Hallucinated but Factual! Inspecting the Factuality of Hallucinations in Abstractive Summarization
文章目录
1 发展背景和要解决的问题是什么?
-
Abstractive summarization systems often generate hallucinations; i.e., content that is not directly inferable from the source text/not supported by the source document.
普遍存在的问题:抽象摘要常生成幻觉(数据表明30%~的占比),也就是说无法从源文本中直接推断出生成的内容。
-
Previous studies commonly assume that hallucination is an undesirable behavior in abstractive summarization systems.
以前的工作一致认为幻觉不好,所以想办法去减少这种幻觉的出现。
-
Despite being assumed incorrect, we find that much hallucinated content is factual, namely consistent with world knowledge. These factual hallucinations can be benefificial in a summary by providing useful background information.
本文有趣的发现:很多幻觉内容是符合事实性的(数据表明50%+),甚至在提供有用背景知识的情况下,幻觉是会给抽象摘要带来好处的。
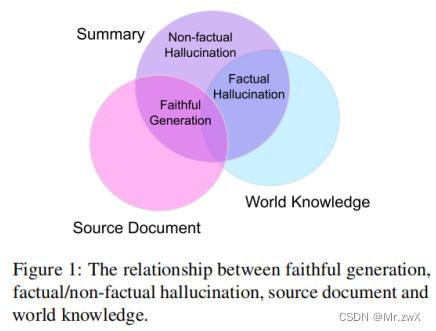
Factual hallucinations refer to content that is verififiable by world knowledge but not inferable from source text.
事实性幻觉可以被现实知识所推断,而无法被源文本推断。
-
Propose a novel detection approach that separates factual from non-factual hallucinations of entities.
本文要解决的问题:探索构造一种全新的检测方法,检测某个entity是否是幻觉的,如果是幻觉的,则去区分幻觉中的事实性和非事实性,实现factuality classification and hallucination detection两个任务。
Definition:
-
Factual hallucinations: cannot be directly entailed from the source document but are factually correct based on world knowledge.
事实性幻觉:不能直接被原文档推断出来,但是基于真实知识是正确的、符合事实的。
-
Non-factual hallucinations:entities that are neither inferable from the source nor factual.
非事实性幻觉:实体不能被原文档或真实知识所推断出来。
-
2 为什么重要?
-
Many factual hallucinations provide additional world knowledge that is important for summary comprehension.
本文研究的重要意义(本文的立场):幻觉不总是不期望的,很多事实性幻觉提供额外的对于摘要理解重要的知识。

3 为什么有挑战性?
-
Challenge => The lack of fine-grained hallucination anotation.
数据集缺少细粒度的幻觉标注(entity-level)
Solution => Create an entity-level hallucination and factuality annotation on the
XSUMdataset.作者自己构造了带事实检测标注的数据集(在XSUM数据集的基础上)
-
Challenge => One problem in the off-line RL setting is that expert demonstrations, which in our case are the reference summaries, are often noisy and contain content that cannot be inferred from the source document. The commonly used teacher forcing training encourages the model to blindly imitate the training data, which leads to model hallucination at inference time.
离线RL设置存在一个问题,参考摘要经常是有噪声并包含无法从原文档推断的内容。常用的教师强迫训练鼓励模型盲目模仿训练数据,导致了推断时的幻觉。
Solution => Use the predictions from our classifier as factuality reward signals to guide the training of the summarization model.
使用来自分类器的预测结果作为事实性奖励信号,来指导摘要模型的训练。
4 方法的核心insight是什么?
-
An entity’s prior and posterior probabilities can be used to infer whether it is hallucinated and factual. Based on this hypothesis, we propose a novel approach for entity-level hallucination detection and factuality checking.
一个实体的先验概率和后验概率可以用来推断它是否是幻觉和事实,正式基于这样一个假设,提出了实体级幻觉检测和事实检查。
-
Why prior and posterior probabilities?
-
This approach is inspired by the observation that many hallucinated entities are generated with low probabilities. This observation suggests that the summarization model’s confidence correlates with the factuality statuses of generated entities. In other words, the uncertainty is indicative of the likelihood of whether generated entities are hallucinated and non-factual.
方法受到观察到许多幻觉实体是以低概率产生的。这一观察结果表明,摘要模型的置信度与生成实体的事实状态相关。换句话说,这种不确定性表明了所产生的实体是否产生幻觉和非事实的可能性。
-
If an entity in a generated summary results in a factual error, giving the source should not provide more evidence for it, resulting in a small change in probability between the prior and the posterior.
如果一个生成摘要中的一个实体导致事实错误,给出源文本不应该给它提供更多证据,导致先验概率和后验概率之间的小改变。
-
-
Use the predictions from the detector as factuality reward signals for RL model can alleviate problems caused by hallucination.
用事实检测器的预测结果作为RL的奖励信号会缓解幻觉带来的问题
5 方法主体是什么?
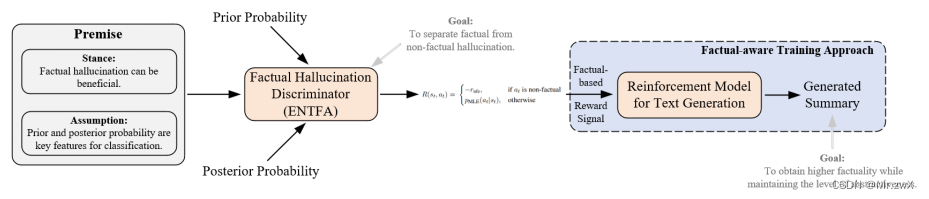
这篇paper并没有画出 figure 来说明方法的框架,所以我根据原文的描述简单制作了一个:
-
Separate factual from non-factual hallucinations of entities by training a KNN classifier with the prior and posterior probabilities (key features).
用先验概率和后验概率作为关键特征,训练一个KNN分类器以分离幻觉实体中的事实性实体和非事实性实体。
-
Propose a factuality-aware training approach for summarization systems that combines our factuality assessment model with the latest offline RL technique.
提出针对摘要系统的事实感知训练方法,结合事实性评估模型和最新的离线RL技术。
6 关键技术点和解决方法?
-
The Prior & Posterior Probability of an Entity
-
Define prior probability as the probability of its generation by a language model that does not have access to the source text.
先验概率就是生成文本时不考虑源文本的概率大小,只考虑上下文的信息。这里的MLM就是指的Masked Language Model,可能是BERT这类语言模型。
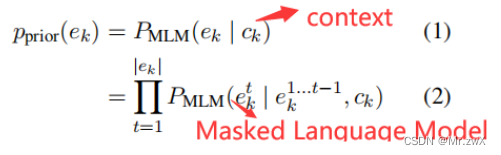
-
The posterior probability of entity is the conditional probability of the entity given the context and the source text.
后验概率是同时考虑了上下文和源文本的条件概率大小。这里的CMLM是指Conditional Masked Language Model,也就是给定源文本和一部分被masked的目标文本去预测目标文本。为了正确生成缺失部分,模型需要参考刚刚说的两部分数据。
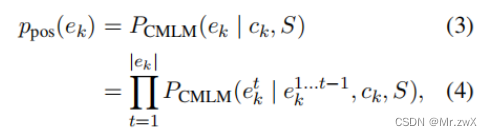
CMLM: conditional masked language model. Encoder-decoder model that is trained with a masked language model objective on a parallel dataset. Need to condition on source text and masked target text. Can be replaced by CLM.
-
-
Training a Discriminator
-
Chosen model: KNN
-
Reasons: requires no training, makes minimal assumptions about the form of the decision boundary, non-parametric method, offers adequate interpretability
采用KNN作为基础判别器,原因主要是不需要训练,非参数模型,能提供可解释性。
-
Training: KNN is trained using the prior and posterior probabilities as features on labeled dataset.
训练过程中用先验概率和后验概率作为特征。
-
Also add a binary overlap feature that indicates whether the entity appears in the document.
加入了二元覆盖特征来指示这个实体是否出现在文档中。
-
Train two classifiers for hallucination detection and factuality checking tasks respectively.
之前说到幻觉检测和事实检测两个任务,这里采用分别训练两个KNN的方式进行。
-
-
Improving the Factuality of Abstractive Summarization Systems
Propose a factuality-aware training approach for summarization systems that combines our factuality assessment model with the latest offline RL technique.
提出一种事实感知的训练方式,其实就是将事实评估模型融入到RL中。
-
RL for Text Generation
Sequence generation of the tokens in the summary text can be viewed as a finite Markov Decision Process (MDP).
State Agent Action Reward Policy
每个时刻,state包含源文本和之前生成的token;agent是摘要模型,做出生成新token的action;基于action,agent得到一个reward,然后过渡到下一个state中;每个action(token)的概率由policy所决定。agent的目标是在这个过程中最大化累计奖励值。
-
Training with a Factuality-based Reward
non-factual => a negative reward
factual => posterior probability from a MLE-trained model as token-level rewards
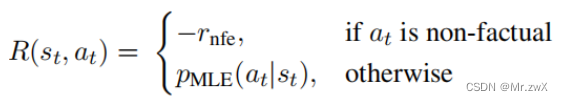
-
7 关键发现是什么?
-
Despite being assumed incorrect, we find that much hallucinated content is factual, namely consistent with world knowledge. These factual hallucinations can be benefificial in a summary by providing useful background information.
本文有趣的发现:很多幻觉内容是符合事实性的(数据表明50%+),甚至在提供有用背景知识的情况下,幻觉是会给抽象摘要带来好处的。
-
The proposed detector, when used as a reward signal in an off-line reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm, significantly improves the factuality of summaries while maintaining the level of abstractiveness.
将检测器作为离线RL模型的奖励机制,会显著提高生成摘要的事实性,同时保持摘要的抽象水平。
8 主要实验结论是什么?
-
Datasets
-
XSUM
-
XENT: a dataset has annotations of entity- or token-level hallucination. (created by authors)
-
CNN/Dailymail
-
-
Evaluation tools
-
Automatic faithfulness evaluation tools FEQA and DAE.
-
ROUGE score
-
The percentage of n-grams (reflects the extractiveness of summarization model)
反应摘要模型的提取性
-
The percentage of entities in the generated summaries that are not found in the source document (ENFS)
生成摘要中的实体无法在源文档中找到的百分比
-
-
Classification Experiments
-
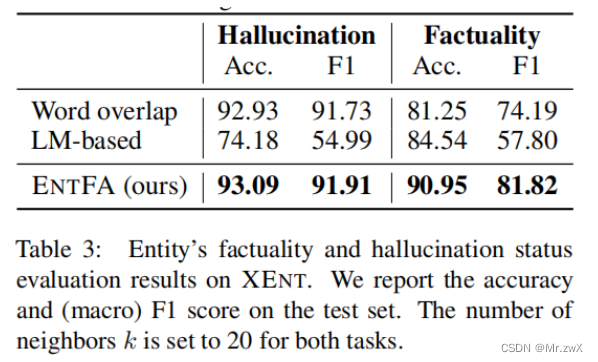
Evaluation Results on XENT
-
Our approach outperforms two baselines by large margins on the factuality classifification task.
在事实分类任务上大大优于两个基线。
-
On the hallucination detection task, the word-overlap baseline achieves a relatively high accuracy. However, the word-overlap model alone cannot distinguish between factual and non-factual hallucinations. This is the reason for its performance degradation on factuality classifification task.
在幻觉检测任务中,词重叠baseline达到了相对较高的准确性,然而,单独的词重叠模型不能区分事实幻觉和非事实幻觉,这就是为什么它在事实性分类任务上的性能下降的原因。
-
For hallucination classifification, the reason computing word overlap with the source does not completely solve the hallucination detection problem is that hallucination is defined based on the semantic relationship between the source and the summary. There can exist words that are not in the source document but which can nevertheless be inferred from it.
在幻觉分类中,计算词与源文本重叠不能完全解决幻觉检测问题,原因是幻觉是基于源文本与摘要之间的语义关系来定义的。可以存在不在源文档中,但仍然可以从其中推断出来的单词。
-
-
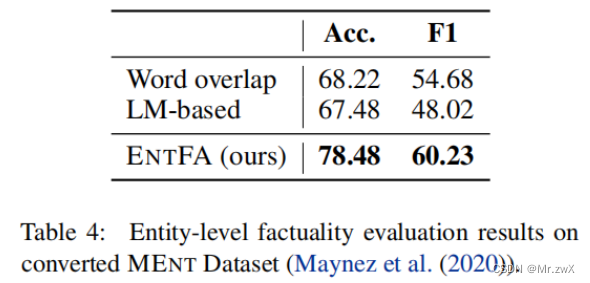
Evaluation Results on MENT
-
Demonstrate the generalizability of ENTFA.
说明ENTFA评估是具有泛化性的。
-
The performance of all models is lower on this dataset. This may be due to fact that the converted dataset is noisier than the XENT dataset.
在MENT数据集上的性能均低于XENT,这可能是因为转换数据集后噪声更多。
-
-
Factuality Evaluation Results of Summarization Systems
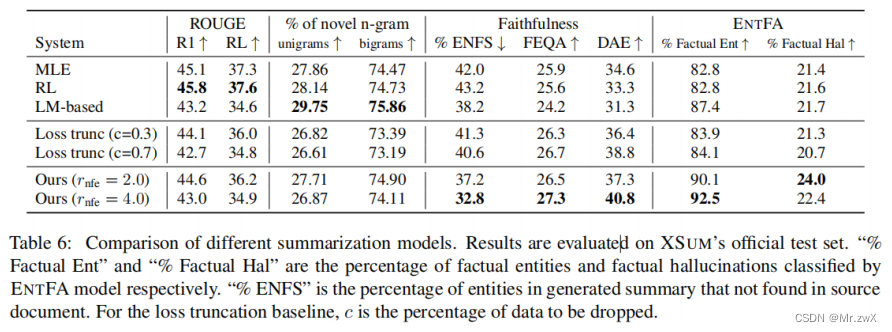
-
Outperforms all baselines with fewer non-factual entities and higher faithfulness scores.
超过所有baselines,拥有更少的非事实实体和更高的忠诚度。
-
This approach has the lowest ENFS rate while having the highest percentage of factual hallucinations.
本方法具有最低的ENFS率(生成摘要中的实体无法在源文档中找到的百分比),同时有最高的事实性幻觉百分比。
-
Compared with the loss truncation baseline, this method produces more novel n-grams. Show that this method does not improve the factuality of the model by simply making the model more extractive.
与loss truncation baseline相比,本方法生成更多的novel n-grams,所以表明本文方法不是通过简单让模型更具有提取性来提高事实性的。
-
-
Ablation Study
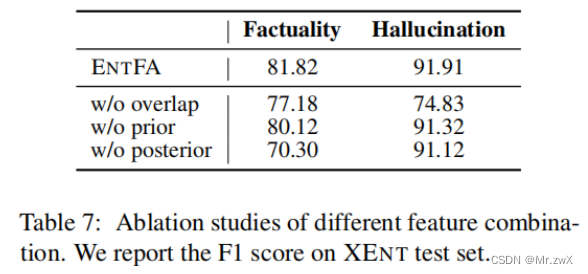
-
The posterior probability is crucial for factuality classification.
后验概率对于事实分类是至关重要的。
-
The word-overlap feature has the most signification impact on hallucination performance.
词覆盖率对于幻觉检测是非常重要的,前面有说这种覆盖特征并不能完全解决检测幻觉的问题。
-
-
Where Does the Model Learn to Hallucinate?
-
Since the BART is pre-trained on a large text corpus and fine-tuned on XSUM, the knowledge of hallucinated entities could come from either the pre-training corpus or the XSUM training set.
因为BART在很大的语料库上预训练,并在XSUM数据集上微调,这种幻觉实体要么从预训练语料库中产生,要么从XSUM训练集上产生。
于是做了如下的实验,将CMLM语言模型在两个数据集上进行训练,看看究竟事实性的幻觉实体倾向于哪个数据集的分布。
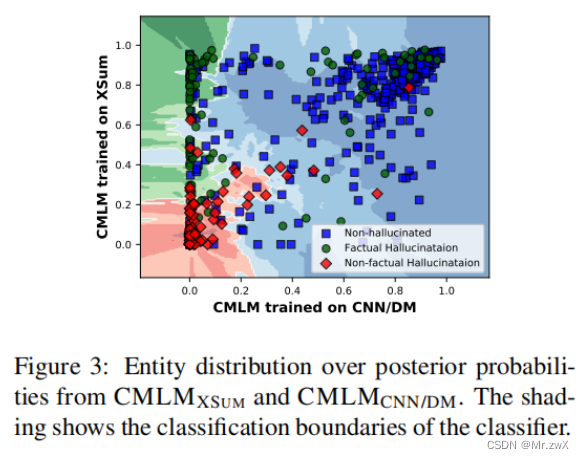
- Knowledge of many factual hallucinations comes from the XSUM training set.
事实性幻觉来自XSUM训练数据集中。
-
-
Why not Use CLM?
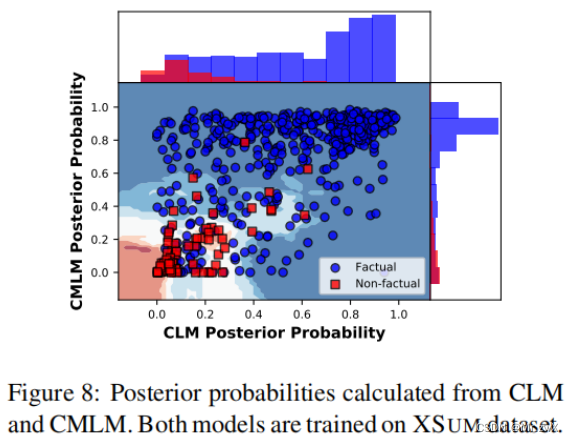
-
We can find that most factual entities (blue points) are above the x = y line. This means CMLM gives more certainty to the same factual entity than CLM.
大多数的Factual points都是在y=x的上方,所以CMLM给相同的事实性实体更多的确定性。
-
9 总结和核心takeaway(如何帮助自己的工作?)
提炼出本文的几个key points:
- Entity-level:本文是在entity-level做检测(e.g., persons, locations, dates, cardinal numbers) ,而不是sentence-level。
- Text summarization:本文提出的方法是面向文本摘要生成任务的。
- Hallucination detection and factuality checking:本文主体任务是幻觉检测和事实性检查/分类(将幻觉实体中的事实性文本和非事实性文本分离开)。
- Hallucinations are not always undesirable:本文对于幻觉现象有完全不同于之前工作的立场,认为一些幻觉是有益的。
- The prior and posterior probability of an entity for the task:用先验概率和后验概率作为检测的关键特征。
- Detector can be used as a reward signal in an off-line reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm:训练好的检测器可以作为离线RL模型的奖励机制。
Takeaways
-
Provide us with a novel perspective that hallucinations are not always undesirable, and factual hallucination can be beneficial to abstract summary task.
-
Introduce a factual checking model into RL model as a reward signal.