多层感知机
多层感知机就是含有至少一个隐藏层的由全连接层组成的神经网络,且每个隐藏层的输出通过激活函数进行变换,多层感知机的层数个各个隐藏层中隐藏单元个数都是超参数,输出可以通过以下公式计算得出:
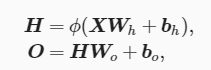
其中Φ代表激活函数;
隐藏层
多层感知机在单层神经网络的基础上引入一到多个隐藏层(hidden layer),位于输入层和输入层之间,其中的隐藏层和输出层都是全连接层,神经网络图如下:
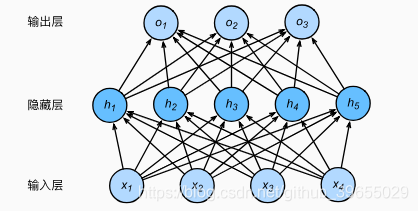
虽然神经网络引入了隐藏层,但依然等价于一个单层神经网络,这是因为全连接层只是对数据做仿射变换(affine transformation),而多个仿射变换的叠加仍然是一个仿射变换;
激活函数
为解决添加多个隐藏层也只能与仅含输出层的单层神经网络等价问题,故引入非线性变换,如对隐藏变量使用按元素运算的非线性函数进行变换,然后再作为下一个全连接层的输入,这个非线性函数叫做激活函数(activation function);以下介绍几种激活函数:
-
ReLU函数
ReLU(rectfied linear unit)提供了一种简单的非线性变换,给定元素x,则函数定义为:ReL(x) = max(x, 0),它将负数元素清零,只保留整数元素; -
Sigmoid函数
Sigmoid函数可以将元素和值变换到0和1之间,sigmoid(x)=1/(1 + exp(-x)); -
tanh函数
tanh(双曲正切)函数将元素的值变换到-1和1之间,tanh(x)=(1-exp(-2x))/(1+exp(-2x)),当输入接近0时,tanh函数接近线性变换; -
相关代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2019/4/20 10:40
# @Author : cunyu
# @Site : cunyu1943.github.io
# @File : MultiLayer.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# ReLU
import d2lzh as d2l
from mxnet import autograd, nd
# 绘图函数
def xyplot(x_vals, y_vals, name):
d2l.set_figsize(figsize=(5, 2.5))
d2l.plt.plot(x_vals.asnumpy(), y_vals.asnumpy())
d2l.plt.xlabel('x')
d2l.plt.ylabel(name + '(x)')
x = nd.arange(-8.0, 8.0, 0.1)
x.attach_grad()
with autograd.record():
y = x.relu()
xyplot(x, y, 'relu')
y.backward()
xyplot(x, x.grad, 'grad of relu')
d2l.plt.show()
# sigmoid函数
with autograd.record():
y = x.sigmoid()
xyplot(x, y, 'sigmoid')
d2l.plt.show()
y.backward()
xyplot(x, x.grad, 'grad of sigmoid')
d2l.plt.show()
# tanh函数
with autograd.record():
y = x.tanh()
xyplot(x, y, 'tanh')
d2l.plt.show()
y.backward()
xyplot(x, x.grad, 'grad of tanh')
d2l.plt.show()
多层感知机的实现
- 从零开始实现多层感知机, 代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2019/4/20 11:45
# @Author : cunyu
# @Site : cunyu1943.github.io
# @File : MultiLayer0.py
# @Software: PyCharm
import d2lzh as d2l
from mxnet import nd
from mxnet.gluon import loss as gloss
# 获取和读取数据
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
# 定义模型参数
num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens = 784, 10, 256
w1 = nd.random.normal(scale=0.01, shape=(num_inputs, num_hiddens))
b1 = nd.zeros(num_hiddens)
w2 = nd.random.normal(scale=0.01, shape=(num_hiddens, num_outputs))
b2 = nd.zeros(num_outputs)
params = [w1, b1, w2, b2]
for param in params:
param.attach_grad()
# 定义激活函数
def relu(X):
return nd.maximum(X, 0)
# 定义模型
def net(X):
X = X.reshape((-1, num_inputs))
H = relu(nd.dot(X, w1) + b1)
return nd.dot(H, w2) + b2
# 定义损失函数
loss = gloss.SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss()
# 训练模型
num_epochs, lr = 5, 0.5
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, batch_size, params, lr)
- 简洁实现多层感知机,代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2019/4/20 13:43
# @Author : cunyu
# @Site : cunyu1943.github.io
# @File : MultiLayerSimple.py
# @Software: PyCharm
import d2lzh as d2l
from mxnet import gluon, init
from mxnet.gluon import loss as gloss, nn
# 定义模型
net = nn.Sequential()
net.add(nn.Dense(256,activation='relu'), nn.Dense(10))
net.initialize(init.Normal(sigma=0.01))
# 读取数据并训练模型
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
loss = gloss.SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss()
trainer = gluon.Trainer(net.collect_params(), 'sgd', {'learning_rate':0.5})
num_epochs = 5
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, batch_size, None, None, trainer)
