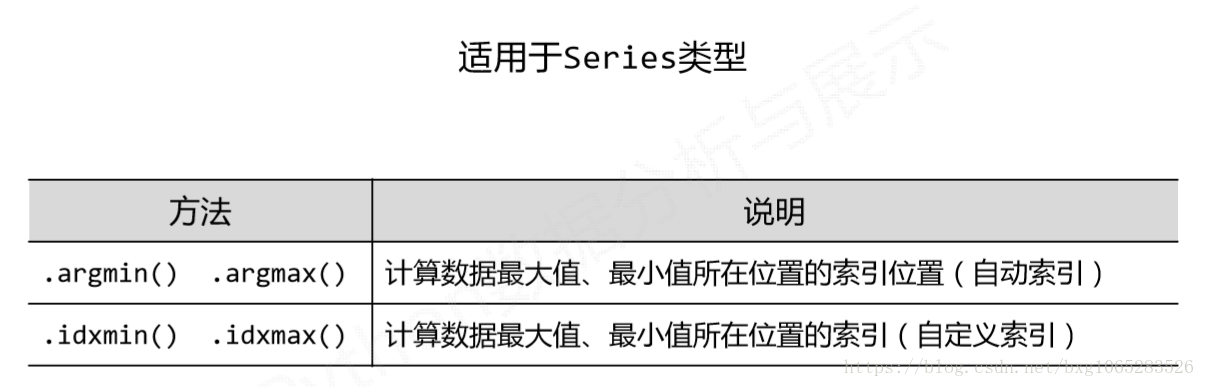
1.数据的排序
pandas库的数据排序:
.sort_index()方法在指定轴上根据索引进行排序,默认升序
.sort_index(axis=0, ascending=True)
import pandas as pd import numpy as np b=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5), index=['c','a','d','b']) print(b) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # a 5 6 7 8 9 # d 10 11 12 13 14 # b 15 16 17 18 19 print(b.sort_index()) # 0 1 2 3 4 # a 5 6 7 8 9 # b 15 16 17 18 19 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # d 10 11 12 13 14 print(b.sort_index(ascending=False)) # 0 1 2 3 4 # d 10 11 12 13 14 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # b 15 16 17 18 19 # a 5 6 7 8 9 print(b.sort_index(axis=1,ascending=False)) # 4 3 2 1 0 # c 4 3 2 1 0 # a 9 8 7 6 5 # d 14 13 12 11 10 # b 19 18 17 16 15
.sort_values()方法在指定轴上根据数值进行排序,默认升序
Series.sort_values(axis=0, ascending=True)
DataFrame.sort_values(by, axis=0, ascending=True)
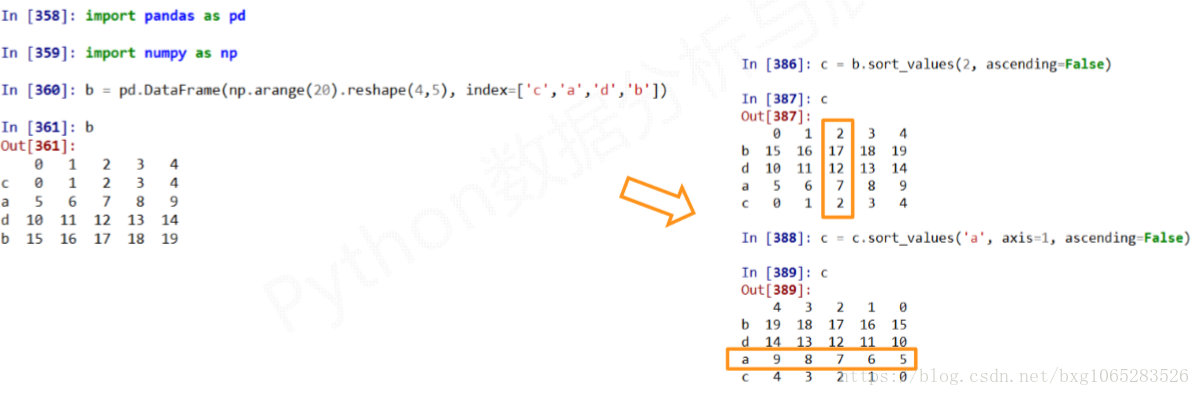
import pandas as pd import numpy as np b=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5), index=['c','a','d','b']) print(b) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # a 5 6 7 8 9 # d 10 11 12 13 14 # b 15 16 17 18 19 c=b.sort_values(2,ascending=False) # 0 1 2 3 4 # b 15 16 17 18 19 # d 10 11 12 13 14 # a 5 6 7 8 9 # c 0 1 2 3 4 print(c) c=c.sort_values('a',axis=1,ascending=False) print(c) # 4 3 2 1 0 # b 19 18 17 16 15 # d 14 13 12 11 10 # a 9 8 7 6 5 # c 4 3 2 1 0
NaN统一放到排序末尾
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
145431 查看本文章


import pandas as pd import numpy as np a=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),index=['a','b','c']) print(a) # 0 1 2 3 # a 0 1 2 3 # b 4 5 6 7 # c 8 9 10 11 b=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5), index=['c','a','d','b']) print(b) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # a 5 6 7 8 9 # d 10 11 12 13 14 # b 15 16 17 18 19 c=a+b print(c) # 0 1 2 3 4 # a 5.0 7.0 9.0 11.0 NaN # b 19.0 21.0 23.0 25.0 NaN # c 8.0 10.0 12.0 14.0 NaN # d NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN print(c.sort_values(2,ascending=False)) # 0 1 2 3 4 # b 19.0 21.0 23.0 25.0 NaN # c 8.0 10.0 12.0 14.0 NaN # a 5.0 7.0 9.0 11.0 NaN # d NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN print(c.sort_values(2,ascending=True)) # 0 1 2 3 4 # a 5.0 7.0 9.0 11.0 NaN # c 8.0 10.0 12.0 14.0 NaN # b 19.0 21.0 23.0 25.0 NaN # d NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2.数据的基本统计分析
import pandas as pd import numpy as np a=pd.Series([9,8,7,6],index=['a','b','c','d']) print(a) # a 9 # b 8 # c 7 # d 6 # dtype: int64 print(a.describe()) # count 4.000000 # mean 7.500000 # std 1.290994 # min 6.000000 # 25% 6.750000 # 50% 7.500000 # 75% 8.250000 # max 9.000000 # dtype: float64 print(type(a.describe())) # <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'> print(a.describe()['count']) # 4.0 print(a.describe()['max']) # 9.0 b=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5), index=['c','a','d','b']) print(b.describe()) # 0 1 2 3 4 # count 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 # mean 7.500000 8.500000 9.500000 10.500000 11.500000 # std 6.454972 6.454972 6.454972 6.454972 6.454972 # min 0.000000 1.000000 2.000000 3.000000 4.000000 # 25% 3.750000 4.750000 5.750000 6.750000 7.750000 # 50% 7.500000 8.500000 9.500000 10.500000 11.500000 # 75% 11.250000 12.250000 13.250000 14.250000 15.250000 # max 15.000000 16.000000 17.000000 18.000000 19.000000 print(type(b.describe())) # <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> print(b.describe()[2]) # count 4.000000 # mean 9.500000 # std 6.454972 # min 2.000000 # 25% 5.750000 # 50% 9.500000 # 75% 13.250000 # max 17.000000 # Name: 2, dtype: float64
3.数据的累计统计分析
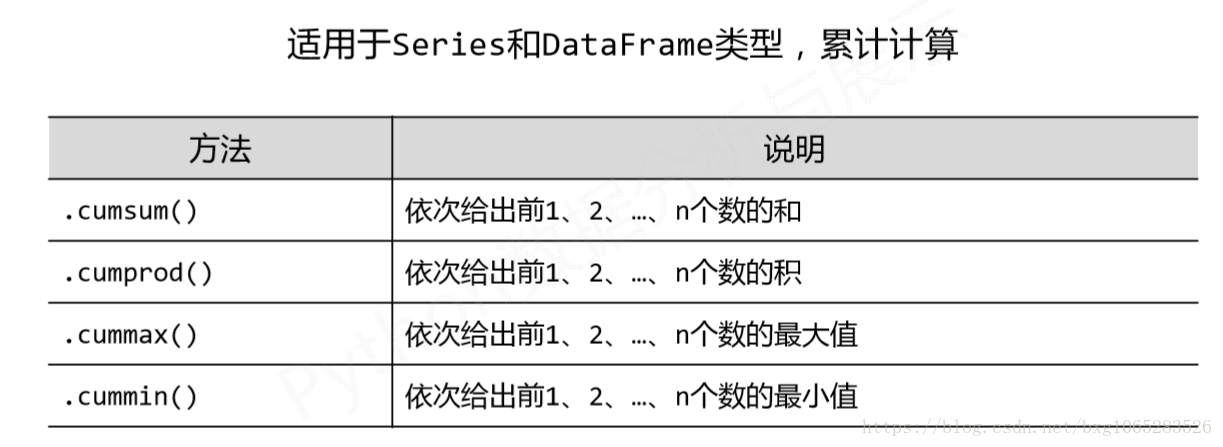
import pandas as pd import numpy as np b=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5), index=['c','a','d','b']) print(b) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # a 5 6 7 8 9 # d 10 11 12 13 14 # b 15 16 17 18 19 print(b.cumsum()) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # a 5 7 9 11 13 # d 15 18 21 24 27 # b 30 34 38 42 46 print(b.cumprod()) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # a 0 6 14 24 36 # d 0 66 168 312 504 # b 0 1056 2856 5616 9576 print(b.cummin()) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # a 0 1 2 3 4 # d 0 1 2 3 4 # b 0 1 2 3 4 print(b.cummax()) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # a 5 6 7 8 9 # d 10 11 12 13 14 # b 15 16 17 18 19
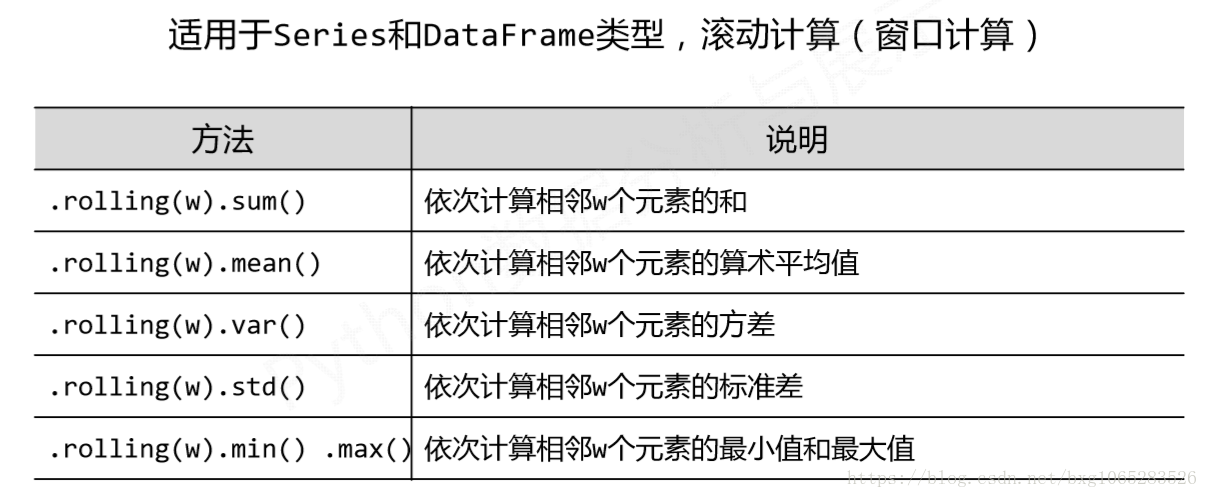
import pandas as pd import numpy as np b=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5), index=['c','a','d','b']) print(b) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c 0 1 2 3 4 # a 5 6 7 8 9 # d 10 11 12 13 14 # b 15 16 17 18 19 print(b.rolling(2).sum()) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN # a 5.0 7.0 9.0 11.0 13.0 # d 15.0 17.0 19.0 21.0 23.0 # b 25.0 27.0 29.0 31.0 33.0 print(b.rolling(3).sum()) # 0 1 2 3 4 # c NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN # a NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN # d 15.0 18.0 21.0 24.0 27.0 # b 30.0 33.0 36.0 39.0 42.0
5.数据的相关分析
相关性:
•X增大,Y增大,两个变量正相关
•X增大,Y减小,两个变量负相关
•X增大,Y无视,两个变量不相关
协方差:
•协方差>0, X和Y正相关
•协方差<0, X和Y负相关
•协方差=0, X和Y独立无关
Person相关系数:r取值范围[‐1,1]
•0.8‐1.0 极强相关
•0.6‐0.8 强相关
•0.4‐0.6 中等程度相关
•0.2‐0.4 弱相关
•0.0‐0.2 极弱相关或无相关
实例:
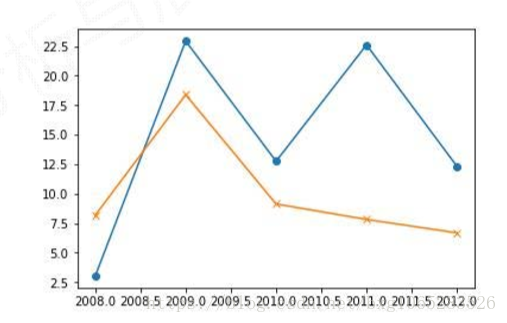
import pandas as pd import numpy as np hprice=pd.Series([3.04,22.93,12.75,22.6,12.33], index=['2008','2009','2010','2011','2012']) m2=pd.Series([8.18,18.38,9.13,7.82,6.69], index=['2008','2009','2010','2011','2012']) print(hprice.corr(m2)) #0.5239439145220387