
plt.title("X-Y")
plt.plot(xs,ys)
plt.plot(xs,ys_pre)
plt.legend(["y","y_pre"])
plt.show()
- 运行结果
log:
w0 b0 [array([[-0.4106835]], dtype=float32), array([[0.]], dtype=float32)]
%d steps loss is %f 0 11.149577
%d steps loss is %f 50 0.37165892
%d steps loss is %f 100 0.16953693
%d steps loss is %f 150 0.07829344
%d steps loss is %f 200 0.03710342
%d steps loss is %f 250 0.018508982
%d steps loss is %f 300 0.010114888
%d steps loss is %f 350 0.0063255588
%d steps loss is %f 400 0.0046149325
%d steps loss is %f 450 0.0038427087
w b [array([[1.9863906]], dtype=float32), array([[-0.9746746]], dtype=float32)]
1.9863906 -0.9746746
运行结果图
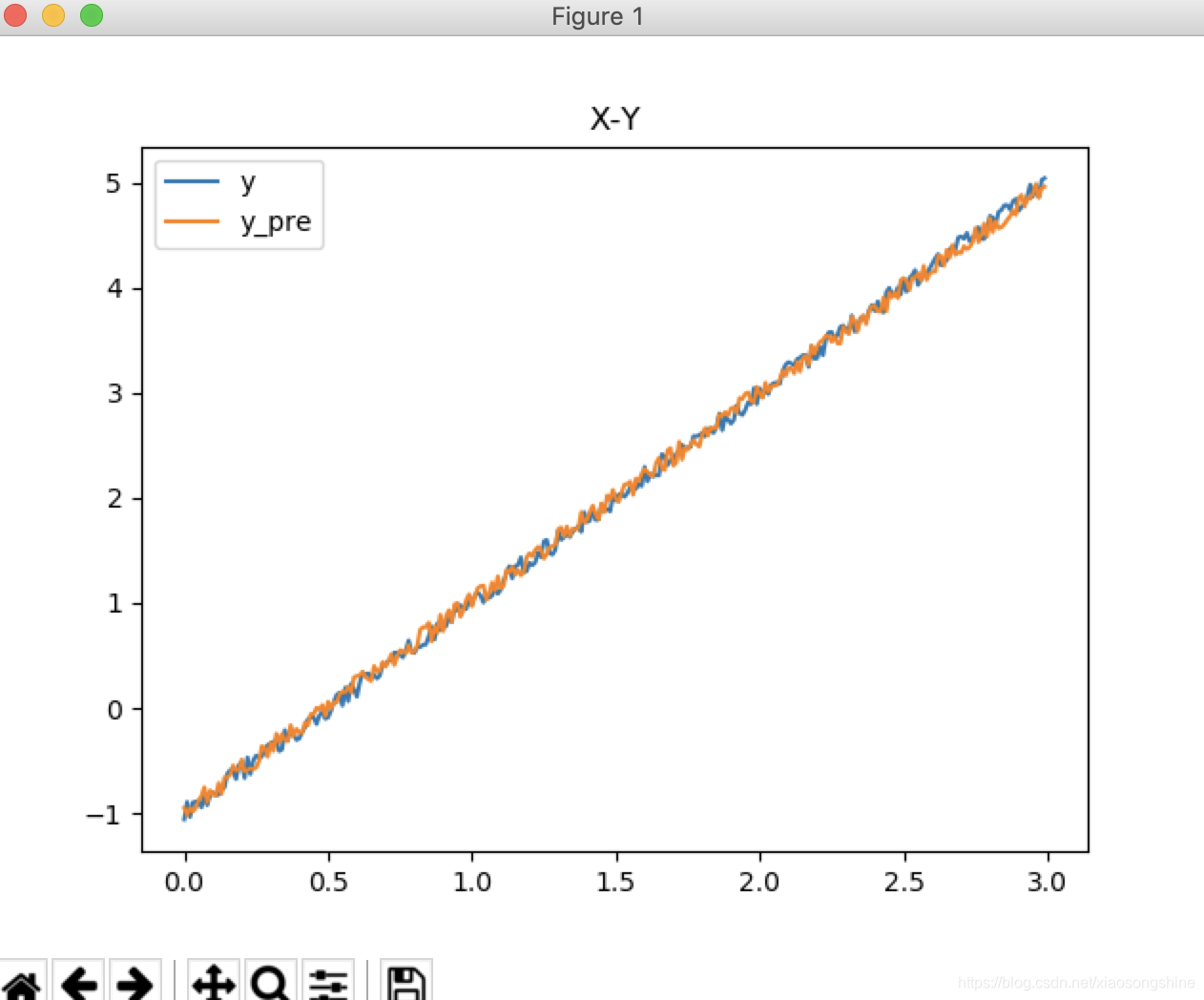
- 完整代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
def get_data(x,w,b):
c,r = x.shape
y = (x * w + b)+ (0.1*(2*np.random.rand(c,r)-1))
return(y)
xs = np.arange(0,3,0.01).reshape(-1,1)
ys = get_data(xs,2,-1)
print(ys.shape)
"""plt.title("X-Y")
plt.plot(xs,ys)
plt.show()"""
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])
w = tf.get_variable("w1",initializer=tf.random_normal([1,1]))
b = tf.get_variable("b1",initializer=tf.zeros([1,1]))
y = w*x + b
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_))
opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.02).minimize(loss)
with tf.Session() as sess:
srun = sess.run
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
srun(init)
print("w0 b0",srun([w,b]))
for e in range(500):
loss_val,_ = srun([loss,opt],{x:xs,y_:ys})
if(e%50 ==0):
print("%d steps loss is %f",e,loss_val)
print("w b",srun([w,b]))
w_pre,b_pre =srun(w)[0,0],srun(b)[0,0]
print(w_pre,b_pre)
ys_pre = get_data(xs,w_pre,b_pre)
plt.title("X-Y")
plt.plot(xs,ys)
plt.plot(xs,ys_pre)
plt.legend(["y","y_pre"])
plt.show()