本文实例讲述了python实现树的深度优先遍历与广度优先遍历。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
广度优先(层次遍历)
从树的root开始,从上到下从左到右遍历整个树的节点
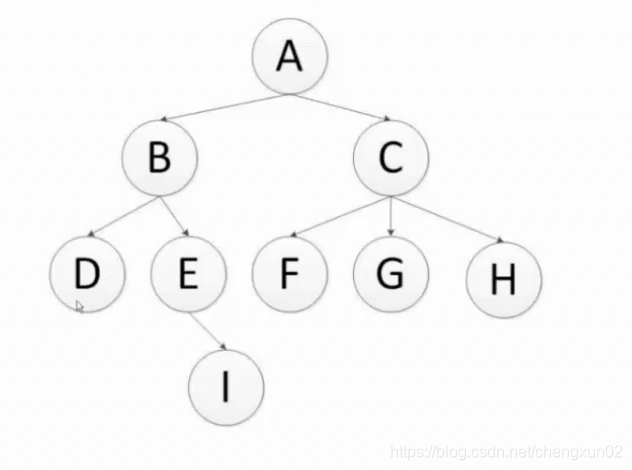
数和二叉树的区别就是,二叉树只有左右两个节点
广度优先 顺序:A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I
代码实现
def breadth_travel(self, root):
"""利用队列实现树的层次遍历"""
if root == None:
return
queue = []
queue.append(root)
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
print node.elem,
if node.lchild != None:
queue.append(node.lchild)
if node.rchild != None:
queue.append(node.rchild)
深度优先
深度优先有三种算法:前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历
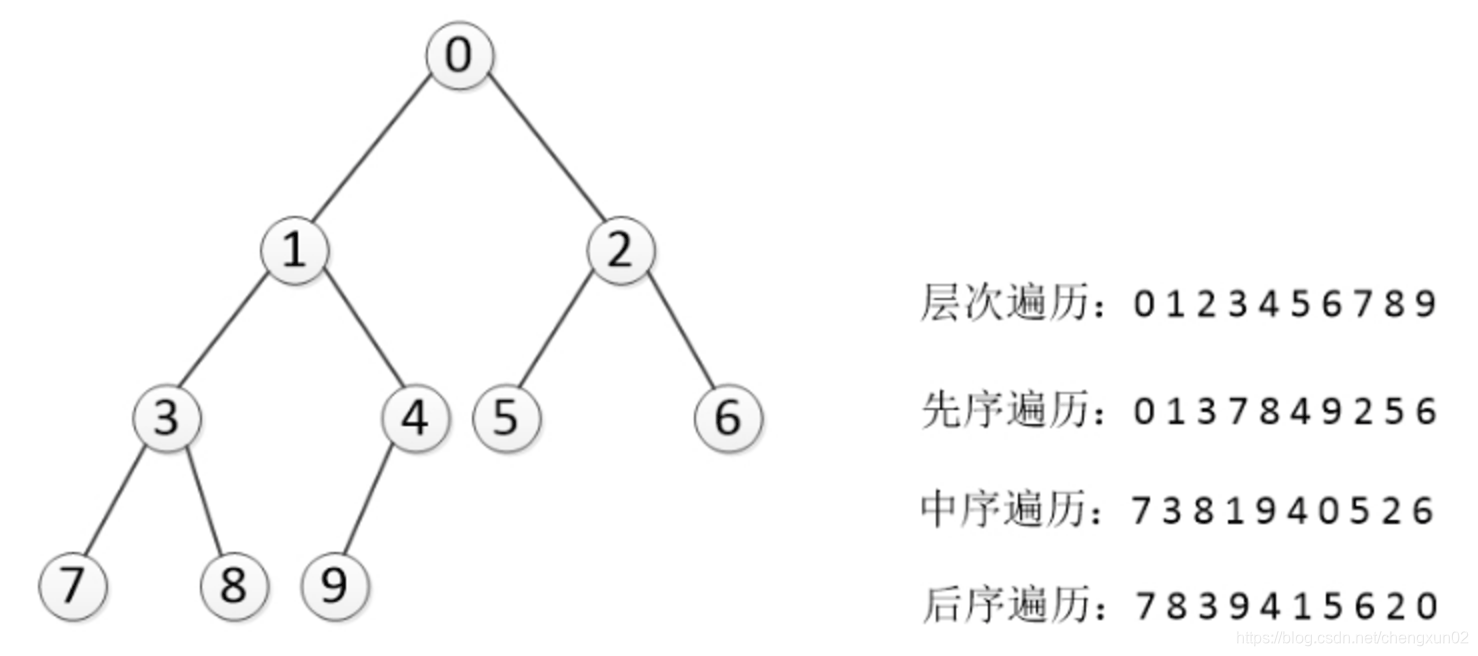
先序遍历 在先序遍历中,我们先访问根节点,然后递归使用先序遍历访问左子树,再递归使用先序遍历访问右子树
根节点->左子树->右子树
#实现 1
def preorder(self, root):
"""递归实现先序遍历"""
if root == None:
return
print root.elem
self.preorder(root.lchild)
self.preorder(root.rchild)
#实现 2
def depth_tree(tree_node):
if tree_node is not None:
print (tree_node._data)
if tree_node._left is noe None:
return depth_tree(tree_node._left)
if tree_node._right is not None:
return depth_tree(tree_node._right)
中序遍历 在中序遍历中,我们递归使用中序遍历访问左子树,然后访问根节点,最后再递归使用中序遍历访问右子树
左子树->根节点->右子树
def inorder(self, root):
"""递归实现中序遍历"""
if root == None:
return
self.inorder(root.lchild)
print root.elem
self.inorder(root.rchild)
后序遍历 在后序遍历中,我们先递归使用后序遍历访问左子树和右子树,最后访问根节点
左子树->右子树->根节点
def postorder(self, root):
"""递归实现后续遍历"""
if root == None:
return
self.postorder(root.lchild)
self.postorder(root.rchild)
print root.elem
内容就以上怎么多,最后给大家推荐一个口碑不错的公众号【程序员学府】,这里有很多的老前辈学习技巧,学习心得,面试技巧,职场经历等分享,更为大家精心准备了零基础入门资料,实战项目资料,每天都有程序员定时讲解Python技术,分享一些学习的方法和需要留意的小细节
