参考链接:
ubuntu下配置Caffe:https://blog.csdn.net/a_z666666/article/details/72853346
https://www.cnblogs.com/go-better/p/7161006.html
注意防坑点:Python和OpenCV版本都是采用的2.版本。(一开始在github上下载的,Python是3.6.4(由于安装了anaconda)和OpenCV和4.0版本,Caffe还不支持4.0的OpenCV;后来OpenCV降到3.1.0版本,安装还是各种坑。索性把Python和OpenCV都降到2.版本(先卸载了anaconda),我采用的Python是Ubuntu16.04自带的2.7.12,OpenCV是2.4.11版本,一次即配置成功。)
下面开始介绍Caffe实现物体分类的具体流程:
前期准备参考上一篇博客链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/wmr95/p/9022415.html ,这里train和test的lmdb准备还是一样(这里test.txt没有标签,可以先默认所有标签都是1,然后生成lmdb,最后在acc层可以来预测test的lmdb来得到每个的预测结果,可以把预测结果写入到一个txt中)。
(这里采用的是SENet,顺便介绍下配置SENet的过程。)github链接:https://github.com/hujie-frank/SENet (Momenta大佬写的)
(采用其他网络如resnet也是一样的步骤,而且不需要添加新的层。直接配置prototxt即可。)
1. 首先配置好senet的prototxt(SENet-50_train.prototxt,SENet-50_deploy.prototxt,SENet-50_solver.prototxt)
大部分的配置都在example下:
a. SENet-50_solver.prototxt的配置:
net: "examples/signboard/senet/SENet-50_train.prototxt" base_lr: 0.0001 lr_policy: "step" gamma: 0.1 stepsize: 500 display: 20 max_iter: 2000 momentum: 0.9 weight_decay: 0.0005 snapshot: 100 snapshot_prefix: "examples/signboard/model/senet" solver_mode: CPU
net:表示训练网络的路径,solver_mode:表示CPU模式。
b. SENet-50_train.prototxt的配置改了下输入和输出:
输入部分:
name: "SE-ResNet-50" layer { name: "data" type: "Data" top: "data" top: "label" include { phase: TRAIN } data_param { source: "examples/signboard/train_lmdb" batch_size: 16 backend: LMDB } }
输出部分:
layer { name: "pool5/7x7_s1" type: "Pooling" bottom: "conv5_3" top: "pool5/7x7_s1" pooling_param { pool: AVE kernel_size: 3 #注意这里kersize改为3,这个可能是根据你输入图像的大小,我这里resize成224 stride: 1 } } layer { name: "fc" #这里原来name为classifier,报错。问题链接:https://blog.csdn.net/raby_gyl/article/details/72357269 type: "InnerProduct" bottom: "pool5/7x7_s1" top: "fc" #这里同样将classifier改成fc,下面bottom也要记得修改 inner_product_param { num_output: 100 #这里改成你自己的分类数目 } } layer { name: "accuracy" type: "Accuracy" bottom: "fc" bottom: "label" top: "accuracy" include { phase: TEST } } layer { name: "loss" type: "SoftmaxWithLoss" bottom: "fc" bottom: "label" top: "loss" }#
c. SENet-50_deploy.prototxt配置:
输入部分:
name: "SE-ResNet-50" layer { name: "data" type: "Data" top: "data" top: "label" include { phase: TEST } data_param { source: "examples/signboard/senet/test_lmdb" batch_size: 20 backend: LMDB } }
输出部分:(这里解释同train.prototxt)
layer { name: "pool5/7x7_s1" type: "Pooling" bottom: "conv5_3" top: "pool5/7x7_s1" pooling_param { pool: AVE kernel_size: 3 stride: 1 } } layer { name: "fc" type: "InnerProduct" bottom: "pool5/7x7_s1" top: "fc" inner_product_param { num_output: 100 } } layer { name: "prob" type: "Softmax" bottom: "fc" top: "prob" } layer { name: "accuracy" type: "Accuracy" bottom: "fc" bottom: "label" top: "accuracy" include { phase: TEST } }
2. 接下来在Caffe中添加并编译Axpy层,在Caffe中主要添加三个文件:caffe/include/caffe/layers文件夹下:axpy_layer.hpp;caffe/src/caffe/layers文件夹下:axpy_layer.cpp和axpy_layer.cu文件。这三个文件在git上都有:https://github.com/hujie-frank/SENet
添加完之后,在caffe/src/caffe/proto中的caffe.proto中message LayerParameter中为新层添加参数:

这里注意AxpyParameter的ID不能和现有的重复,我这里取148。另外添加一个新的message,如果有参数就写进去,没有就空着。
3. 接下来在Caffe的路径下进行make all就行了。执行命令:make all -j20
4. 接下来,编写执行脚本进行训练:
在caffe的路径下新建一个train_senet.sh,输入以下内容:
#!usr/bin/env sh ./build/tools/caffe train --solver=./examples/signboard/senet/SENet-50_solver.prototxt \ --weights=./examples/signboard/senet/SE-ResNet-50.caffemodel
执行train_senet.sh文件,便OK啦。
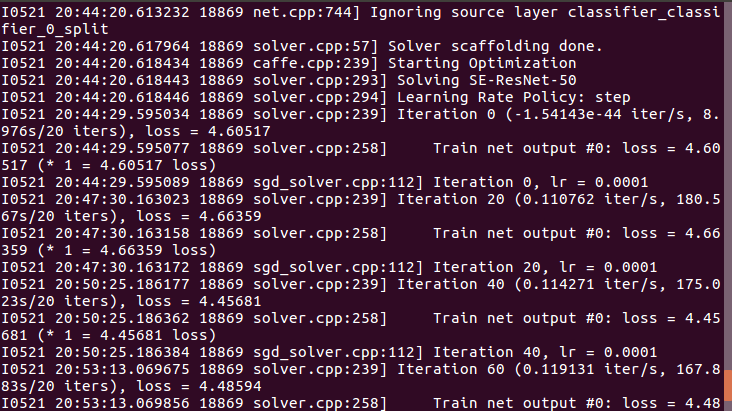
最后训练模型完成之后,要进行test数据的预测,我这里想把每个图片预测的分类写到一个txt中。
1. 这里只修改caffe/src/caffe/layers/的accuracy_layer.cpp中的Forward_cpu部分:(因为我们在deploy.prototxt中写了acc层,预测结果可以从这里获取)
template <typename Dtype> void AccuracyLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) { ofstream fout; fout.open("/home/wanglaotou/Caffe/caffe-master/out.txt", std::ios::out | std::ios::app); Dtype accuracy = 0;//准确率 const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();//100*10 const Dtype* bottom_label = bottom[1]->cpu_data();//100*1,100个图像对应的类 const int dim = bottom[0]->count() / outer_num_;//dim=10 const int num_labels = bottom[0]->shape(label_axis_); //全连接后的blob数据都是2维的,label_axis_=1,所以shape就应该是N*D中的D(这块可以看我上一篇文章) //所以bottom[0]->shape(1)=10,也就是类别数 vector<Dtype> maxval(top_k_+1); vector<int> max_id(top_k_+1); if (top.size() > 1) { caffe_set(nums_buffer_.count(), Dtype(0), nums_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data()); caffe_set(top[1]->count(), Dtype(0), top[1]->mutable_cpu_data()); } int count = 0; //LOG(INFO) << "outer_num_: "<<outer_num_<<"\n"; //LOG(INFO) << "inner_num_: "<<inner_num_<<"\n"; for (int i = 0; i < outer_num_; ++i) {//outer_num_=100 for (int j = 0; j < inner_num_; ++j) {//inner_num_为每个图像所对应的类别数,所以=1 const int label_value = static_cast<int>(bottom_label[i * inner_num_ + j]); //将bottom_label的值赋给label_value,[i * inner_num_ + j]其实就是一个图像一个类嘛 if (has_ignore_label_ && label_value == ignore_label_) { continue; } if (top.size() > 1) ++nums_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data()[label_value]; DCHECK_GE(label_value, 0); DCHECK_LT(label_value, num_labels);//label_value(0~9)肯定小于 num_labels(10) // Top-k accuracy // top_k为取前k个最高评分(的预测标签) std::vector<std::pair<Dtype, int> > bottom_data_vector; //这个主要就是用于对接下来两步把测试评分与类别ID挂勾,并对评分排序(这里我其实是比较迷糊的,测试评分指的是bottom_data,难道说经过全连接后,得到的向量就是测试评分? 迷糊中~~~) for (int k = 0; k < num_labels; ++k) { bottom_data_vector.push_back(std::make_pair( bottom_data[i * dim + k * inner_num_ + j], k)); //把测试评分与类别ID挂勾, } std::partial_sort( bottom_data_vector.begin(), bottom_data_vector.begin() + top_k_, bottom_data_vector.end(), std::greater<std::pair<Dtype, int> >());//排序 // check if true label is in top k predictions //LOG(INFO) << "top_k_: "<<top_k_<<"\n"; for (int k = 0; k < top_k_; k++) { //if (bottom_data_vector[k].second == label_value) { // ++accuracy; // .second指的是类别,如果跟label_value相等,那就说明准确 // if (top.size() > 1) ++top[1]->mutable_cpu_data()[label_value]; // break; //} LOG(INFO) << "label_value: "<<bottom_data_vector[k].second + 1<<"\n"; fout <<"label_value: "<<bottom_data_vector[k].second + 1<<"\n"; fout.flush(); } ++count; } } LOG(INFO) << "Accuracy: " << accuracy; top[0]->mutable_cpu_data()[0] = accuracy / count; if (top.size() > 1) { for (int i = 0; i < top[1]->count(); ++i) { top[1]->mutable_cpu_data()[i] = nums_buffer_.cpu_data()[i] == 0 ? 0 : top[1]->cpu_data()[i] / nums_buffer_.cpu_data()[i]; } } fout.close(); // Accuracy layer should not be used as a loss function. }
2. 编写test.sh脚本文件进行测试:
#!usr/bin/env sh ./build/tools/caffe test --iterations=50 --model=./examples/signboard/senet/SENet-50_deploy.prototxt \ --weights=./examples/signboard/model/senet_iter_2000.caffemodel
3. 执行脚本完后会得到一个out.txt文件,内容如下:
到此,大功告成~