1. Sigmoid函数及其实现
对于一个标量x,其sigmoid函数定义为:![]()
对于n维向量x,其sigmoid函数定义为:

Python代码:
import numpy as np # this means you can access numpy functions by writing np.function() instead of numpy.function()
def sigmoid(x):
"""
Compute the sigmoid of x
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array of any size
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
### END CODE HERE ###
return s2. Sigmoid函数的梯度(导数、斜率)计算
计算公式:
![]()
推导过程:
Python代码:
def sigmoid_derivative(x):
"""
Compute the gradient (also called the slope or derivative) of the sigmoid function with respect to its input x.
You can store the output of the sigmoid function into variables and then use it to calculate the gradient.
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array
Return:
ds -- Your computed gradient.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
s = sigmoid(x)
ds = s *(1-s)
### END CODE HERE ###
return ds3. 数组Reshape(形变、展开(unroll))
图片一般以3维数组(长,宽,深度)形式存储,可使用reshape函数将其展开为n维向量(n=长*宽*深度)

Python代码:
def image2vector(image):
"""
Argument:
image -- a numpy array of shape (length, height, depth)
Returns:
v -- a vector of shape (length*height*depth, 1)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
v = image.reshape((image.shape[0] * image.shape[1] * image.shape[2], 1))
### END CODE HERE ###
return v4. 数组的归一化(normalization)
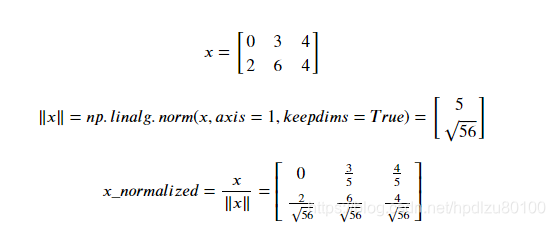
Python代码:
def normalizeRows(x):
"""
Implement a function that normalizes each row of the matrix x (to have unit length).
Argument:
x -- A numpy matrix of shape (n, m)
Returns:
x -- The normalized (by row) numpy matrix. You are allowed to modify x.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
# Compute x_norm as the norm 2 of x. Use np.linalg.norm(..., ord = 2, axis = ..., keepdims = True)
x_norm = np.linalg.norm(x, ord = 2, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
print(x_norm.shape)
# Divide x by its norm.
x = x / x_norm
print(x.shape)
### END CODE HERE ###
return x5. softmax函数
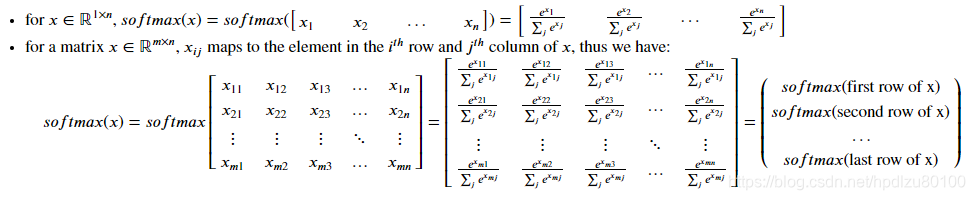
def softmax(x):
"""Calculates the softmax for each row of the input x.
Your code should work for a row vector and also for matrices of shape (n, m).
Argument:
x -- A numpy matrix of shape (n,m)
Returns:
s -- A numpy matrix equal to the softmax of x, of shape (n,m)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)
# Apply exp() element-wise to x. Use np.exp(...).
x_exp = np.exp(x)
# Create a vector x_sum that sums each row of x_exp. Use np.sum(..., axis = 1, keepdims = True).
x_sum = np.sum(x_exp, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
# Compute softmax(x) by dividing x_exp by x_sum. It should automatically use numpy broadcasting.
s = x_exp / x_sum
### END CODE HERE ###
return s6. L1,L2范数损失函数


L1实现:
def L1(yhat, y):
"""
Arguments:
yhat -- vector of size m (predicted labels)
y -- vector of size m (true labels)
Returns:
loss -- the value of the L1 loss function defined above
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
loss = np.sum(abs(yhat-y))
### END CODE HERE ###
return lossL2实现:
def L2(yhat, y):
"""
Arguments:
yhat -- vector of size m (predicted labels)
y -- vector of size m (true labels)
Returns:
loss -- the value of the L2 loss function defined above
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
#loss = np.sum((y - yhat) ** 2)
loss = np.sum(np.dot(y - yhat,y - yhat))
### END CODE HERE ###
return loss7. 要点汇总
What you need to remember:
- np.exp(x) works for any np.array x and applies the exponential function to every coordinate
- the sigmoid function and its gradient
- image2vector is commonly used in deep learning
- np.reshape is widely used. In the future, you'll see that keeping your matrix/vector dimensions straight will go toward eliminating a lot of bugs.
- numpy has efficient built-in functions
- broadcasting is extremely useful
- Vectorization is very important in deep learning. It provides computational efficiency and clarity.
- You have reviewed the L1 and L2 loss.
- You are familiar with many numpy functions such as np.sum, np.dot, np.multiply, np.maximum, etc...
参考文章:
吴恩达深度学习学习笔记——C1W2——神经网络基础——作业1——Python及Numpy基础
