| http://www.aboutyun.com/thread-19729-1-1.html
问题导读:
1、Spark Job Stage划分算法有哪些?
2、Task最佳计算位置算法如何理解?
3、Task任务本地算法运用场景有哪些?

一、Stage划分算法
由于Spark的算子构建一般都是链式的,这就涉及了要如何进行这些链式计算,Spark的策略是对这些算子,先划分Stage,然后在进行计算。
由于数据是分布式的存储在各个节点上的,所以为了减少网络传输的开销,就必须最大化的追求数据本地性,所谓的数据本地性是指,在计算时,数据本身已经在内存中或者利用已有缓存无需计算的方式获取数据。
1.Stage划分算法思想
(1)一个Job由多个Stage构成
一个Job可以有一个或者多个Stage,Stage划分的依据就是宽依赖,产生宽依赖的算子:reduceByKey、groupByKey等等
(2)根据依赖关系,从前往后依次执行多个Stage
SparkApplication 中可以因为不同的Action触发众多的Job,也就是说一个Application中可以有很多的Job,每个Job是有一个或者多个Stage构成,后面的Stage依赖前面的Stage,也就是说只有前面的Stage计算完后,后面的Stage才会运行。
(3)Stage的执行时Lazy级别的
所有的Stage会形成一个DAG(有向无环图),由于RDD的Lazy特性,导致Stage也是Lazy级别的,只有遇到了Action才会真正发生作业的执行,在Action之前,Spark框架只是将要进行的计算记录下来,并没有真的执行。
Action导致作业执行的代码如下:触发作业,发送消息。
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
/**
* Return an array that contains all of the elements in this RDD.
*/
def collect(): Array[T] = withScope {
val results = sc.runJob(this, (iter: Iterator[T]) => iter.toArray)
Array.concat(results: _*)
}
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
/**
* Run a job on all partitions in an RDD and return the results in an array.
*/
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag](rdd: RDD[T], func: Iterator[T] => U): Array[U] = {
runJob(rdd, func, 0 until rdd.partitions.length)
}
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 |
/**
* Run a job on a given set of partitions of an RDD, but take a function of type
* `Iterator[T] => U` instead of `(TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U`.
*/
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: Iterator[T] => U,
partitions: Seq[Int]): Array[U] = {
val cleanedFunc = clean(func)
runJob(rdd, (ctx: TaskContext, it: Iterator[T]) => cleanedFunc(it), partitions)
}
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 |
/**
* Run a function on a given set of partitions in an RDD and return the results as an array.
*/
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int]): Array[U] = {
val results = new Array[U](partitions.size)
runJob[T, U](rdd, func, partitions, (index, res) => results(index) = res)
results
}
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
/**
* Run a function on a given set of partitions in an RDD and pass the results to the given
* handler function. This is the main entry point for all actions in Spark.
*/
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit): Unit = {
if (stopped.get()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("SparkContext has been shutdown")
}
val callSite = getCallSite
val cleanedFunc = clean(func)
logInfo("Starting job: " + callSite.shortForm)
if (conf.getBoolean("spark.logLineage", false)) {
logInfo("RDD's recursive dependencies:\n" + rdd.toDebugString)
}
dagScheduler.runJob(rdd, cleanedFunc, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, localProperties.get)
progressBar.foreach(_.finishAll())
rdd.doCheckpoint()
}
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 |
def runJob[T, U](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit,
properties: Properties): Unit = {
val start = System.nanoTime
val waiter = submitJob(rdd, func, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, properties)
waiter.awaitResult() match {
case JobSucceeded =>
logInfo("Job %d finished: %s, took %f s".format
(waiter.jobId, callSite.shortForm, (System.nanoTime - start) / 1e9))
case JobFailed(exception: Exception) =>
logInfo("Job %d failed: %s, took %f s".format
(waiter.jobId, callSite.shortForm, (System.nanoTime - start) / 1e9))
// SPARK-8644: Include user stack trace in exceptions coming from DAGScheduler.
val callerStackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace.tail
exception.setStackTrace(exception.getStackTrace ++ callerStackTrace)
throw exception
}
}
def submitJob[T, U](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit,
properties: Properties): JobWaiter[U] = {
// Check to make sure we are not launching a task on a partition that does not exist.
val maxPartitions = rdd.partitions.length
partitions.find(p => p >= maxPartitions || p < 0).foreach { p =>
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Attempting to access a non-existent partition: " + p + ". " +
"Total number of partitions: " + maxPartitions)
}
val jobId = nextJobId.getAndIncrement()
if (partitions.size == 0) {
// Return immediately if the job is running 0 tasks
return new JobWaiter[U](this, jobId, 0, resultHandler)
}
assert(partitions.size > 0)
val func2 = func.asInstanceOf[(TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _]
val waiter = new JobWaiter(this, jobId, partitions.size, resultHandler)
eventProcessLoop.post(JobSubmitted(
jobId, rdd, func2, partitions.toArray, callSite, waiter,
SerializationUtils.clone(properties)))
waiter
}
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 |
/** A result-yielding job was submitted on a target RDD */
private[scheduler] case class JobSubmitted(//这里面封装了哪些Partition要进行计算,
//joblistener作业监听等等
jobId: Int,
finalRDD: RDD[_],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,
partitions: Array[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
listener: JobListener,
properties: Properties = null)
extends DAGSchedulerEvent
|
& 例如 collect 会导致SparkContext中的runJob方法的执行,最终会导致DAGScheduler中的submit的执行。这其中最为核心的是通过发送一个名为JobSubmit的case class对象给eventProcessLoop。
这里的eventProcessLoop是DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop的具体实例,DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop是EventLoop的子类,具体实现了EventLoop的doOnReceive;而DAGScheduler是EventLoop的子类,EventLoop内部有一个线程EventThread,EventThread的run方法会不断循环消息队列,不断从eventQueue(LinkedBlockingDeque[E]())中获取消息,然后调用DAGScheduler的doOnReceiver方法,同时传入DAGSchedulerEvent类型的event来处理通过post方法传过来的消息。 [AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 1 |
private[scheduler] val eventProcessLoop = new DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop(this)
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 1 |
private[scheduler] class DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop(dagScheduler: DAGScheduler)<pre name="code" class="plain"> extends EventLoop[DAGSchedulerEvent]("dag-scheduler-event-loop") with Logging
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
private[spark] abstract class EventLoop[E](name: String) extends Logging {
/**
* Put the event into the event queue. The event thread will process it later.
*/
def post(event: E): Unit = {
eventQueue.put(event)
}
def start(): Unit = { //启动一个
if (stopped.get) {
throw new IllegalStateException(name + " has already been stopped")
}
// Call onStart before starting the event thread to make sure it happens before onReceive
onStart()
eventThread.start()
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 |
private val eventThread = new Thread(name) {
setDaemon(true)
override def run(): Unit = {
try {
while (!stopped.get) {
val event = eventQueue.take()//取出放入的消息
try {
onReceive(event)
}
protected def onReceive(event: E): Unit//抽象方法调用子类的实现。
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
/** DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop
* The main event loop of the DAG scheduler.
*/
override def onReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = {
val timerContext = timer.time()
try {
doOnReceive(event)//4
} finally {
timerContext.stop()
}
}
[plain] view plain copy
print?
//4处被调用
private def doOnReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = event match {//处理消息
case JobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties) =>
dagScheduler.handleJobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties)
|
消息的接收和处理:
(1)DAGScheduler启动一个线程EventLoop(消息循环器),不断地从消息队列中取消息。消息是通过EventLoop的put方法放入消息队列,当EventLoop拿到消息后会回调DAGScheduler的OnReceive,进而调用doOnReceive方法进行处理。
& 为什么要开辟线程来执行消息的读、取?这样可以提交更多的Job,异步处理多Job,处理的业务逻辑一致(调用自己方法也是发送消息),解耦合,扩展性好。
(2)在doOnReceive中通过模式匹配的方式把JobSubmitted封装的内容路由到handleJobSubmitted。
(3)在handleJobSubmitted中首先创建finalStage。 [AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
private[scheduler] def handleJobSubmitted(jobId: Int,
finalRDD: RDD[_],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,
partitions: Array[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
listener: JobListener,
properties: Properties) {
var finalStage: ResultStage = null
try {
// New stage creation may throw an exception if, for example, jobs are run on a
// HadoopRDD whose underlying HDFS files have been deleted.
finalStage = newResultStage(finalRDD, func, partitions, jobId, callSite) //5
} catch {
…
}
jobIdToActiveJob(jobId) = job
activeJobs += job
finalStage.setActiveJob(job)
val stageIds = jobIdToStageIds(jobId).toArray
val stageInfos = stageIds.flatMap(id => stageIdToStage.get(id).map(_.latestInfo))
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerJobStart(job.jobId, jobSubmissionTime, stageInfos, properties))
submitStage(finalStage)
submitWaitingStages()
}
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
/**
* Create a ResultStage associated with the provided jobId. 5处被调用
*/
private def newResultStage(
rdd: RDD[_],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,
partitions: Array[Int],
jobId: Int,
callSite: CallSite): ResultStage = {
//下面这个函数会生成我们的DAG,需重点关注
val (parentStages: List[Stage], id: Int) = getParentStagesAndId(rdd, jobId)
val stage = new ResultStage(id, rdd, func, partitions, parentStages, jobId, callSite)
stageIdToStage(id) = stage //将Stage的id放入stageIdToStage结构中。
updateJobIdStageIdMaps(jobId, stage) //更新JobIdStageIdMaps
stage
}
|
(4)通过递归的方式创建DAG。 [AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 |
/**
* Helper function to eliminate some code re-use when creating new stages.
*/
private def getParentStagesAndId(rdd: RDD[_], firstJobId: Int): (List[Stage], Int) = {
//计算父Stage
val parentStages = getParentStages(rdd, firstJobId)
//计算开始计算的id
val id = nextStageId.getAndIncrement()
(parentStages, id)
}
|
下面,我们将看到本节课最重要的一个函数。 [AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
/**
* Get or create the list of parent stages for a given RDD. The new Stages will be created with
* the provided firstJobId.
*/
private def getParentStages(rdd: RDD[_], firstJobId: Int): List[Stage] = {
//记录父Stage
val parents = new HashSet[Stage]
//记录已被访问的RDD
val visited = new HashSet[RDD[_]]
// We are manually maintaining a stack here to prevent StackOverflowError
// caused by recursively visiting
//存储需要被处理的RDD,Stack中的的RRD都需要被处理
val waitingForVisit = new Stack[RDD[_]]
//采用广度优先遍历rrd生成的依赖树
def visit(r: RDD[_]) {
if (!visited(r)) {
visited += r
// Kind of ugly: need to register RDDs with the cache here since
// we can't do it in its constructor because # of partitions is unknown
//这里只是缓存RDD的信息,并未真正计算,因为此时我们并没有partition的信息。
//遍历RDD的所有父RDD
for (dep <- r.dependencies) {
dep match {
//如果是宽依赖,则创建新的Stage
case shufDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _] =>
//这里是真正创建Stage的步骤
parents += getShuffleMapStage(shufDep, firstJobId) //6
case _ =>
//如果是窄依赖,则将其父RDD加入待访问遍历集合。即即将该RDD加入原来的Stage
waitingForVisit.push(dep.rdd)
}
}
}
}
//以resultRDD作为第一个需要处理的RDD,然后从该rdd开始,顺序处理其parent rdd
waitingForVisit.push(rdd)
//直到所有的等待访问的RDD全访问完,也就是所有RDD都有自己所属的Stage时,退出循环。
while (waitingForVisit.nonEmpty) {
//否则按照后入先出的顺序访问waitingForVisit的RDD。每次visit如果遇到了
//ShuffleDependency,那么会形成一个Stage,否则这些RDD属于同一个Stage
visit(waitingForVisit.pop())
}
parents.toList
}
|
可以看出,我们将Result RDD和firstJobId(由于有些Job在执行中会触发其他Job)作为出入参数,调用getParentStages方法,来创建我们Job的DAG。从源码上来看,是将我们前面的第二十三讲的思想,具体实现为代码。
这里,我们来看看宽依赖划分Stage的过程。 [AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
/**
* Get or create a shuffle map stage for the given shuffle dependency's map side.
*/
//6处被调用
private def getShuffleMapStage(
shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _],
firstJobId: Int): ShuffleMapStage = {
//根据shuffleId查找Stage是否存在
shuffleToMapStage.get(shuffleDep.shuffleId) match {
//如果这个Shuffle Stage已存在,则返回该Stage
case Some(stage) => stage
//如果不存在
case None =>
// We are going to register ancestor shuffle dependencies
//注册以前的shuffle dependency,并将shuffle dependency转换为新的Stage或已存在
//的Stage
getAncestorShuffleDependencies(shuffleDep.rdd).foreach { dep => //7
shuffleToMapStage(dep.shuffleId) = newOrUsedShuffleStage(dep, firstJobId) //8
}
// Then register current shuffleDep
//注册当前的shuffle dependency
val stage = newOrUsedShuffleStage(shuffleDep, firstJobId) //8
shuffleToMapStage(shuffleDep.shuffleId) = stage
stage
}
}
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
//寻找DAG中当前shuffle dependency的rdd树中以前的shuffle dependency 7处被调用
private def getAncestorShuffleDependencies(rdd: RDD[_]): Stack[ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]] = {
//存储前面的shuffle dependency
val parents = new Stack[ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]]
val visited = new HashSet[RDD[_]]
// We are manually maintaining a stack here to prevent StackOverflowError
// caused by recursively visiting
val waitingForVisit = new Stack[RDD[_]]
def visit(r: RDD[_]) {
if (!visited(r)) {
visited += r
for (dep <- r.dependencies) {
dep match {
case shufDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _] =>
if (!shuffleToMapStage.contains(shufDep.shuffleId)) {
parents.push(shufDep)
}
case _ =>
}
waitingForVisit.push(dep.rdd)
}
}
}
waitingForVisit.push(rdd)
while (waitingForVisit.nonEmpty) {
visit(waitingForVisit.pop())
}
parents
}
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 1 |
<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">//8处被调用</span>
|
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
private def newOrUsedShuffleStage(
shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _],
firstJobId: Int): ShuffleMapStage = {
//由shuffleDependency找到父rdd
val rdd = shuffleDep.rdd
//计算父rdd的分片数量
val numTasks = rdd.partitions.length
//创建新的shuffleMapStage。
val stage = newShuffleMapStage(rdd, numTasks, shuffleDep, firstJobId, rdd.creationSite) //9
if (mapOutputTracker.containsShuffle(shuffleDep.shuffleId)) {
//Stage已经被计算过,从mapOutputTracer中获取计算结果
val serLocs = mapOutputTracker.getSerializedMapOutputStatuses(shuffleDep.shuffleId)
val locs = MapOutputTracker.deserializeMapStatuses(serLocs)
(0 until locs.length).foreach { i =>
// locs(i)等于空表示
if (locs(i) ne null) {
//记录Stage的output的元数据信息
stage.addOutputLoc(i, locs(i))
}
}
} else {
// 由于具体的partition我们并不知道,所以我们只能在内存中记录rdd以及映射output
//Tracker
logInfo("Registering RDD " + rdd.id + " (" + rdd.getCreationSite + ")")
mapOutputTracker.registerShuffle(shuffleDep.shuffleId, rdd.partitions.length)
}
stage
}
|
& 这里需要说明,ShuffleMapTask的计算结果都会传给Driver端的mapOutputTracker,其他的Task可以通过查询它来获得这些结果。mapOutputTracker.registerShuffle(…)实现了存储这些元数据信息的占位,而ShuffleMapTask的结果通过registerMapOutputs来保存计算结果。这个结果是数据所在位置、大小等元数据信息,这样下一个Stage的Task就可以通过这些元数据信息获取需要处理的数据了。 [AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
private def newShuffleMapStage(
rdd: RDD[_],
numTasks: Int,
shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _],
firstJobId: Int,
callSite: CallSite): ShuffleMapStage = {
//递归调用getParentStagesAndId获得前面Stage的列表
val (parentStages: List[Stage], id: Int) = getParentStagesAndId(rdd, firstJobId)
val stage: ShuffleMapStage = new ShuffleMapStage(id, rdd, numTasks, parentStages,
firstJobId, callSite, shuffleDep)
stageIdToStage(id) = stage
updateJobIdStageIdMaps(firstJobId, stage)
stage
}
|
具体流程图如下:
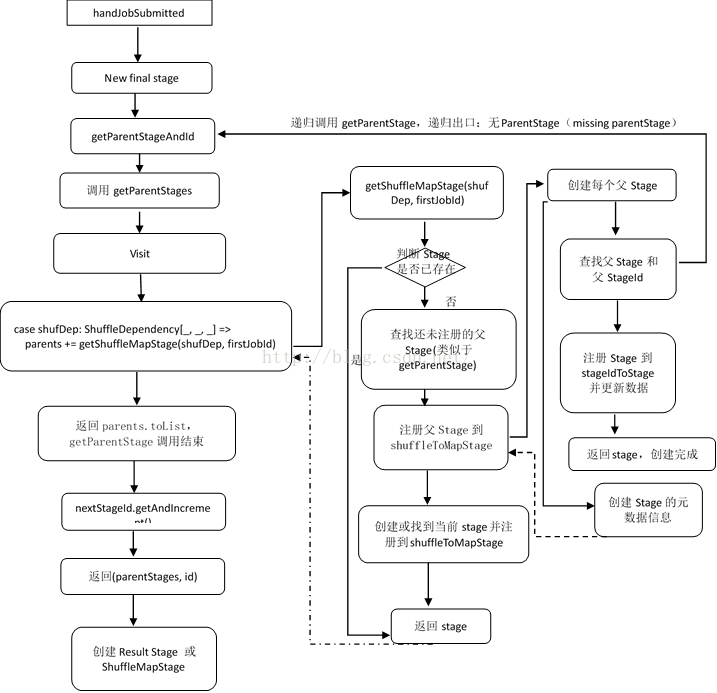
由于创建DAG的过程是递归进行的,所以在创建后一个Stage时,必然保证其直接父Stage已经创建(未创建,便会递归调用getParentStage来创建父Stage),知道递归的最底层,也就是遇到了DAG中的最左边的RDD,此时会为这个时候的ShuffleDependency创建Stage0,并跳出底层递归,然后逐层创建stage,并返回给上一层,知道最后来到顶层也就是Result Stage,创建Result Stage,完成DAG的创建。
& 注意:1.在每层递归中getParentStage只是查找当前Stage的直接父Stage(Stages)。
2.由于是递归调用,而Stage的id是在递归调用结束前利用nextStageId.getAndIncreme来设置的所以,父Stage的id小于子Stage的id。
二、Task任务本地性算法
1.Task任务本算法运用场景
在上一节,我们介绍了Job Stage划分算法,并最终得到了DAG图中的Result Stage(final Stage)。接下来我们通过查看Task任务本地性(为了保证Data Locality)的运用场景----Task的运行调度处理,来引入Task任务本地性算法。
在得到逻辑上Result Stage,Spark为了进行计算就必须先报任务以一定的集群可识别形式提交给集群进行计算。Spark的任务提交过程如下:
(1)生成ActiveJob,为提交finalStage做准备。 [AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
private[scheduler] def handleJobSubmitted(jobId: Int,
finalRDD: RDD[_],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,
partitions: Array[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
listener: JobListener,
properties: Properties) {
……//省略部分代码
val job = new ActiveJob(jobId, finalStage, callSite, listener, properties)
//清空内存中上一个Job留下的Tracker信息
clearCacheLocs()
logInfo("Got job %s (%s) with %d output partitions".format(
job.jobId, callSite.shortForm, partitions.length))
logInfo("Final stage: " + finalStage + " (" + finalStage.name + ")")
logInfo("Parents of final stage: " + finalStage.parents)
logInfo("Missing parents: " + getMissingParentStages(finalStage))
val jobSubmissionTime = clock.getTimeMillis()
//将Job加入到jobIdToActiveJob和等待执行集合
jobIdToActiveJob(jobId) = job
activeJobs += job
finalStage.setActiveJob(job)
val stageIds = jobIdToStageIds(jobId).toArray
val stageInfos = stageIds.flatMap(id => stageIdToStage.get(id).map(_.latestInfo))
//将要运行的Job加入监控中,然后提交finalStage
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerJobStart(job.jobId, jobSubmissionTime, stageInfos, properties))
submitStage(finalStage) //9
//等待finalStage执行结果。
submitWaitingStages()
}
|
(2)提交finalStage [AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
/**提交Stage,如果有未提交的ParentStage,则会递归提交这些ParentStage,只有所有ParentStage都计算完了,才能提交当前Stage */
//9处被调用
private def submitStage(stage: Stage) {
val jobId = activeJobForStage(stage)
//查找定义的JobId,未找到则会报错
if (jobId.isDefined) {
logDebug("submitStage(" + stage + ")")
//如果当前Stage不再等待parent Stage的返回,也不是正在运行的Stage,并且也没有提
//示提交失败,那么我们就尝试提交Stage
if (!waitingStages(stage) && !runningStages(stage) && !failedStages(stage)) {
//验证当前Stage是否有父Stage还未进行提交或计算
val missing = getMissingParentStages(stage).sortBy(_.id)
logDebug("missing: " + missing)
if (missing.isEmpty) {
//如果父Stage都计算了。
logInfo("Submitting " + stage + " (" + stage.rdd + "), which has no missing parents")
//则提交Stage所包含的Task进行计算
submitMissingTasks(stage, jobId.get) //10
} else {
//否则还有父Stage没进行计算,就递归提交这些父Stage
for (parent <- missing) {
submitStage(parent)
}
waitingStages += stage
}
}
} else {//无效作业,停止它。
abortStage(stage, "No active job for stage " + stage.id, None)
}
}
|
(3)提交MissingTask [AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 |
//10处被调用
private def submitMissingTasks(stage: Stage, jobId: Int) {
logDebug("submitMissingTasks(" + stage + ")")
// Get our pending tasks and remember them in our pendingTasks entry
stage.pendingPartitions.clear()
//找到需要计算的Partition id
val partitionsToCompute: Seq[Int] = stage.findMissingPartitions()
//修正内部累加器
if (stage.internalAccumulators.isEmpty || stage.numPartitions == partitionsToCompute.size) {
stage.resetInternalAccumulators()
}
//添加Stage环境
val properties = jobIdToActiveJob(jobId).properties
//将当前Stage加入运行Stage队列
runningStages += stage
//省略部分代码
//获得Task的本地性
val taskIdToLocations: Map[Int, Seq[TaskLocation]] = try {
stage match {
case s: ShuffleMapStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id => (id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, id))}.toMap
case s: ResultStage =>
val job = s.activeJob.get
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p = s.partitions(id)
(id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, p))
}.toMap
}
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
stage.makeNewStageAttempt(partitionsToCompute.size)
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stage.latestInfo, properties))
abortStage(stage, s"Task creation failed: $e\n${e.getStackTraceString}", Some(e))
runningStages -= stage
return
}
stage.makeNewStageAttempt(partitionsToCompute.size, taskIdToLocations.values.toSeq)
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stage.latestInfo, properties))
//省略序列化处理部分的代码
//根据不同的Stage类型创建不同的tasks队列
val tasks: Seq[Task[_]] = try {
stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
//为每一个Partition创建ShuffleMapTask
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)
val part = stage.rdd.partitions(id)
new ShuffleMapTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptId,
taskBinary, part, locs, stage.internalAccumulators)
}
case stage: ResultStage =>
val job = stage.activeJob.get
//为每个Partition创建ResultTask
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p: Int = stage.partitions(id)
val part = stage.rdd.partitions(p)
val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)
new ResultTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptId,
taskBinary, part, locs, id, stage.internalAccumulators)
}
}
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
abortStage(stage, s"Task creation failed: $e\n${e.getStackTraceString}", Some(e))
runningStages -= stage
return
}
//如果还有task没完成,则提交tasks去执行
if (tasks.size > 0) {
logInfo("Submitting " + tasks.size + " missing tasks from " + stage + " (" + stage.rdd + ")")
stage.pendingPartitions ++= tasks.map(_.partitionId)
logDebug("New pending partitions: " + stage.pendingPartitions)
//将Tasks封装到TaskSet中,并将TaskSet提交给TaskScheduler。
taskScheduler.submitTasks(new TaskSet(
tasks.toArray, stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptId, jobId, properties))
stage.latestInfo.submissionTime = Some(clock.getTimeMillis())
} else {
// 如果Tasks执行完了,表示该Stage执行完成
markStageAsFinished(stage, None)
val debugString = stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
s"Stage ${stage} is actually done; " +
s"(available: ${stage.isAvailable}," +
s"available outputs: ${stage.numAvailableOutputs}," +
s"partitions: ${stage.numPartitions})"
case stage : ResultStage =>
s"Stage ${stage} is actually done; (partitions: ${stage.numPartitions})"
}
logDebug(debugString)
}
}
|
从源码中,我们可以发现,我们的missingTask会最先会再到需要计算的分片,然后对Stage的运行环境进行设定,然后取得Task计算的本地性级别,最后会根据这些信息建立Tasks来处理每个分片,在提交给底层TaskScheduler之前,Spark还会将Tasks封装成TaskSet。最后提交TaskSet给TaskScheduler,等待TaskScheduler最终向集群提交这些Task,并且DAGScheduler会监听这些Task的状态。
2.数据本地性
(1)这里我们来着重讲解获取数据本地性部分的代码:
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
val taskIdToLocations: Map[Int, Seq[TaskLocation]] = try {
stage match {
case s: ShuffleMapStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id => (id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, id))}.toMap //11
case s: ResultStage =>
val job = s.activeJob.get
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p = s.partitions(id)
(id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, p))
}.toMap
}
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
stage.makeNewStageAttempt(partitionsToCompute.size)
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stage.latestInfo, properties))
abortStage(stage, s"Task creation failed: $e\n${e.getStackTraceString}", Some(e))
runningStages -= stage
return
}
|
这里会将要计算的分片(Partition)转换为(id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, id)) 类型的truple,进而由truple转换未一个Map映射,在Task构造时需要一个locs参数,便可以利用这个映射由id得到相应Partition的本地性级别。
(2)在每个分片(Partition)内部则是通过getPreferredLocs方法得到的 [AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码 ?
| 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
//11处被调用
private[spark] def getPreferredLocs(rdd: RDD[_], partition: Int): Seq[TaskLocation] = {
getPreferredLocsInternal(rdd, partition, new HashSet)
}
private def getPreferredLocsInternal(
rdd: RDD[_],
partition: Int,
visited: HashSet[(RDD[_], Int)]): Seq[TaskLocation] = {
// 如果已访问过RDD,即以获得RDD的TaskLocation则不需再次获得
if (!visited.add((rdd, partition))) {
// Nil has already been returned for previously visited partitions.
return Nil
}
// 如果RDD缓存在内存中,我们访问RDD实例化时的信息便可知道RDD在那个节点上
val cached = getCacheLocs(rdd)(partition)
if (cached.nonEmpty) {
return cached
}
// 利用RDD在创建时重写的preferredLocations获得数据Location,从而确定Task的本地性
val rddPrefs = rdd.preferredLocations(rdd.partitions(partition)).toList
if (rddPrefs.nonEmpty) {
return rddPrefs.map(TaskLocation(_))
}
// 如果RDD是窄依赖,则递归查找窄依赖链条上的第一个RDD的第一个Partition的
//数据Location作为locs
rdd.dependencies.foreach {
case n: NarrowDependency[_] =>
for (inPart <- n.getParents(partition)) {
val locs = getPreferredLocsInternal(n.rdd, inPart, visited)
if (locs != Nil) {
return locs
}
}
case _ =>
}
Nil
}
|
在具体算法实现的时候,首先查询DAGScheduler的内存数据结构中是否存在当前partition的数据本地性信息,若有的话就直接放回该信息;若没有首先会调用rdd.getPreferredLocations来得到数据的本地性。
& 例如想让Spark运行在HBase上或者是一种现在Spark还没有直接支持的数据库上,此时开发者需要自定义RDD,为了保证Task计算的数据本地性,最为关键的方式就是必须实现RDD的getPreferredLocations方法,来支持各种来源的数据。
(3)DAGScheduler计算数据本地性时,巧妙的借助了RDD自身的getPreferredLocations中的数据,最大化的优化效率,因为getPreferredLocations中表明了每个Partition的数据本地性。虽然当然Partition可能被persist或checkpoint,但是persist或checkpoint默认情况下肯定和getPreferredLocations中的partition的数据本地性是一致的。所以,这中算法就极大的简化了Task数据本地性算法的实现,并且优化了效率 |

