学习资料参考:
张平.《OpenCV算法精解:基于Python与C++》.[Z].北京.电子工业出版社.2017.
Roberts算子
原理
使用Roberts进行边缘检测,也就是使用以下两个卷积核与图像进行分别卷积。(图中阴影部分数值为锚点所在)
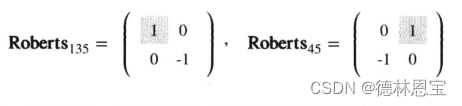
注意在实际讨论中一般将相近两点的函数值差值作为斜率。如
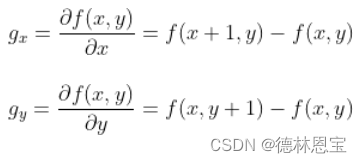
那么上述的两个卷积核也就好理解了。类似于
f(x,y) - f(x + 1,y + 1)与f(x,y) - f(x - 1,y + 1)两个函数差值。
在边缘我们知道,边缘处的像素差值较大,斜率较大。那么下列给出四种衡量标准:
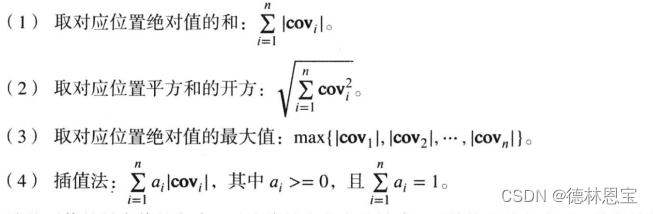
程序实现
import numpy as np
import cv2
from scipy import signal
def roberts(I, _boundary='fill', _fillvalue=0):
# 图像的高和宽
H1, W1 = I.shape
# 卷积核的大小
H2, W2 = 2, 2
# 卷积核1以及锚点位置
R1 = np.array([[1, 0], [0, -1]], np.float32)
kr1, kc1 = 0, 0
# 计算full卷积
IconR1 = signal.convolve2d(I, R1, mode='full', boundary=_boundary, fillvalue=_fillvalue)
IconR1 = IconR1[H2 - kr1 - 1:H1 + H2 - kr1 - 1, W2 - kc1 - 1:W1 + W2 - kc1 - 1]
# 卷积核2
R2 = np.array([[0, 1], [-1, 0]], np.float32)
# 先计算full卷积
IconR2 = signal.convolve2d(I, R2, mode='full', boundary=_boundary, fillvalue=_fillvalue)
# 锚点的位置
kr2, kc2 = 0, 1
# 根据锚点的位置截取full卷积,从而得到same卷积
IconR2 = IconR2[H2 - kr2 - 1:H1 + H2 - kr2 - 1, W2 - kc2 - 1:W1 + W2 - kc2 - 1]
return IconR1, IconR2
if __name__ == "__main__":
image = cv2.imread(r"C:\Users\1\Pictures\test.jpg", 0)
cv2.imshow("imgae", image)
# 卷积,边界扩充采用symm
IconR1, IconR2 = roberts(image, 'symm')
# 45度方向上的边缘强度的灰度级显示
IconR1 = np.abs(IconR1)
edge_45 = IconR1.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow("edge_45", edge_45)
# 135度方向上的边缘强度
IconR2 = np.abs(IconR2)
edge_135 = IconR2.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow("edge_135", edge_135)
# 用平方和的开方来衡量最后输出的边缘
edge = np.sqrt(np.power(IconR1, 2.0) + np.power(IconR2, 2.0))
edge = np.round(edge)
edge[edge > 255] = 255
edge = edge.astype(np.uint8)
# 显示边缘
cv2.imshow("edge", edge)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
运行结果

综合分析输出图片可知,在edge45与edge135上,轮廓较明显分别在45度方向与135度方向,而edge是两者的综合。
Prewitt算子
原理
与Roberts算子类似,prewitt算子也是两个卷积核。(并且其中带阴影部分的数字是锚点所在)
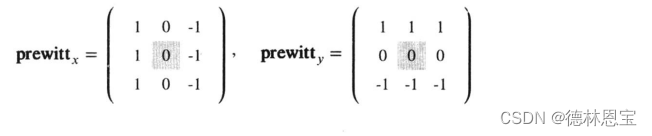
并且发现上述两个矩阵是可以进行分离的,如下所示
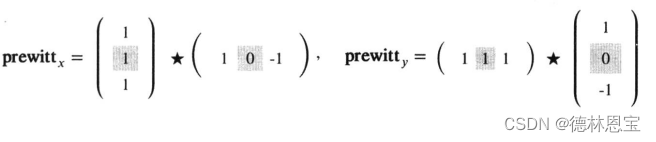
根据分离的结果可知, p r e w i t t x prewitt_x prewittx算子的卷积可以分为先进行垂直方向的均值平滑,然后进行水平方向的差分。同理, p r e w i t t y prewitt_y prewitty也可类似进行理解。
程序实现
import numpy as np
import cv2
from scipy import signal
def prewitt(I, _boundary='symm'):
# prewitt_x卷积运算
# 垂直方向的均值平滑
ones_y = np.array([[1], [1], [1]], np.float32)
i_conv_pre_x = signal.convolve2d(I, ones_y, mode='same', boundary=_boundary)
# 水平方向的差分
diff_x = np.array([[1, 0, -1]], np.float32)
i_conv_pre_x = signal.convolve2d(i_conv_pre_x, diff_x, mode='same', boundary=_boundary)
# prewitt_y卷积运算
# 水平方向的均值平滑
ones_x = np.array([[1], [1], [1]], np.float32)
i_conv_pre_y = signal.convolve2d(I, ones_x, mode='same', boundary=_boundary)
# 垂直方向的差分
diff_y = np.array([[1, 0, -1]], np.float32)
i_conv_pre_y = signal.convolve2d(i_conv_pre_y, diff_y, mode='same', boundary=_boundary)
return i_conv_pre_x, i_conv_pre_y
if __name__ == "__main__":
image = cv2.imread(r"C:\Users\1\Pictures\test1.jpg", 0)
cv2.imshow("imgae", image)
# 卷积,边界扩充采用symm
i_conv_pre_x, i_conv_pre_y = prewitt(image)
# 取绝对值
abs_i_conv_pre_x = np.abs(i_conv_pre_x)
abs_i_conv_pre_y = np.abs(i_conv_pre_y)
# 边缘强度的灰度值显示
edge_x = abs_i_conv_pre_x.copy()
edge_y = abs_i_conv_pre_y.copy()
# 截断
edge_x[edge_x > 255] = 255
edge_y[edge_y > 255] = 255
# 类型转换
edge_x = edge_x.astype(np.uint8)
edge_y = edge_y.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow("edge_x", edge_x)
cv2.imshow("edge_y", edge_y)
# 求解边缘强度
edge = 0.5 * i_conv_pre_x + 0.5 * i_conv_pre_y
edge[edge > 255] = 255
# 显示边缘
edge = edge.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.imshow("edge", edge)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
运行结果
