- 为什么要引入正则化?
在做线性回归或者逻辑回归的时候,会遇到过拟合问题,即,在训练集上的error很小,但是在测试集上的偏差却很大。因此,引入正则化项,防止过拟合。保证在测试集上获得和在训练集上相同的效果。
例如:对于线性回归,不同幂次的方程如下

通过训练得到的结果如下:

明显,对于低次方程,容易产生欠拟合,而对于高次方程,容易产生过拟合现象。
因此,我们引入正则化项:

其他的正则化因子

- 关于线性回归的正则化
(1)首先,绘制数据图像:
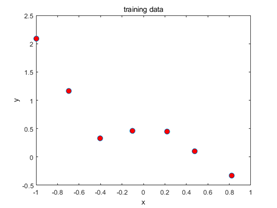
我们可以看到,只有7个数据点,因此,很容易过拟合,(训练数据集越大,越不容易过拟合)。
(2)我们用一个五次的多项式做线性回归:
![]()
之所以是线性回归,是因为对于每一个x的不同幂次,它们是线性组合的。对于初始的x,它是一个一维的特征,因此,我们将x重新构造,得到一个六维的向量。
m=length(y);
x=[ones(m,1),x,x.^2,x.^3,x.^4,x.^5];
如上实现,那么对于x的每一个维度,它们都是线性无关的,h(x)是它们的线性组合,因此,此时问题是一个多维线性回归问题。
(3)损失函数

其中λ是正则化参数。
(4)采用正规方程方式求解

注意:λ后的矩阵,θ0不参与计算,即不对θ0进行惩罚。
对于不同的参数λ,如果过大,则会把所有的参数都最小化了,导致模型编程常数θ0
即造成欠拟合。
(5)计算方法:
lambda=1;
Lambda=lambda.*eye(6);
Lambda(1)=0;
theta=(x'*x+Lambda)\x'*y
figure;
x_=(minx:0.01:maxx)';
x_1=[ones(size(x_)),x_,x_.^2,x_.^3,x_.^4,x_.^5]
hold on
plot(x0, y0, 'o', 'MarkerFacecolor', 'r', 'MarkerSize', 8);
plot(x_,x_1*theta,'--b','LineWidth',2);
legend({'data','5-th line'})
title('\lambda=1')
xlabel('x')
ylabel('y')
hold off


其中λ取0,1,10.结果如下:
计算结果如下:
Theta(λ=0) = 6×1 0.4725 0.6814 -1.3801 -5.9777 2.4417 4.7371Theta(λ=1) = 6×1 0.3976 -0.4207 0.1296 -0.3975 0.1753 -0.3394Theta(λ=10) = 6×1 0.5205 -0.1825 0.0606 -0.1482 0.0743 -0.1280
我们可以看出,当λ=0时,曲线很好的拟合了数据点,但是也明显产生了过拟合;而当λ=1时,数据点相对均匀地分布在曲线的两侧,而λ=10时,欠拟合现象明显。
- 关于逻辑回归的正则化
- 绘制原始数据

其中,‘+’表示正例,‘o’表示反例。
绘制方法如下:
pos = find(y); neg = find(y == 0);
plot (x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'+')
hold on
plot (x(neg,1),x(neg,2),'o')
- 预测函数与x的转化

注意:x是一个二维的向量,我们此处将x转化为一个高维的向量,同时,最高次数为6.特征映射函数如下:
function out = map_feature(feat1, feat2)
degree = 6;
out = ones(size(feat1(:,1)));
for i = 1:degree
for j = 0:i
out(:, end+1) = (feat1.^(i-j)).*(feat2.^j);
end
end

正则化后的损失函数

参数θ的更新规则,其中H是Hessian矩阵,另一个参数为J的梯度。
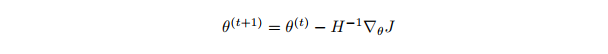
- 迭代求解
-
[m, n] = size(x);
theta = zeros(n, 1);
g =@(z)(1.0 ./ (1.0 + exp(-z)));
% disp(theta)
lambda=0
iteration=20
J = zeros(iteration, 1);
for i=1:iteration
z = x*theta;% x:117x28 theta 28x1
h = g(z) ;% sigmoid h
% Calculate J (for testing convergence)
J(i) =-(1/m)*sum(y.*log(h)+(1-y).*log(1-h))+ ...
(lambda/(2*m))*norm(theta(2:end))^2; %不包括theta(0)
%norm求的是向量theta的欧几里德范数
% Calculate gradient and hessian.
G = (lambda/m).*theta; G(1) = 0; % gradient
L = (lambda/m).*eye(n); L(1) = 0;% Hessian
grad = ((1/m).*x' * (h-y)) + G;
H = ((1/m).*x'*diag(h)*diag(1-h)*x) + L;
% Here is the actual update
theta = theta - H\grad;
end
计算出θ的值,然后绘制决策边界,可视化展示计算结果。
- 结果展示
-
其中λ的取值同样为0,1,10;
注意,采用MATLAB中的contour函数通过等高线的方式进行绘制,同时,在取值连线的时候注意要对u,v做同样的处理,如下:
% Define the ranges of the grid
u = linspace(-1, 1.5, 200);
v = linspace(-1, 1.5, 200);
% Initialize space for the values to be plotted
z = zeros(length(u), length(v));
% Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid
for i = 1:length(u)
for j = 1:length(v)
% Notice the order of j, i here!
z(j,i) = map_feature(u(i), v(j))*theta;
end
end
绘制图像结果如下:

-

-

-
同样,我们可以看到对于λ=0,过拟合,λ=10,欠拟合。
附录 源代码
附录:程序源代码
1. 线性回归+正则化
2. clc,clear
3. x=load("ex5Linx.dat");
4. y=load("ex5Liny.dat");
5. x0=x,y0=y
6. figure;
7. plot(x, y, 'o', 'MarkerFacecolor', 'r', 'MarkerSize', 8);
8. title('training data')
9. xlabel('x')
10. ylabel('y')
11. minx=min(x);
12. maxx=max(x);
13. m=length(y);
14. x=[ones(m,1),x,x.^2,x.^3,x.^4,x.^5];
15. disp(size(x(1,:))) %1x6
16. theta=zeros(size(x(1,:)))
17. lambda=0;
18. Lambda=lambda.*eye(6);
19. Lambda(1)=0;
20. theta=(x'*x+Lambda)\x'*y
21. figure;
22. x_=(minx:0.01:maxx)';
23. x_1=[ones(size(x_)),x_,x_.^2,x_.^3,x_.^4,x_.^5]
24. hold on
25. plot(x0, y0, 'o', 'MarkerFacecolor', 'r', 'MarkerSize', 8);
26. plot(x_,x_1*theta,'--b','LineWidth',2);
27. legend({'data','5-th line'})
28. title('\lambda=0')
29. xlabel('x')
30. ylabel('y')
31. hold off
32. lambda=1;
33. Lambda=lambda.*eye(6);
34. Lambda(1)=0;
35. theta=(x'*x+Lambda)\x'*y
36. figure;
37. x_=(minx:0.01:maxx)';
38. x_1=[ones(size(x_)),x_,x_.^2,x_.^3,x_.^4,x_.^5]
39. hold on
40. plot(x0, y0, 'o', 'MarkerFacecolor', 'r', 'MarkerSize', 8);
41. plot(x_,x_1*theta,'--b','LineWidth',2);
42. legend({'data','5-th line'})
43. title('\lambda=1')
44. xlabel('x')
45. ylabel('y')
46. hold off
47. lambda=10;
48. Lambda=lambda.*eye(6);
49. Lambda(1)=0;
50. theta=(x'*x+Lambda)\x'*y
51. figure;
52. x_=(minx:0.01:maxx)';
53. x_1=[ones(size(x_)),x_,x_.^2,x_.^3,x_.^4,x_.^5]
54. hold on
55. plot(x0, y0, 'o', 'MarkerFacecolor', 'r', 'MarkerSize', 8);
56. plot(x_,x_1*theta,'--b','LineWidth',2);
57. legend({'data','5-th line'})
58. title('\lambda=10')
59. xlabel('x')
60. ylabel('y')
61. hold off
2. 逻辑回归+正则化
1. clc,clear;
2. x = load ('ex5Logx.dat') ;
3. y = load ('ex5Logy.dat') ;
4. x0=x
5. y0=y
6. figure
7. % Find the i n d i c e s f or th e 2 c l a s s e s
8. pos = find(y); neg = find(y == 0);
9. plot (x(pos,1),x(pos,2),'+')
10. hold on
11. plot (x(neg,1),x(neg,2),'o')
12. u=x(:,1)
13. v=x(:,2)
14. x = map_feature (u,v)
15. [m, n] = size(x);
16. theta = zeros(n, 1);
17. g =@(z)(1.0 ./ (1.0 + exp(-z)));
18. % disp(theta)
19. lambda=0
20. iteration=20
21. J = zeros(iteration, 1);
22. for i=1:iteration
23. z = x*theta;% x:117x28 theta 28x1
24. h = g(z) ;% sigmoid h
25.
26. % Calculate J (for testing convergence)
27. J(i) =-(1/m)*sum(y.*log(h)+(1-y).*log(1-h))+ ...
28. (lambda/(2*m))*norm(theta(2:end))^2; %不包括theta(0)
29. %norm求的是向量theta的欧几里德范数
30.
31. % Calculate gradient and hessian.
32. G = (lambda/m).*theta; G(1) = 0; % gradient
33. L = (lambda/m).*eye(n); L(1) = 0;% Hessian
34.
35. grad = ((1/m).*x' * (h-y)) + G;
36. H = ((1/m).*x'*diag(h)*diag(1-h)*x) + L;
37.
38. % Here is the actual update
39. theta = theta - H\grad;
40.
41. end
42. % Define the ranges of the grid
43. u = linspace(-1, 1.5, 200);
44. v = linspace(-1, 1.5, 200);
45.
46. % Initialize space for the values to be plotted
47. z = zeros(length(u), length(v));
48.
49. % Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid
50. for i = 1:length(u)
51. for j = 1:length(v)
52. % Notice the order of j, i here!
53. z(j,i) = map_feature(u(i), v(j))*theta;
54. end
55. end
56. % Because of the way that contour plotting works
57. % in Matlab, we need to transpose z, or
58. % else the axis orientation will be flipped!
59. z = z'
60. % Plot z = 0 by specifying the range [0, 0]
61. contour(u,v,z,[0,0], 'LineWidth', 2)
62. xlim([-1.00 1.50])
63. ylim([-0.8 1.20])
64. legend({'y=1','y=0','Decision Boundary'})
65. title('\lambda=0')
66. xlabel('u')
67. ylabel('v')
68. lambda=1
69. % lambda=10
70. iteration=20
71. J = zeros(iteration, 1);
72. for i=1:iteration
73. z = x*theta;% x:117x28 theta 28x1
74. h = g(z) ;% sigmoid h
75.
76. % Calculate J (for testing convergence)
77. J(i) =-(1/m)*sum(y.*log(h)+(1-y).*log(1-h))+ ...
78. (lambda/(2*m))*norm(theta(2:end))^2; %不包括theta(0)
79. %norm求的是向量theta的欧几里德范数
80.
81. % Calculate gradient and hessian.
82. G = (lambda/m).*theta; G(1) = 0; % gradient
83. L = (lambda/m).*eye(n); L(1) = 0;% Hessian
84.
85. grad = ((1/m).*x' * (h-y)) + G;
86. H = ((1/m).*x'*diag(h)*diag(1-h)*x) + L;
87.
88. % Here is the actual update
89. % disp(H\grad)
90. theta = theta - H\grad;
91. % disp(theta)
92. % disp(i)
93. end
94. % Define the ranges of the grid
95. u = linspace(-1, 1.5, 200);
96. v = linspace(-1, 1.5, 200);
97.
98. % Initialize space for the values to be plotted
99. z = zeros(length(u), length(v));
100.
101. % Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid
102. for i = 1:length(u)
103. for j = 1:length(v)
104. % Notice the order of j, i here!
105. z(j,i) = map_feature(u(i), v(j))*theta;
106. end
107. end
108. % Because of the way that contour plotting works
109. % in Matlab, we need to transpose z, or
110. % else the axis orientation will be flipped!
111. z = z'
112. % Plot z = 0 by specifying the range [0, 0]
113. figure;
114. pos = find(y0); neg = find(y0 == 0);
115. plot (x0(pos,1),x0(pos,2),'+')
116. hold on
117. plot (x0(neg,1),x0(neg,2),'o')
118. contour(u,v,z,[0,0], 'LineWidth', 2)
119. xlim([-1.00 1.50])
120. ylim([-0.8 1.20])
121. legend({'y=1','y=0','Decision Boundary'})
122. title('\lambda=1')
123. xlabel('u')
124. ylabel('v')
125. lambda=10
126. iteration=20
127. J = zeros(iteration, 1);
128. for i=1:iteration
129. z = x*theta;% x:117x28 theta 28x1
130. h = g(z) ;% sigmoid h
131.
132. % Calculate J (for testing convergence)
133. J(i) =-(1/m)*sum(y.*log(h)+(1-y).*log(1-h))+ ...
134. (lambda/(2*m))*norm(theta(2:end))^2; %不包括theta(0)
135. %norm求的是向量theta的欧几里德范数
136.
137. % Calculate gradient and hessian.
138. G = (lambda/m).*theta; G(1) = 0; % gradient
139. L = (lambda/m).*eye(n); L(1) = 0;% Hessian
140.
141. grad = ((1/m).*x' * (h-y)) + G;
142. H = ((1/m).*x'*diag(h)*diag(1-h)*x) + L;
143.
144. % Here is the actual update
145. theta = theta - H\grad;
146. end
147. % Define the ranges of the grid
148. u = linspace(-1, 1.5, 200);
149. v = linspace(-1, 1.5, 200);
150.
151. % Initialize space for the values to be plotted
152. z = zeros(length(u), length(v));
153.
154. % Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid
155. for i = 1:length(u)
156. for j = 1:length(v)
157. % Notice the order of j, i here!
158. z(j,i) = map_feature(u(i), v(j))*theta;
159. end
160. end
161. % Because of the way that contour plotting works
162. % in Matlab, we need to transpose z, or
163. % else the axis orientation will be flipped!
164. z = z'
165. % Plot z = 0 by specifying the range [0, 0]
166. figure;
167. pos = find(y0); neg = find(y0 == 0);
168. plot (x0(pos,1),x0(pos,2),'+')
169. hold on
170. plot (x0(neg,1),x0(neg,2),'o')
171. contour(u,v,z,[0,0], 'LineWidth', 2)
172. xlim([-1.00 1.50])
173. ylim([-0.8 1.20])
174. legend({'y=1','y=0','Decision Boundary'})
175. title('\lambda=10')
176. xlabel('u')
177. ylabel('v')
