前言
粒子特效是一种视觉效果,可以模拟出许多粒子在空间中的运动和变化,形成各种美丽的图案和动态效果。常见的粒子特效包括烟雾、火焰、水流、星空、气泡等,可以在电影、电视、游戏等领域中得到广泛应用。实现粒子特效,需要使用计算机图形学技术,如粒子系统、计算流体力学等。
一、粒子特效案例
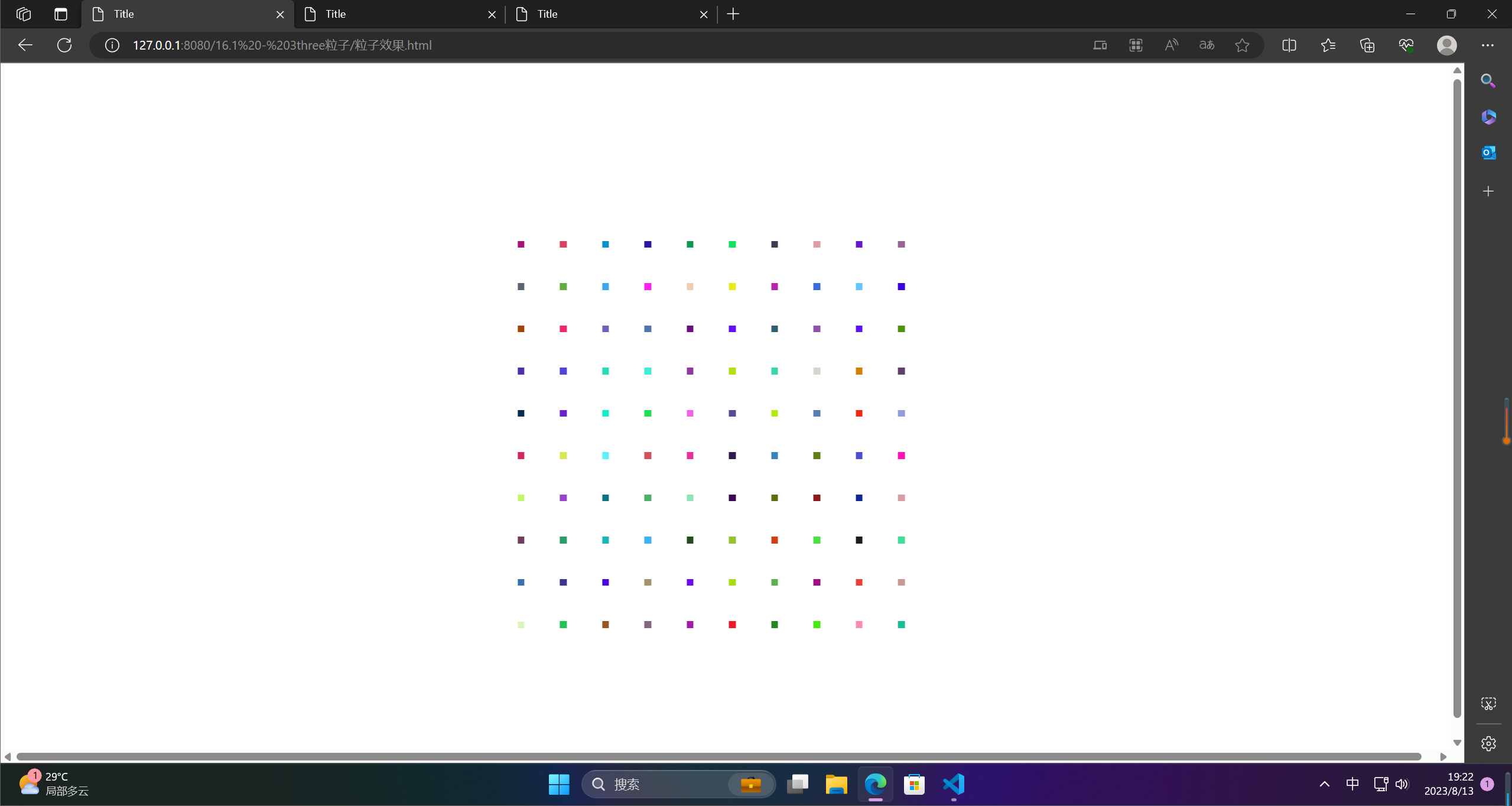
1.粒子平面
粒子平面是指在计算机图形学中,用于呈现粒子特效的平面。粒子特效是通过模拟大量的粒子运动和变化来实现的,而为了在视觉上呈现这些粒子,需要将它们以一定的规律排列在一个平面上,使得观众可以看到这些粒子的动态变化。因此,粒子平面常常被用作粒子特效的载体,通过对平面上的粒子进行位置、速度、颜色等的计算和控制,来实现各种不同的粒子效果。在实际应用中,粒子平面可以应用于游戏场景、电影特效、虚拟现实等领域中,为用户带来更加生动的视觉体验。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
<script src="../lib/three/three.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
<script>
const clock = new THREE.Clock()
// 创建一个场景
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
// 创建一个相机 视点
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 1, 1000);
// 设置相机的位置
camera.position.set(0,0,200);
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(0,0,0));
// 创建一个渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
// 设置渲染器尺寸
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
renderer.setClearColor(0xffffff);
// 添加灯光
const spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0xffffff);
spotLight.position.set(2000,8000,4000);
scene.add(spotLight);
createSystemSprite();
// 创建一个基础的粒子
function createNormalSprite() {
for (let i = -5; i < 5; i++) {
for (let j = -5; j < 5; j++) {
const material = new THREE.SpriteMaterial({
color: Math.random() * 0xffffff
})
const sprite = new THREE.Sprite(material);
sprite.position.set(i * 10, j * 10, 0);
sprite.scale.set(2,2,2);
scene.add(sprite);
}
}
}
// 粒子系统来创建粒子
function createSystemSprite() {
const geometry = new THREE.Geometry();
const material = new THREE.PointCloudMaterial({
size: 4,
vertexColors: true,
})
for (let i = -5; i < 5; i++) {
for (let j = -5; j < 5; j++) {
geometry.vertices.push(new THREE.Vector3(i * 10, j * 10, 0))
geometry.colors.push(new THREE.Color(Math.random() * 0xffffff))
}
}
scene.add(new THREE.PointCloud(geometry, material))
}
const animation = () => {
// 渲染
renderer.render(scene, camera);
requestAnimationFrame(animation);
}
animation()
</script>
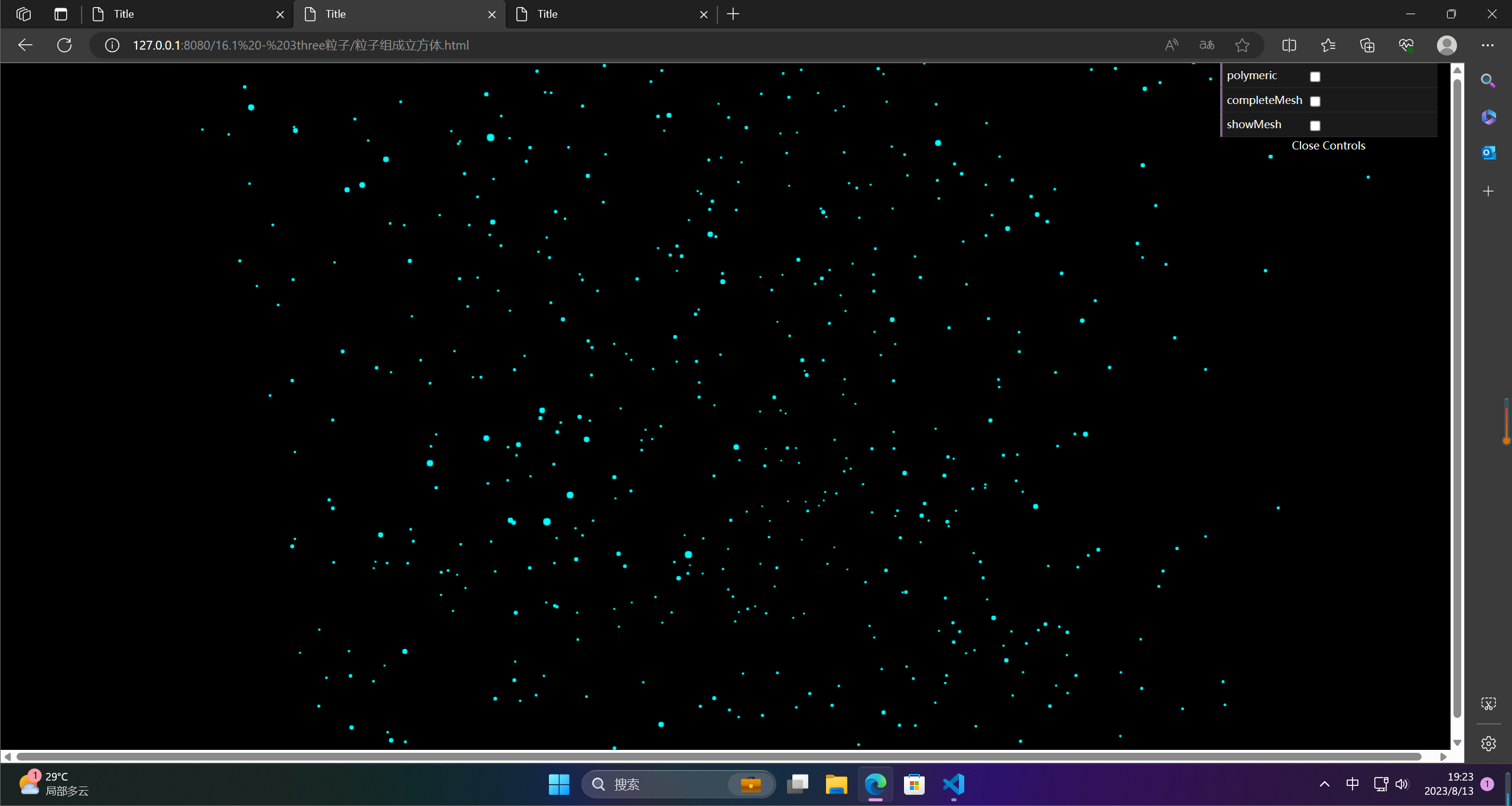
2.粒子立方体
粒子立方体是一个三维的立方体网格,每个网格中包含一个粒子。粒子立方体广泛应用于流体动力学和材料科学等领域,用于模拟流体的运动和材料的行为。 在流体动力学中,粒子立方体被用来模拟流体的粒子。 这些粒子可以在立方体内相互作用,从而模拟流体的动态行为。 在材料科学中,粒子立方体可用于模拟材料的行为,如塑性变形,断裂等。 它也可以用于模拟材料的力学特性,如弹性模量和泊松比等。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
<script src="../lib/three/three.js"></script>
<script src="../lib/three/tween.min.js"></script>
<script src="../lib/three/dat.gui.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
<script>
const clock = new THREE.Clock()
// 创建一个场景
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
// 创建一个相机 视点
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 1, 1000);
// 设置相机的位置
camera.position.set(0,30,100);
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(0,0,0));
// 创建一个渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
// 设置渲染器尺寸
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// 添加灯光
const spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0xffffff);
spotLight.position.set(2000,8000,4000);
scene.add(spotLight);
// 创建一个立方体
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10);
function getSprite() {
const canvas = document.createElement('canvas')
const size = 8
canvas.width = size * 2;
canvas.height = size * 2;
const c = canvas.getContext('2d')
const gradient = c.createRadialGradient(size, size, 0, size, size, size);
gradient.addColorStop(0.1, 'rgba(0,255,255,1)')
c.fillStyle = gradient;
c.arc(size, size, size / 2, 0, Math.PI * 2);
c.fill();
const texture = new THREE.Texture(canvas)
texture.needsUpdate = true;
return texture;
}
// 存储原始坐标
const indexList = [];
// 设定当前随机的范围
const range = 100;
const controls = {
polymeric: false, // 是否要组合成立方体
completeMesh: false, // 组合之后是否要显示立方体
showMesh: false, // 是否要现在显示立方体
};
let cloud;
function createMesh() {
cloud = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.BoxGeometry(10,10,10,10,10,10), new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial())
scene.add(cloud);
}
function createRandomPosition(i) {
geometry.vertices[i].x = Math.random() * range - range / 2;
geometry.vertices[i].y = Math.random() * range - range / 2;
geometry.vertices[i].z = Math.random() * range - range / 2;
}
function createPointCloud() {
let listen = false;
for (let i = 0; i < geometry.vertices.length; i++) {
indexList.push({
x: geometry.vertices[i].x,
y: geometry.vertices[i].y,
z: geometry.vertices[i].z
})
createRandomPosition(i);
if (controls.polymeric) {
const tween = new TWEEN.Tween(geometry.vertices[i]).to(indexList[i], 2000).start();
if (!listen) {
listen = true;
if (controls.completeMesh) {
tween.onComplete(() => {
scene.remove(cloud);
createMesh();
})
}
}
}
}
const material = new THREE.PointCloudMaterial({
size: 2,
transparent: true,
map: getSprite(),
})
cloud = new THREE.PointCloud(geometry, material);
cloud.sortParticles = true;
scene.add(cloud);
}
createPointCloud()
const gui = new dat.GUI();
const onChange = () => {
scene.remove(cloud);
controls.showMesh ? createMesh() : createPointCloud();
}
for (const key in controls) {
gui.add(controls, key).onChange(onChange);
}
const animation = () => {
scene.rotation.y += 0.01;
// 渲染
renderer.render(scene, camera);
TWEEN.update();
requestAnimationFrame(animation);
}
animation()
</script>
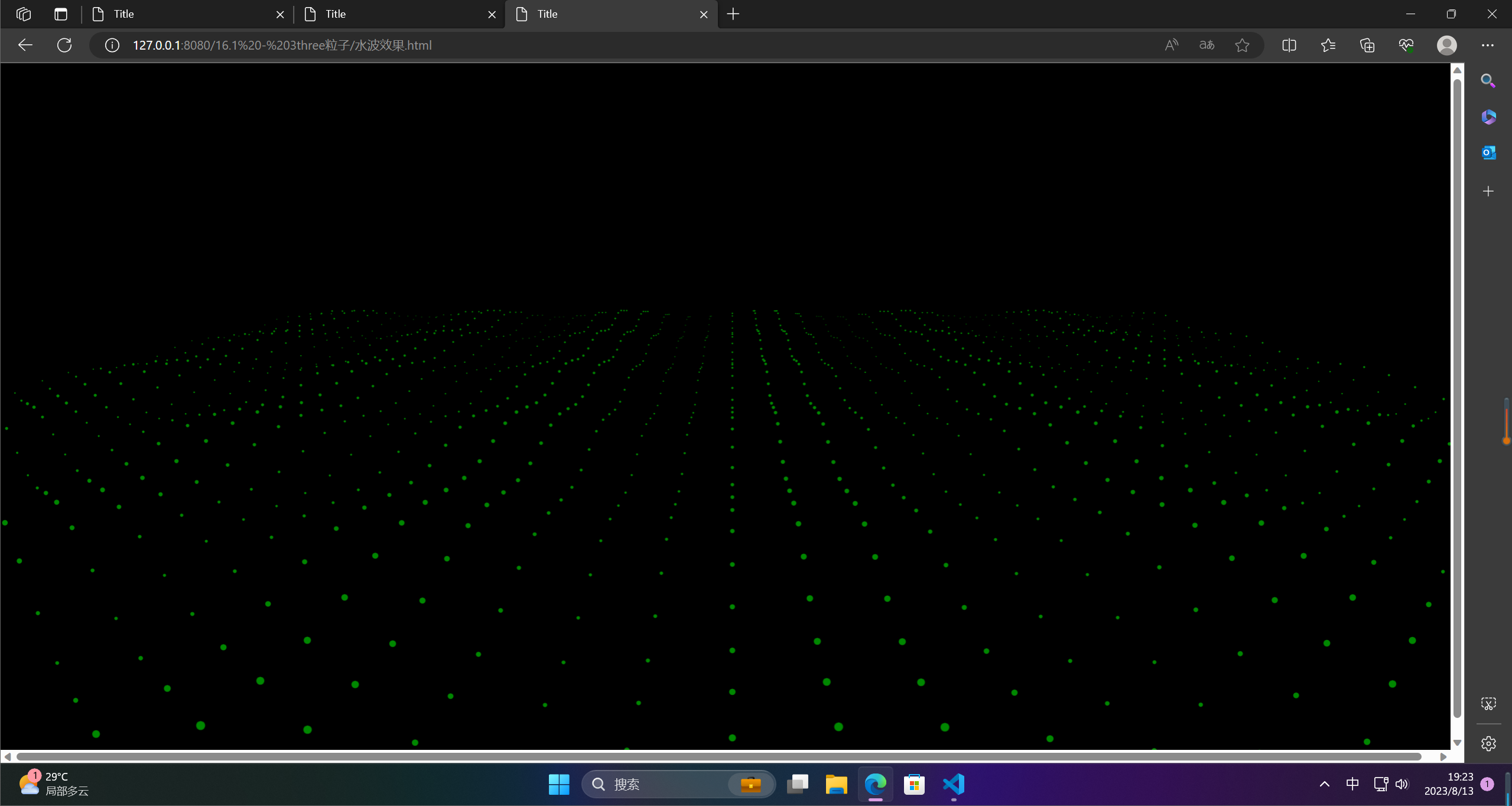
3.水波纹
水波纹是指水面上因为外界因素而产生的波动现象,通常表现为由中心向周围扩散的圆形波纹。水波纹可以由风吹、岸边拍打、水体震动等因素引起。在光线的折射与反射下,水波纹还会呈现出美丽的光影效果。水波纹是一种自然美景,也是很多人喜欢拍摄的主题之一。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
<script src="../lib/three/three.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
<script>
const clock = new THREE.Clock()
// 创建一个场景
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
// 创建一个相机 视点
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 1, 1000);
// 设置相机的位置
camera.position.set(0,50,200);
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(0,0,0));
// 创建一个渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
// 设置渲染器尺寸
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// 添加灯光
const spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0xffffff);
spotLight.position.set(2000,8000,4000);
scene.add(spotLight);
const total = 20;
const spriteList = [];
createNormalSprite();
// 使用canvas贴图来实现圆形
function getSprite() {
const canvas = document.createElement('canvas')
const size = 8
canvas.width = size * 2;
canvas.height = size * 2;
const c = canvas.getContext('2d')
c.fillStyle = '#00ff00';
c.arc(size, size, size / 1.5, 0, Math.PI * 2);
c.fill();
const texture = new THREE.Texture(canvas)
texture.needsUpdate = true;
return texture;
}
// 创建一个基础的粒子
function createNormalSprite() {
const material = new THREE.SpriteMaterial({
color: 0x008800,
map: getSprite(),
})
for (let i = -total; i < total; i++) {
for (let j = -total; j < total; j++) {
const sprite = new THREE.Sprite(material);
sprite.position.set(i * 10, 0, j * 10);
spriteList.push(sprite);
scene.add(sprite);
}
}
}
// 变化的速度
const speed = 0.1;
// 波浪的高度
const height = 5;
// 波浪的幅度
const step = 0.3;
let status = 0;
const animation = () => {
// 渲染
renderer.render(scene, camera);
requestAnimationFrame(animation);
let index = -1;
for (let x = 0; x < total * 2; x++) {
for (let y = 0; y < total * 2; y++) {
index++;
spriteList[index].position.y = (Math.sin(x + status) * step) * height + (Math.sin(y + status) * step) * height
// 缩放系数
const scaleValue = (Math.sin(x + status) * step) + 1
spriteList[index].scale.set(scaleValue,scaleValue,scaleValue)
}
}
status += speed;
}
animation()
</script>
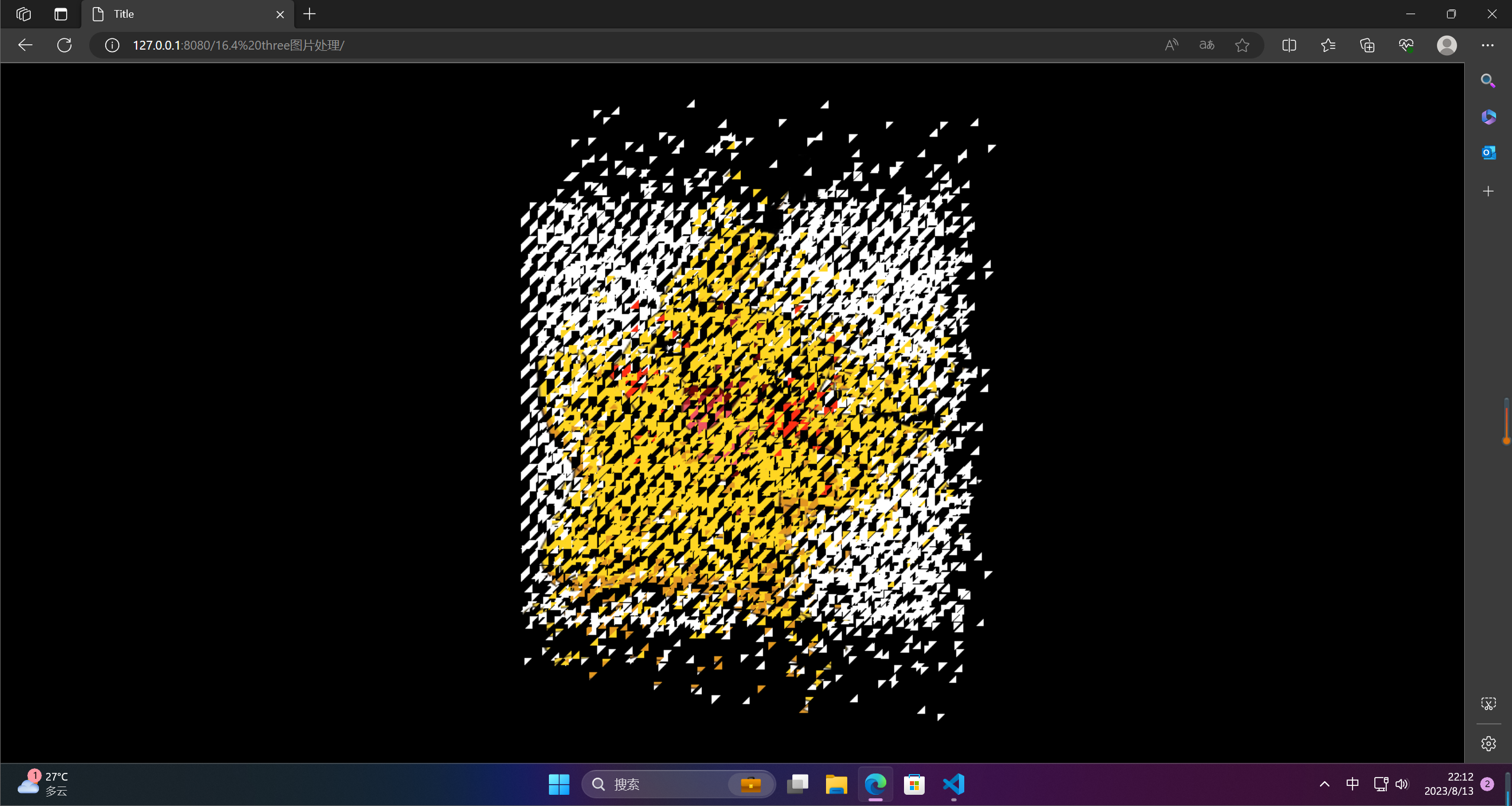
4.图片拆分重组
图片拆分重组是一种图像处理技术,它将一张图片拆分成多个小图片,再重新组合成新的图片。这种技术可以用于图片压缩、图片加密、图片转换等多种应用场景。
在图片拆分重组过程中,一般会将原始图片分成多个小块,每个小块可以是固定大小或者根据某种算法自适应大小。然后,可以通过不同的算法对这些小块进行重组,形成新的图片。比如可以按照某种规律将小块重新排列,或者通过加密算法对小块进行重新组合,从而生成一张新的图片。
图片拆分重组技术可以用于保护个人隐私、图像传输等领域,同时也可以用于美化图片、卡通化处理等应用。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from 'https://cdn.skypack.dev/[email protected]';
const clock = new THREE.Clock()
// 创建一个场景
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
// 创建一个相机 视点
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 1, 1000);
// 设置相机的位置
camera.position.set(0,0,100);
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(0,0,0));
// 创建一个渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
// 设置渲染器尺寸
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// 添加灯光
const spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0xffffff);
spotLight.position.set(2000,8000,4000);
scene.add(spotLight);
const geometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(50,50,50,50)
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: new THREE.TextureLoader().load('../assets/pikachu.png'),
})
const indexList = geometry.index.array;
const {
position, normal, uv } = geometry.attributes;
const p = position.array;
const n = normal.array;
const u = uv.array;
const positionList = []
const uvList = []
const normalList = []
Array.from(indexList).forEach(i => {
positionList.push(p[i * 3], p[i * 3 + 1], p[i * 3 + 2])
normalList.push(n[i * 3], n[i * 3 + 1], n[i * 3 + 2])
uvList.push(u[i * 2], u[i * 2 + 1])
})
// 缓冲几何体
const bufferGeometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry()
bufferGeometry.setAttribute('position', new THREE.BufferAttribute(new Float32Array(positionList), 3))
bufferGeometry.setAttribute('originPosition', new THREE.BufferAttribute(new Float32Array(positionList), 3))
bufferGeometry.setAttribute('normal', new THREE.BufferAttribute(new Float32Array(normalList), 3))
bufferGeometry.setAttribute('uv', new THREE.BufferAttribute(new Float32Array(uvList), 2))
const plane = new THREE.Mesh(bufferGeometry, material)
scene.add(plane)
// 生成一些配置信息,
const animate = []
for (let i = 0; i < positionList.length; i += 9) {
animate.push({
// 开始动画的时间
// 动画的完成程度是多少
// 每一个动画的起点、终点、和控制点信息
startTime: null,
process: 0,
start: {
x: 0, y: 0, z: 0},
end: {
x: 0, y: 0, z: 0},
c1: {
x: Math.random() * 10, y: Math.random() * 40 - 20, z: 0 },
c2: {
x: Math.random() * 10, y: Math.random() * 40 - 20, z: 0 },
})
}
// 贝塞尔曲线
const bezier = (start, c1, c2, end, p) => {
const result = {
}
const key = ['x', 'y', 'z']
const p1 = p * p * p
const p2 = p * p * (1 - p)
const p3 = p * (1 - p) * (1 - p)
const p4 = (1 - p) * (1 - p) * (1 - p)
for (const k of key) {
result[k] =
start[k] * p4 +
c1[k] * p3 * 3 +
c2[k] * p2 * 3 +
end[k] * p1;
}
return result;
}
// 是否开始,开始的时间。总的动画时间
let startTotal = Date.now();
// 总的进度
let progress = 0;
const circle = 2000;
const animation = () => {
// 粒子运动
// 进度
progress = (Date.now() - startTotal) / circle
if (progress > 1) {
progress = 1;
}
const x = -50 / 2 + 50 * progress;
animate.forEach((item,index) => {
if (!item.startTime && positionList[index * 2] < x) {
item.startTime = Date.now();
}
// 已经开始动画
if (item.startTime && item.process < 1) {
item.process = (Date.now() - item.startTime) / circle;
if (item.process > 1) {
item.process = 1;
}
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i ++) {
const cIndex = index * 3 + i;
const originPosition = {
x: positionList[cIndex * 3],
y: positionList[cIndex * 3 + 1],
z: positionList[cIndex * 3 + 2]
}
const {
start, end, c1, c2} = item;
const bezierPosition = bezier(start, c1, c2, end, item.process);
const newPosition = {
x: originPosition.x + bezierPosition.x,
y: originPosition.y + bezierPosition.y,
z: originPosition.z + bezierPosition.z,
}
bufferGeometry.attributes.position.setXYZ(cIndex, newPosition.x, newPosition.y, newPosition.z);
}
}
})
plane.geometry = bufferGeometry.clone();
// 渲染
renderer.render(scene, camera);
requestAnimationFrame(animation);
}
animation()
</script>