Blast算法初探Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
Sequence Databst Search
BLAST是一种启发式的算法, 也就是说,它并不确保能找到最优解,但尽力在更短时间内找到足够好的解
全局比对:dp
F ( 0 , 0 ) = 0 F ( i , j ) = max { F ( i − 1 , j − 1 ) + s ( x i , y j ) F ( i − 1 , j ) + d F ( i , j − 1 ) + d G l o b a l A l i g n m e n t \begin{array}{l} F(0,0)=0 \\ F(i, j)=\max \left\{\begin{array}{l} F(i-1, j-1)+s\left(x_{i}, y_{j}\right) \\ F(i-1, j)+d \\ F(i, j-1)+d \end{array}\right. \end{array} Global Alignment F(0,0)=0F(i,j)=max⎩⎨⎧F(i−1,j−1)+s(xi,yj)F(i−1,j)+dF(i,j−1)+dGlobalAlignment
为什么提出局部比对:
- 功能相关的pr在整体序列上相差甚远,但是有相同的功能域,序列片段能发挥独立生物学功能,全局比不出来
- 内含子
局部比对blast:减少dp矩阵,计算最优比对路径,找局部最优,限制了最低的分数,计算局部的相似性
F ( 0 , 0 ) = 0 F ( i , j ) = max { F ( i − 1 , j − 1 ) + s ( x i , y j ) F ( i − 1 , j ) + d F ( i , j − 1 ) + d 0 L o c a l A l i g n m e n t \begin{array}{l} F(0,0)=0 \\ F(i, j)=\max \left\{\begin{array}{l} F(i-1, j-1)+s\left(x_{i}, y_{j}\right) \\ F(i-1, j)+d \\ F(i, j-1)+d \\ 0 \end{array}\right. \end{array} LocalAlignment F(0,0)=0F(i,j)=max⎩⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎧F(i−1,j−1)+s(xi,yj)F(i−1,j)+dF(i,j−1)+d0LocalAlignment

Traceback: Decode the Local Alignment.
Trace back begins at the highest score in the matrix and continues until you reach 0.
可能会存在多条局部匹配结果。
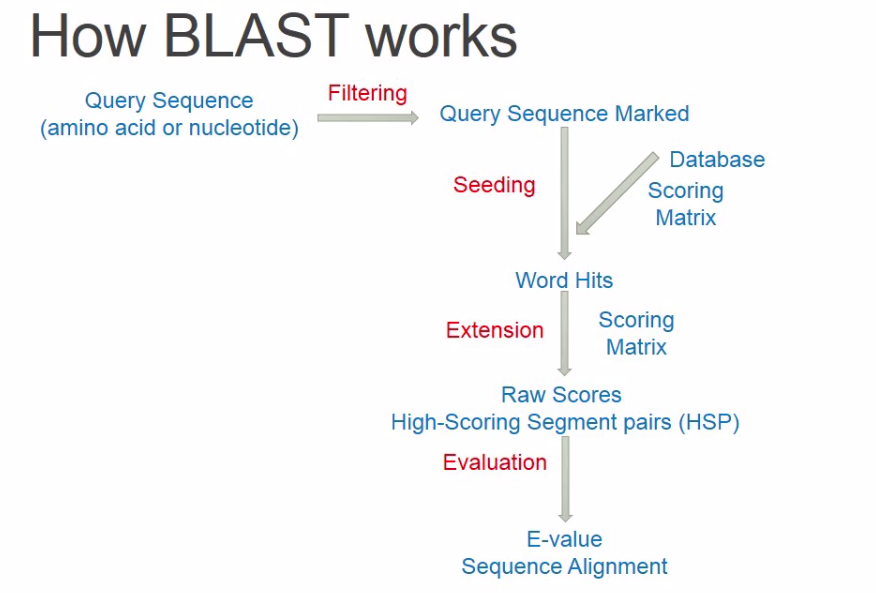
Blast Ideas:Seeding and extending
-
Find matches(seed)between the query and subject.
(先找到种子)
-
Extend seed into High Scoring Segment Pairs (HSPs)-Run Smith-Waterman algorithm on the specified region only.
(以种子为基础向两端延展并构建比对)
-
Assess the reliability of the alignment.
(计算统计显著性)

Seeding
For a given word length w (usually 3 for proteins and 11 fornucleotides), slicing the query sequence into multiple continuous “seed words”
给定长度w

Speedup: Index database
The database was pre-indexed to quickly locate all positions in the database for a given seed.(近似常数时间/线性)
将seed与预先索引好的序列进行比对

Diagonal and Two-hits
最优比对路径绝应当平行于主对角线(分数最大),可以去掉零散的hits,连续>2的保留,减少搜索空间

对hit cluser为基础向左右方向延申和扩展,直到总分的下降超过x就停止。
扩展区域可以用右下角的算法。

Speedup: mask low-complexity
Low complexity
sequences yield false positives.
- CACACACACACACACA,K=0.36
- KLKLKLKLKLKL
屏蔽重复性的低复杂度区域,以免产生太多假阳性hit

事先定不出来,用的时候找哪个可能不适合
neighbourhood words
To improve sensitivity, in addition to the seedword itself, the BLAST also use these highly similar"neighbourhood words" (based on thesubstitution matrix) for seeding.
具体来说,对seed word所有可能变形根据替代矩阵来计算分数。
- DKT seed
- DRT=6+2+5=13等等,当前版本分数>=11才考虑进来(降低假阳性)
评估统计显著性Quality Assessment
Given the large data volume, it’s critical to provide some measures for assessing the statistical significance of a given hit.
得到最终的比对之后评估QA
确保比对不是由随机因素引起的(数据库够大的时候随机产生的序列也能匹配到结果)
E-Value: How a match is likely to arise by chance
The expected number of alignments with a given score that would be expected to occur at random in the database that has been searched
随机情况下,获得比当前比对分数相等或更高分数的比对条数。
- e.g. if E=10, 10 matches with scores this high are expected to be found by chance
E = k m n e − λ S E=k m n e^{-\lambda S} E=kmne−λS
- Expectation>1
- m是query sequence length
- n是database size
- s是分数
- k和λ是和打分矩阵相关的,相当于normalization factor。
n数据库越大,随机匹配可能性越大;e值也和m(查询序列长度)成正比,因为blast是局部比对不需要全长匹配;e和s负相关,也就是说分数越高,随机碰上的概率越小;k和λ平衡不同打分矩阵和搜索空间对结果影响。
E期望和p进行转换

为了方便解释,我们可以进一步的把p值和E值进行相互转换, 从图上可以看出,在小于0.1时, E值和p值,也就是概率值,几乎相等。 特别的,当p取0.05时,对应的E-value为0.0513, 因此也常有人将0.05作为E-value的cut-off。
与Needleman-Wunsch、Smith-Waterman等基于动态规划的算法不同, BLAST是一种启发式的算法, 也就是说,它并不确保能找到最优解,但尽力在更短时间内找到足够好的解。 具体来说,BLAST通过应用Seeding-and-extending策略,只在有限区域应用动态规划算法, 从而有效地降低了计算量、提高了计算速度。 然而,速度的提高是以灵敏度的下降为代价的, 这也是一系列启发式算法所共有的trade-off。
参考:北大生物信息学