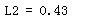吴恩达神经网络与深度学习——神经网络基础习题
python numpy 基础
1.使用iPython Notebooks
2.使用numpy 函数 and numpy矩阵或向量操作
3.理解"broadcasting"
4.向量化代码
用numpy建立一个基础函数
sigmoid 函数
math库
# GRADED FUNCTION: basic_sigmoid
import math
def basic_sigmoid(x):
"""
Compute sigmoid of x.
Arguments:
x -- A scalar
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
s = 1/(1+math.exp(-x))
### END CODE HERE ###
return s

实际上,我们很少在深度学习中使用math库,因为函数的输入是实数。在深度学习中,我们主要使用矩阵和向量。这就是为什么numpy更有用。
numpy库
事实上,如果x = ( x1,x2,...xn )是行向量,则np.exp(x)将对x的每个元素应用指数函数。因此输出将是np.exp(x)=(ex1,ex2...exn)
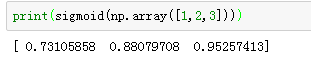
# GRADED FUNCTION: sigmoid
import numpy as np # this means you can access numpy functions by writing np.function() instead of numpy.function()
def sigmoid(x):
"""
Compute the sigmoid of x
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array of any size
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
### END CODE HERE ###
return s
Sigmoid 导数
sigmoid_derivative.py
# GRADED FUNCTION: sigmoid_derivative
def sigmoid_derivative(x):
"""
Compute the gradient (also called the slope or derivative) of the sigmoid function with respect to its input x.
You can store the output of the sigmoid function into variables and then use it to calculate the gradient.
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array
Return:
ds -- Your computed gradient.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
s = sigmoid(x)
ds = s*(1-s)
### END CODE HERE ###
return ds
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print ("sigmoid_derivative(x) = " + str(sigmoid_derivative(x)))
Reshaping arrays
X.shape:得到矩阵或向量的维度
X.reshape():将X转化成别的维度
def image2vector(image):
v = image.reshape(image.shape[0]*image.shape[1]*image.shape[2],1)
return v
import numpy as np
image = np.random.rand(3,3,3)
image2vector(image)
Normalizing rows

# GRADED FUNCTION: normalizeRows
def normalizeRows(x):
"""
Implement a function that normalizes each row of the matrix x (to have unit length).
Argument:
x -- A numpy matrix of shape (n, m)
Returns:
x -- The normalized (by row) numpy matrix. You are allowed to modify x.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
# Compute x_norm as the norm 2 of x. Use np.linalg.norm(..., ord = 2, axis = ..., keepdims = True)
x_norm = np.linalg.norm(x,ord=2,axis = 1,keepdims = True)
# Divide x by its norm.
x = x/x_norm
# Divide x by its norm.
### END CODE HERE ###
return x
x = np.array([
[0, 3, 4],
[2, 6, 4]])
print("normalizeRows(x) = " + str(normalizeRows(x)))
print("x shape:"+ str(x.shape))
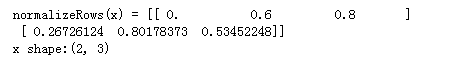
Broadcasting and the softmax function
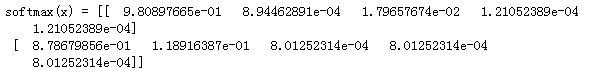
# GRADED FUNCTION: softmax
def softmax(x):
"""Calculates the softmax for each row of the input x.
Your code should work for a row vector and also for matrices of shape (n, m).
Argument:
x -- A numpy matrix of shape (n,m)
Returns:
s -- A numpy matrix equal to the softmax of x, of shape (n,m)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)
# Apply exp() element-wise to x. Use np.exp(...).
x = np.exp(x)
# Create a vector x_sum that sums each row of x_exp. Use np.sum(..., axis = 1, keepdims = True).
x_sum = np.sum(x,axis = 1,keepdims = True)
# Compute softmax(x) by dividing x_exp by x_sum. It should automatically use numpy broadcasting.
s = x/x_sum
### END CODE HERE ###
return s
x = np.array([
[9, 2, 5, 0, 0],
[7, 5, 0, 0 ,0]])
print("softmax(x) = " + str(softmax(x)))
Vectorization
Implement the L1 and L2 loss functions
L1正则化
# GRADED FUNCTION: L1
def L1(yhat, y):
"""
Arguments:
yhat -- vector of size m (predicted labels)
y -- vector of size m (true labels)
Returns:
loss -- the value of the L1 loss function defined above
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
#loss = np.sum(np.abs(y-yhat),axis = 0,keepdims = True)
loss = np.sum(np.abs(y-yhat))
### END CODE HERE ###
return loss
yhat = np.array([.9, 0.2, 0.1, .4, .9])
y = np.array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1])
print("L1 = " + str(L1(yhat,y)))
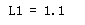
L2正则化
# GRADED FUNCTION: L2
def L2(yhat, y):
"""
Arguments:
yhat -- vector of size m (predicted labels)
y -- vector of size m (true labels)
Returns:
loss -- the value of the L2 loss function defined above
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
loss = np.sum(np.square(y-yhat))
### END CODE HERE ###
return loss
yhat = np.array([.9, 0.2, 0.1, .4, .9])
y = np.array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1])
print("L2 = " + str(L2(yhat,y)))