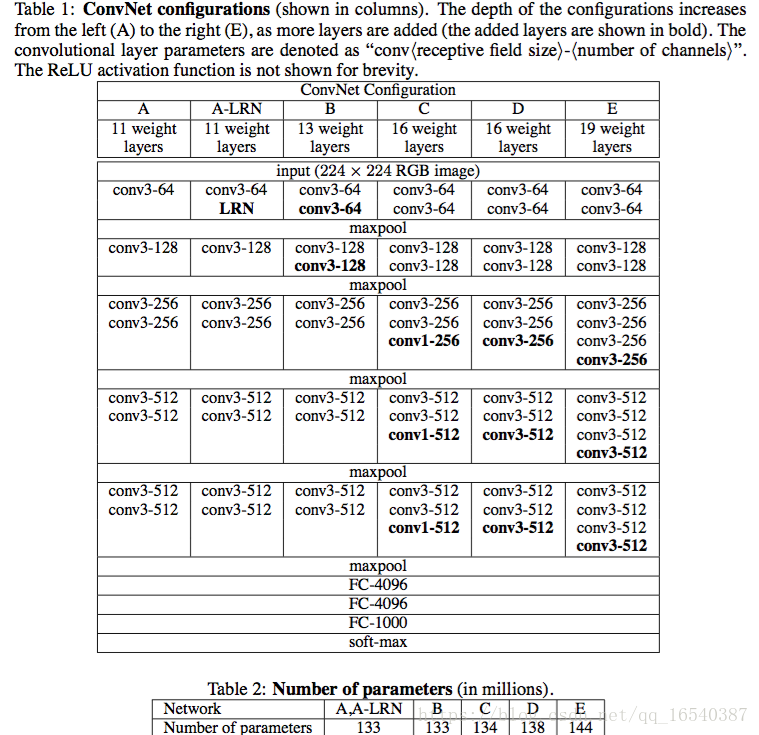
一 VGGNet网络结构及特点
1.网络结构
VGGNet拥有5段卷积层,每一段内有2-3个卷积层,每段尾都会连接一个最大池化层用来缩小图片尺寸。每一段卷积层内的卷积核数目都相同,越靠后卷积核和数目越多。64-128-256-12-512。
其中,两个连在一起的3*3的卷积核相当于一个5×5的像素产生关联,也可以说感受野大小为5×5,这样的设计使得参数数目变为一半,而且引入了更多的非线性(每个卷积层后就有一个relu激活函数),使得模型对特征学习能力更强。
2.multi-scale训练
- 把原始图片放缩到最小边S>224。S属于[256,512]。
- 再提取224×224的片段进行训练。
- 最后在不同尺寸的模型上求品均值。
3.实验小结
- LRN层作用不大。
- 越深的网络结果越好
- 卷积核越大,学习到的空间特征越多。
二 Tensorflow实现VGGNet网络
1导入库初始化函数
- input_op.get_shape()[-1].value获取通道数
from datetime import datetime
import math
import time
import tensorflow as tf
def conv_op(input_op, name, kh, kw, n_out, dh, dw, p):
n_in = input_op.get_shape()[-1].value
with tf.name_scope(name) as scope:
kernel = tf.get_variable(scope+"w",
shape=[kh, kw, n_in, n_out],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer_conv2d())
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input_op, kernel, (1, dh, dw, 1), padding='SAME')
bias_init_val = tf.constant(0.0, shape=[n_out], dtype=tf.float32)
biases = tf.Variable(bias_init_val, trainable=True, name='b')
z = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
activation = tf.nn.relu(z, name=scope)
p += [kernel, biases]
return activation
def fc_op(input_op, name, n_out, p):
n_in = input_op.get_shape()[-1].value
with tf.name_scope(name) as scope:
kernel = tf.get_variable(scope+"w",
shape=[n_in, n_out],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[n_out], dtype=tf.float32), name='b')
activation = tf.nn.relu_layer(input_op, kernel, biases, name=scope)
p += [kernel, biases]
return activation
def mpool_op(input_op, name, kh, kw, dh, dw):
return tf.nn.max_pool(input_op,
ksize=[1, kh, kw, 1],
strides=[1, dh, dw, 1],
padding='SAME',
name=name)2.网络结构
- reshape是卷积层和全连接层之间重构数据结构
def inference_op(input_op, keep_prob):
p = []
# assume input_op shape is 224x224x3
# block 1 -- outputs 112x112x64
conv1_1 = conv_op(input_op, name="conv1_1", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=64, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
conv1_2 = conv_op(conv1_1, name="conv1_2", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=64, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
pool1 = mpool_op(conv1_2, name="pool1", kh=2, kw=2, dw=2, dh=2)
# block 2 -- outputs 56x56x128
conv2_1 = conv_op(pool1, name="conv2_1", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=128, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
conv2_2 = conv_op(conv2_1, name="conv2_2", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=128, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
pool2 = mpool_op(conv2_2, name="pool2", kh=2, kw=2, dh=2, dw=2)
# # block 3 -- outputs 28x28x256
conv3_1 = conv_op(pool2, name="conv3_1", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=256, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
conv3_2 = conv_op(conv3_1, name="conv3_2", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=256, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
conv3_3 = conv_op(conv3_2, name="conv3_3", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=256, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
pool3 = mpool_op(conv3_3, name="pool3", kh=2, kw=2, dh=2, dw=2)
# block 4 -- outputs 14x14x512
conv4_1 = conv_op(pool3, name="conv4_1", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=512, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
conv4_2 = conv_op(conv4_1, name="conv4_2", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=512, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
conv4_3 = conv_op(conv4_2, name="conv4_3", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=512, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
pool4 = mpool_op(conv4_3, name="pool4", kh=2, kw=2, dh=2, dw=2)
# block 5 -- outputs 7x7x512
conv5_1 = conv_op(pool4, name="conv5_1", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=512, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
conv5_2 = conv_op(conv5_1, name="conv5_2", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=512, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
conv5_3 = conv_op(conv5_2, name="conv5_3", kh=3, kw=3, n_out=512, dh=1, dw=1, p=p)
pool5 = mpool_op(conv5_3, name="pool5", kh=2, kw=2, dw=2, dh=2)
# flatten
shp = pool5.get_shape()
flattened_shape = shp[1].value * shp[2].value * shp[3].value
resh1 = tf.reshape(pool5, [-1, flattened_shape], name="resh1")
# fully connected
fc6 = fc_op(resh1, name="fc6", n_out=4096, p=p)
fc6_drop = tf.nn.dropout(fc6, keep_prob, name="fc6_drop")
fc7 = fc_op(fc6_drop, name="fc7", n_out=4096, p=p)
fc7_drop = tf.nn.dropout(fc7, keep_prob, name="fc7_drop")
fc8 = fc_op(fc7_drop, name="fc8", n_out=1000, p=p)
softmax = tf.nn.softmax(fc8)
predictions = tf.argmax(softmax, 1)
return predictions, softmax, fc8, p3.网络测评
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, feed, info_string):
num_steps_burn_in = 10
total_duration = 0.0
total_duration_squared = 0.0
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target, feed_dict=feed)
duration = time.time() - start_time
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print ('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' %
(datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
mn = total_duration / num_batches
vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print ('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' %
(datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))4.主函数
def run_benchmark():
with tf.Graph().as_default():
image_size = 224
images = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size,
image_size,
image_size, 3],
dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1))
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
predictions, softmax, fc8, p = inference_op(images, keep_prob)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allocator_type = 'BFC'
sess = tf.Session(config=config)
sess.run(init)
time_tensorflow_run(sess, predictions, {keep_prob:1.0}, "Forward")
objective = tf.nn.l2_loss(fc8)
grad = tf.gradients(objective, p)
time_tensorflow_run(sess, grad, {keep_prob:0.5}, "Forward-backward")
batch_size=32
num_batches=100
run_benchmark()