本文为原创文章转载请注明出处,博主博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_20259459 和
作者( [email protected] )信息。
(如有需要可以邮件联系我)
上学期神经网最后的project有关CNN的部分我们学习使用了MatConvNet。
从名字我们就知道,Matlab Convolution Neural Network。所以就不做过多介绍了。
正文:
MatConvNet 本身是用Matlab去编译运行C++文件,所以我们需要搭建相关连接。
这里我用到的是Matlab2016a和VS2015两个平台去实现的。这里我极力推荐VS2015版本和Matlab2013以后的版本。
因为我当时尝试了VS2017不可以,VS2010可以但是必须要按照网上的相关步骤去一步一步的按照顺序的安装SDK,相当的麻烦。所以我强烈推荐大家用VS2015.因为只需要在安装的时候选上开发者工具包并一起安装就可以很简单的进行二者的搭建。
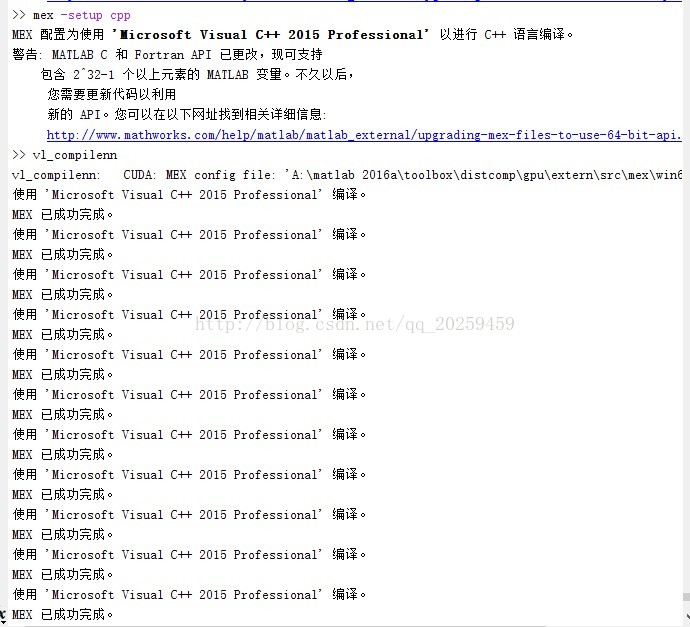
配置方法:
1. 添加MatConvNet内的相关文件夹至Matlab路径中。
2. 输入:mex -setup cpp 等待系统配置。
3. 配置成功之后,输入:vl_compilenn进行搭建相关文件。
如下图:
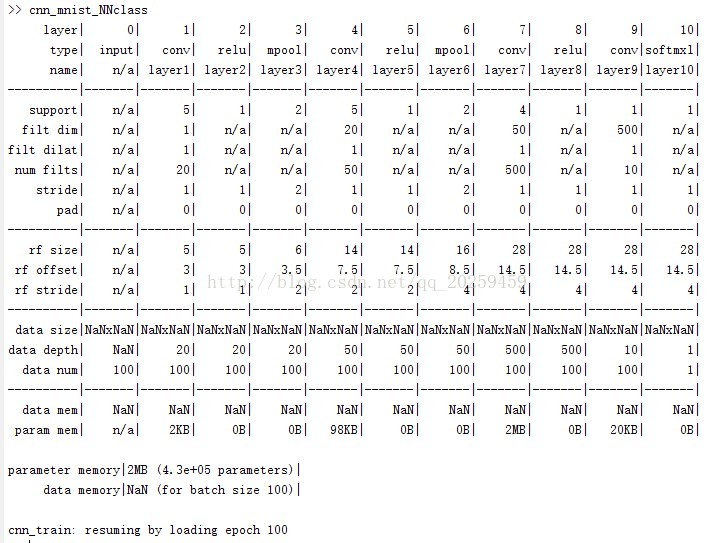
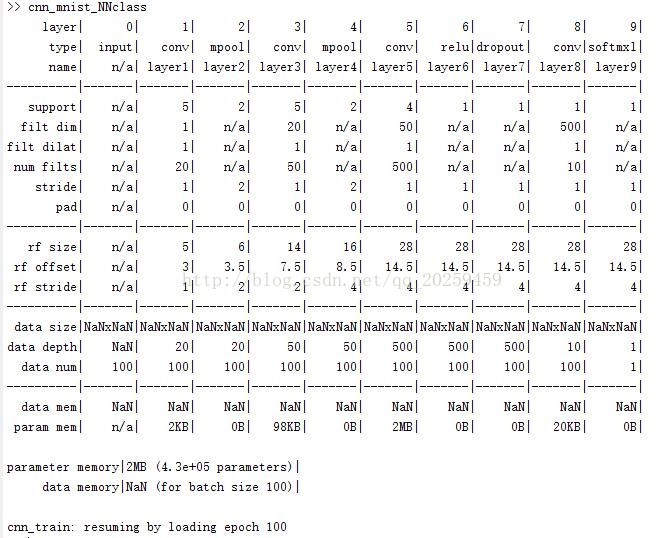
第二步,我们就可以利用MatConvNet自带的数据集进行训练了,不过我们当时并没有使用自带的cnn_mnist_init.m文件来做训练,我的请看下面代码。
下面是我的CNN的编程:
function cnn_mnist_NNclass(varargin)
warning off
% CNN_MNIST Demonstrated MatConNet on MNIST
% run( fullfile(fileparts(mfilename('fullpath')), '../matlab/vl_setupnn.m') ) ;
run('C:\Users\matconvnet-1.0-beta23\matconvnet-1.0-beta23\matlab/vl_setupnn.m') ;
opts.dataDir = 'data/mnist' ;
opts.expDir = 'data/mnist-baseline' ;
opts.imdbPath = fullfile(opts.expDir, 'imdb.mat');
opts.train.batchSize = 100 ;
opts.train.numEpochs = 100 ;
opts.train.continue = true ;
% opts.train.useGpu = [] ;
opts.train.gpus = [];
opts.train.learningRate = 0.001 ;
opts.train.expDir = opts.expDir ;
opts = vl_argparse(opts, varargin);
opts.train.subsetSize = 1e4; % statsogk
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
% Prepare data
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
if exist(opts.imdbPath)
imdb = load(opts.imdbPath) ;
else
imdb = getMnistImdb(opts) ;
mkdir(opts.expDir) ;
save(opts.imdbPath, '-struct', 'imdb') ;
end
% Use a subset of the images for faster training.
if opts.train.subsetSize > 0
imdb = getSubset(imdb,opts);
end
% Define a network similar to LeNet
f=1/100 ;
net.layers = {} ;
net.layers{end+1} = struct('type', 'conv', ...
'filters', f*randn(5,5,1,20, 'single'), ...
'biases', zeros(1, 20, 'single'), ...
'stride', 1, ...
'pad', 0) ;
% net.layers{end+1} = struct('type', 'relu') ;
net.layers{end+1} = struct('type', 'pool', ...
'method', 'max', ...
'pool', [2 2], ...
'stride', 2, ...
'pad', 0) ;
net.layers{end+1} = struct('type', 'conv', ...
'filters', f*randn(5,5,20,50, 'single'),...
'biases', zeros(1,50,'single'), ...
'stride', 1, ...
'pad', 0) ;
% net.layers{end+1} = struct('type', 'relu') ;
net.layers{end+1} = struct('type', 'pool', ...
'method', 'max', ...
'pool', [2 2], ...
'stride', 2, ...
'pad', 0) ;
net.layers{end+1} = struct('type', 'conv', ...
'filters', f*randn(4,4,50,500, 'single'),...
'biases', zeros(1,500,'single'), ...
'stride', 1, ...
'pad', 0) ;
net.layers{end+1} = struct('type', 'relu') ;
net.layers{end+1} = struct('type', 'conv', ...
'filters', f*randn(1,1,500,10, 'single'),...
'biases', zeros(1,10,'single'), ...
'stride', 1, ...
'pad', 0) ;
net.layers{end+1} = struct('type', 'softmaxloss') ;
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
% Train
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
% Take the mean out and make GPU if needed
imdb.images.data = bsxfun(@minus, imdb.images.data, mean(imdb.images.data,4)) ;
% if opts.train.useGpu
if opts.train.gpus
imdb.images.data = gpuArray(imdb.images.data) ;
end
[ net, info ] = cnn_train(net, imdb, @getBatch, opts.train, 'val', find(imdb.images.set == 3)) ;
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function [im, labels] = getBatch(imdb, batch)
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
im = imdb.images.data(:,:,:,batch) ;
labels = imdb.images.labels(1,batch) ;
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
function imdb = getMnistImdb(opts)
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
files = {'train-images-idx3-ubyte', ...
'train-labels-idx1-ubyte', ...
't10k-images-idx3-ubyte', ...
't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte'} ;
mkdir(opts.dataDir) ;
for i=1:4
if ~exist(fullfile(opts.dataDir, files{i}), 'file')
url = sprintf('http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/%s.gz',files{i}) ;
fprintf('downloading %s\n', url) ;
gunzip(url, opts.dataDir) ;
end
end
f=fopen(fullfile(opts.dataDir, 'train-images-idx3-ubyte'),'r') ;
x1=fread(f,inf,'uint8');
fclose(f) ;
x1=permute(reshape(x1(17:end),28,28,60e3),[2 1 3]) ;
f=fopen(fullfile(opts.dataDir, 't10k-images-idx3-ubyte'),'r') ;
x2=fread(f,inf,'uint8');
fclose(f) ;
x2=permute(reshape(x2(17:end),28,28,10e3),[2 1 3]) ;
f=fopen(fullfile(opts.dataDir, 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte'),'r') ;
y1=fread(f,inf,'uint8');
fclose(f) ;
y1=double(y1(9:end)')+1 ;
f=fopen(fullfile(opts.dataDir, 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte'),'r') ;
y2=fread(f,inf,'uint8');
fclose(f) ;
y2=double(y2(9:end)')+1 ;
imdb.images.data = single(reshape(cat(3, x1, x2),28,28,1,[])) ;
imdb.images.labels = cat(2, y1, y2) ;
imdb.images.set = [ones(1,numel(y1)) 3*ones(1,numel(y2))] ;
imdb.meta.sets = {'train', 'val', 'test'} ;
imdb.meta.classes = arrayfun(@(x)sprintf('%d',x),0:9,'uniformoutput',false) ;
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function imdb = getSubset(imdb,opts)
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
assert(opts.train.subsetSize <= nnz(imdb.images.set == 1),...
'Subset size is bigger than the total train set size')
inds = find(imdb.images.set == 1); % indices must be from the train set
inds = randsample(inds, length(inds)-opts.train.subsetSize );
imdb.images.labels(inds) = [];
imdb.images.set(inds) = [];
imdb.images.data(:,:,:,inds) = [];下面是我的运行结果一共为四个(我一共构造了3个网络外加原始网络一共是4个):
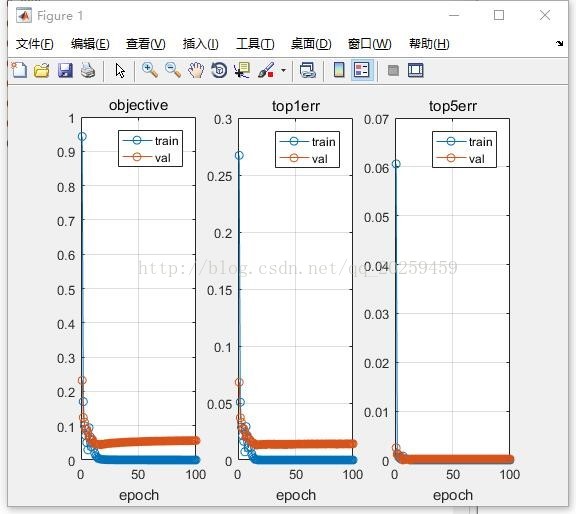
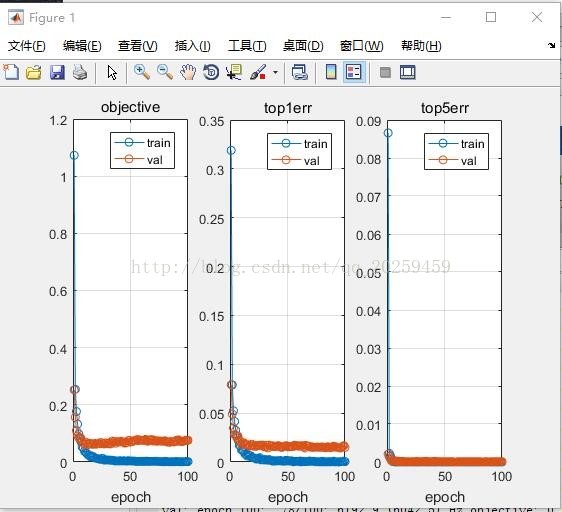
1. 原始CNN(LeNets)的训练结果:
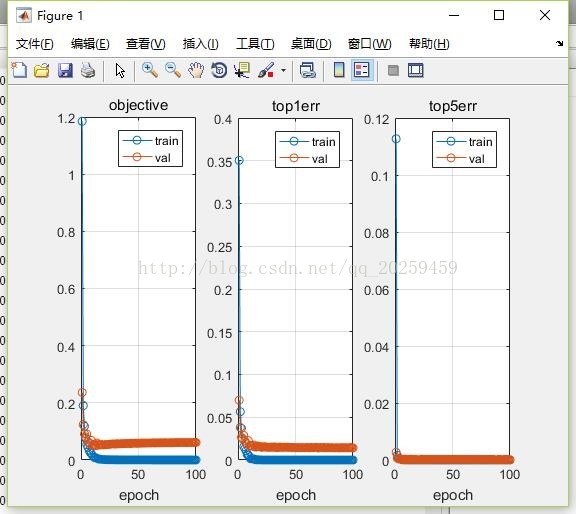
2.减去两层(layer)之后的训练结果:
3.增加两层之后的训练结果:
4.在原始网络中添加Dropout layer之后的训练结果:
实验结果讨论:(在我的project里面我已经写了相关的讨论(英文),大家可以百度翻译一下看看,我这里就不再写了,直接复制粘贴了。)
1. Thediscussion about the Top1 err and Top5 err.
First,you make a prediction using the CNN and obtain the predicted class multinomialdistribution (∑pclass=1∑pclass=1).
Now, inthe case of top-1 score, you check if the top class (the one having the highestprobability) is the same as the target label.
In thecase of top-5 score, you check if the target label is one of your top 5predictions (the 5 ones with the highest probabilities).
In bothcases, the top score is computed as the times a predicted label matched thetarget label, divided by the number of data-points evaluated.
Finally,when 5-CNNs are used, you first average their predictions and follow the sameprocedure for calculating the top-1 and top-5 scores.
2. Thediscussion about the differences between reduced and increased
|
|
Original LeNets |
Reduced |
Increased |
Dropout |
| Object |
0.082 |
0.071 |
0.062 |
0.066 |
| Top1 err |
0.021 |
0.019 |
0.018 |
0.018 |
| Top5 err |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
Generallyif we use more layers, it becomes more complex and more prone to overfitting.To avoid that kind of problem when increasing the layers, I add relu layers.And the result shows that it performs than the original one. But if I addlayers consisting of additional conv-pool , then it would cause overfitting anderror will go up.
Alsowhen decreasing two layers , I got less error than the original one because itreduces the complexity. More complexity means more extract details from thefeature. Through erasing some layers, network becomes nice circumstance andperforms better than the original one.
3. Thediscussion about Dropout Layer.
A dropout layerrandomly sets a layer's input elements to zero with a given probability.
This corresponds to temporarily droppinga randomly chosen unit and all of its connections from the network duringtraining. So, for each new input element, the software randomly selects asubset of neurons, hence forms a different layer architecture. Thesearchitectures use common weights, but because the learning does not depend onspecific neurons and connections, the dropout layer might help preventoverfitting
4. DROPOUT FOR REGULARIZATION
Hinton,Srivastava, Krizhevsky, Sutskever, & Salakhutdinov (2012) introduced thedropout regularization algorithm. Although dropout works in a different waythan L1 and L2, it accomplishes the same goal—the prevention of overfitting.However, the algorithm goes about the task by actually removing neurons and connections—atleast temporarily. Unlike L1 and L2, no weight penalty is added. Dropout doesnot directly seek to train small weights. Most neural network frameworksimplement dropout as a separate layer. Dropout layers function as a regular,densely connected neural network layer. The only difference is that the dropoutlayers will periodically drop some of their neurons during training. You canuse dropout layers on regular feedforward neural networks. Figure 6 showsdropout in action.
本文为原创文章转载请注明出处,博主博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_20259459 和
作者( [email protected] )信息。