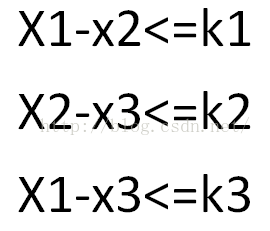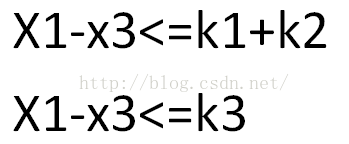Layout
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 10278 | Accepted: 4946 |
Description
Like everyone else, cows like to stand close to their friends when queuing for feed. FJ has N (2 <= N <= 1,000) cows numbered 1..N standing along a straight line waiting for feed. The cows are standing in the same order as they are numbered, and since they can be rather pushy, it is possible that two or more cows can line up at exactly the same location (that is, if we think of each cow as being located at some coordinate on a number line, then it is possible for two or more cows to share the same coordinate).
Some cows like each other and want to be within a certain distance of each other in line. Some really dislike each other and want to be separated by at least a certain distance. A list of ML (1 <= ML <= 10,000) constraints describes which cows like each other and the maximum distance by which they may be separated; a subsequent list of MD constraints (1 <= MD <= 10,000) tells which cows dislike each other and the minimum distance by which they must be separated.
Your job is to compute, if possible, the maximum possible distance between cow 1 and cow N that satisfies the distance constraints.
Input
Line 1: Three space-separated integers: N, ML, and MD.
Lines 2..ML+1: Each line contains three space-separated positive integers: A, B, and D, with 1 <= A < B <= N. Cows A and B must be at most D (1 <= D <= 1,000,000) apart.
Lines ML+2..ML+MD+1: Each line contains three space-separated positive integers: A, B, and D, with 1 <= A < B <= N. Cows A and B must be at least D (1 <= D <= 1,000,000) apart.
Output
Line 1: A single integer. If no line-up is possible, output -1. If cows 1 and N can be arbitrarily far apart, output -2. Otherwise output the greatest possible distance between cows 1 and N.
Sample Input
4 2 1
1 3 10
2 4 20
2 3 3
Sample Output
27
Hint
Explanation of the sample:
There are 4 cows. Cows #1 and #3 must be no more than 10 units apart, cows #2 and #4 must be no more than 20 units apart, and cows #2 and #3 dislike each other and must be no fewer than 3 units apart.
The best layout, in terms of coordinates on a number line, is to put cow #1 at 0, cow #2 at 7, cow #3 at 10, and cow #4 at 27.
Source
题目大意:
一共有n头牛,有ml个关系好的牛的信息,有md个关系不好的牛的信息,对应输入的第一行的三个元素,接下来ml行,每行三个元素A,B,D,表示A牛和B牛相距不希望超过D,接下来md行,每行三个元素A,B,D表示A牛和B牛的相距至少要有D才行。求1号牛和n号牛的最大距离,如果距离无限大输出-2,如果无解输出-1。
思路:
1、因为我们要求1号牛和n号牛的最大距离,那么我们希望得到这样一个不等式(假设n==5):①-⑤<=x,那么这个x就是1号牛和n号牛的最大距离。
2、那么我们引入一个差分约束系统的相关概念:
差分约束系统问题,能够将问题转化为最短路问题。以下给出转化过程:
假设有这样的三个条件:
那么我们可以将不等式1和不等式2相加得到:
那么如果想要得到x1和x3的最大差值,那么其实就是取 min(k1+k2,k3);
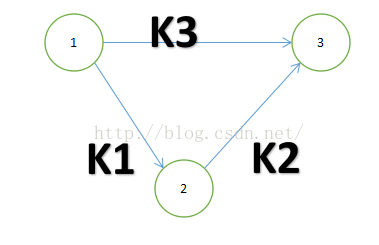
其实问题我们可以将问题转化成图论,将x1,x2,x3看成三个点x1,x2,x3,对应三条边的建立就根据三个不等式来建立,那么边权值如何取呢?显然我们想要最大差值,我们就需要取最大值,那么图可以建立成这样:
那么我们上述过程将不等式1和不等式2相加,然后和不等式3比较值的过程,其实就是最短路计算过程中的判断能否松弛的过程。
那么我们就可以根据不等式建立有向图,然后再通过有向图计算1号点到n号点的最短路,其值就是x1与xn的最大差值。
3、然后我们再回归到这个问题上来。
对应ml条信息:
①牛A和牛B的距离不想超过D,那么建立不等式:posA-posB<=D;加入到图中直接add(A,B,D)即可
对应md条信息:
②牛A和牛B的距离至少要为D,那么建立不等式:posA-posB>=D,那么我们左右两边同乘-1有:posB-posA<=-D,那么加入到图中add(B,A,-D)即可。
4、图建立好之后直接跑最短路即可。
对应输出:
①如果dis【n】==inf,输出-2;
②否则输出dis【n】;
③如果在跑SPFA过程中发现了负环,说明问题无解,那么输出-1.
Ac代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<math.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<stack>
//#define mod 998244353
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define eps 1e-6
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int maxn=2e5+10;
int n,ml,md;
int cnt;
int head[maxn];
struct Edge
{
int to;
int next;
int val;
}edge[maxn<<2];
void addEdge(int from,int to,int val)
{
edge[cnt].to=to;
edge[cnt].val=val;
edge[cnt].next=head[from];
head[from]=cnt++;
}
int dis[maxn];
int qnum[maxn];
bool inq[maxn];
bool spfa(int start)
{
memset(qnum,0,sizeof qnum);
memset(inq,0,sizeof inq);
memset(dis,INF,sizeof dis);
queue<int>q;
q.push(start);
qnum[start]++;
inq[start]=true;
dis[start]=0;
while(!q.empty()){
int cur=q.front();
q.pop();
inq[cur]=false;
for(int i=head[cur];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next){
int to=edge[i].to;
if(dis[to]>dis[cur]+edge[i].val){
dis[to]=dis[cur]+edge[i].val;
if(!inq[to]){
inq[to]=1,q.push(to),qnum[to]++;
if(qnum[to]>n)
return true;//存在负权环
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
cnt=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof head);
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&ml,&md);
int u,v,w;
for(int i=1;i<=ml;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
if(u>v) swap(u,v);
addEdge(u,v,w);
}
for(int i=1;i<=md;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
if(u>v) swap(u,v);
addEdge(v,u,-w);
}
bool flag=spfa(1);
if(flag){
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
if(dis[n]==INF){
printf("-2\n");
return 0;
}
printf("%d\n",dis[n]);
return 0;
}