版权声明:版权所有--转载的小伙伴请告知博主并注明来源哦~ https://blog.csdn.net/u011145745/article/details/81945348
数据结构实验之二叉树一:树的同构
Time Limit: 1000 ms Memory Limit: 65536 KiB
Problem Description
给定两棵树T1和T2。如果T1可以通过若干次左右孩子互换就变成T2,则我们称两棵树是“同构”的。例如图1给出的两棵树就是同构的,因为我们把其中一棵树的结点A、B、G的左右孩子互换后,就得到另外一棵树。而图2就不是同构的。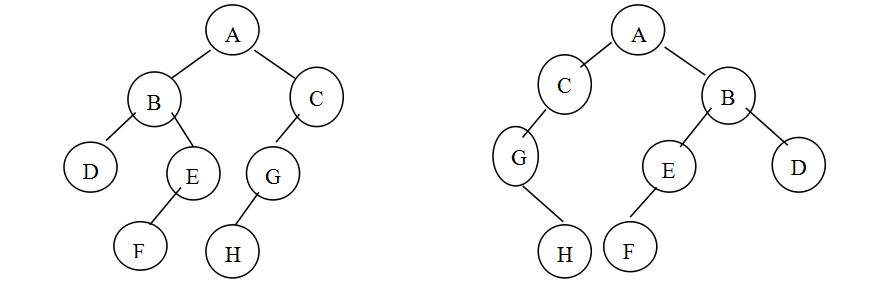
图1

图2
现给定两棵树,请你判断它们是否是同构的。
Input
输入数据包含多组,每组数据给出2棵二叉树的信息。对于每棵树,首先在一行中给出一个非负整数N (≤10),即该树的结点数(此时假设结点从0到N−1编号);随后N行,第i行对应编号第i个结点,给出该结点中存储的1个英文大写字母、其左孩子结点的编号、右孩子结点的编号。如果孩子结点为空,则在相应位置上给出”-”。给出的数据间用一个空格分隔。
注意:题目保证每个结点中存储的字母是不同的。
Output
如果两棵树是同构的,输出“Yes”,否则输出“No”。
Sample Input
8
A 1 2
B 3 4
C 5 -
D - -
E 6 -
G 7 -
F - -
H - -
8
G - 4
B 7 6
F - -
A 5 1
H - -
C 0 -
D - -
E 2 -
Sample Output
Yes
Hint
测试数据对应图1
示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define null -1 // 因为数组下标从0开始,小标为0存在节点,所以指成-1
struct tree
{
char data;
int l, r;
} t1[20], t2[20]; // 结构体数组
int tree_creat(struct tree t[], int n);
int cmp(int root1, int root2);
int main()
{
int n, root1, root2;
while(~scanf("%d", &n)) // 多组输入
{
root1 = tree_creat(t1, n);
scanf("%d", &n); // *********
root2 = tree_creat(t2, n);
if(cmp(root1, root2) == 1)
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
}
return 0;
}
int tree_creat(struct tree t[], int n)
{
int i, root = null;
char cl, cr;
if(n)
{
int check[20] = {0};
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
getchar(); // 用来抵消上次输入的回车
scanf("%c %c %c", &t[i].data, &cl, &cr);
if(cl != '-')
{
t[i].l = cl - '0';
check[t[i].l] = 1;
}
else
t[i].l = null;
if(cr != '-')
{
t[i].r = cr - '0';
check[t[i].r] = 1;
}
else
t[i].r = null;
}
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(check[i] == 0)
{
root = i; // 循环找到根节点
break;
}
}
}
return root;
};
int cmp(int root1, int root2)
{
if(root1 == null && root2 == null) // 两树都为空是同构的
return 1;
if((root1 == null && root2 != null) || (root1 != null && root2 == null)) //有一棵树空另一棵不空则不同构
return 0;
if(t1[root1].data != t2[root2].data) // 两树数据不同不同构
return 0;
if(t1[root1].l == null && t2[root2].l == null) // 如果左儿子都为空判断右儿子是否同构:主要看这三个方面(1)右儿子是否都为空(2)是否一个有右儿子一个没有(3)右儿子数据是否相同(递归调用)
return cmp(t1[root1].r, t2[root2].r);
if(t1[root1].l != null && t2[root2].l != null && t1[t1[root1].l].data == t2[t2[root2].l].data) // 如果两树左儿子都不为空并且数据也是一样的,对左儿子进行递归,同时判断右子树
return (cmp(t1[root1].l, t2[root2].l) && cmp(t1[root1].r, t2[root2].r));
else // 一个空一个不空或者都不空并且数据不同时
return (cmp(t1[root1].l, t2[root2].r) && cmp(t1[root1].r, t2[root2].l));
}