题意:给你只有一行的棋盘,有n列,一定是偶数。奇数的位置为黑色,偶数是白色的。
然后放入n/2个棋子,让你让放的棋子全部是都在黑色(奇数)的或者白色(偶数)上面。输出最小的移动步数。
题解:暴力 对输入的n/2个棋子先排序,x记录所有棋子移动到奇数的步数,y记录移动到偶数的步数。两个里面取最小的。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,a[110],x=0,y=0;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1; i<=n/2; i++)
cin>>a[i];
sort(a+1,a+n/2+1);
for(int i=1; i<=n/2; i++)
{
x+=abs(a[i]-(i*2-1));///排序后把每个没在奇数位置距离和加起来(移动到奇数的步数)
y+=abs(a[i]-i*2);///记录移动到偶数的步数
}
cout<<min(x,y);
return 0;
}
n=int(input())
a=list(map(int,input().split(' ')))
a=sorted(a)
x=0
y=0
for i in range(n//2):
x+=abs(a[i]-i*2-1)
y+=abs(a[i]-i*2-2)
print(min(x,y))
 .
.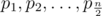 (
( in 4 moves, then
in 4 moves, then  in 3 moves,
in 3 moves,  in 2 moves and
in 2 moves and  in 1 move.
in 1 move.