前言:
C++代码部分借鉴的caffe中自带的classification.cpp稍微改动了一下,这一部分没有花费我太多时间。让我头疼的是CMakeLists.txt文件的编写,从昨天晚上一直搞到现在,终于现在是知道怎么才能正确的写了。期间犯了挺多错误,有的caffe目录还有libboost以及opencv的include目录你不放进去就会出现不识别的报错。没办法,对cmake不够了解,继续加油吧。
一、classify.cpp的编写
#include <caffe/caffe.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iosfwd>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
using namespace caffe; // NOLINT(build/namespaces)
using std::string;
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
/* Pair (label, confidence) representing a prediction. */
typedef std::pair<string, float> Prediction;
class Classifier {
public:
Classifier(const string& model_file,
const string& trained_file,
const string& mean_file,
const string& label_file);
std::vector<Prediction> Classify(const cv::Mat& img, int N = 5);
private:
void SetMean(const string& mean_file);
std::vector<float> Predict(const cv::Mat& img);
void WrapInputLayer(std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels);
void Preprocess(const cv::Mat& img,
std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels);
private:
shared_ptr<Net<float> > net_;
cv::Size input_geometry_;
int num_channels_;
cv::Mat mean_;
std::vector<string> labels_;
};
Classifier::Classifier(const string& model_file,
const string& trained_file,
const string& mean_file,
const string& label_file) {
#ifdef CPU_ONLY
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::CPU);
#else
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::GPU);
#endif
/* Load the network. */
net_.reset(new Net<float>(model_file, TEST));
net_->CopyTrainedLayersFrom(trained_file);
CHECK_EQ(net_->num_inputs(), 1) << "Network should have exactly one input.";
CHECK_EQ(net_->num_outputs(), 1) << "Network should have exactly one output.";
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
num_channels_ = input_layer->channels();
CHECK(num_channels_ == 3 || num_channels_ == 1)
<< "Input layer should have 1 or 3 channels.";
input_geometry_ = cv::Size(input_layer->width(), input_layer->height());
/* Load the binaryproto mean file. */
SetMean(mean_file);
/* Load labels. */
std::ifstream labels(label_file.c_str());
CHECK(labels) << "Unable to open labels file " << label_file;
string line;
while (std::getline(labels, line))
labels_.push_back(string(line));
Blob<float>* output_layer = net_->output_blobs()[0];
CHECK_EQ(labels_.size(), output_layer->channels())
<< "Number of labels is different from the output layer dimension.";
}
static bool PairCompare(const std::pair<float, int>& lhs,
const std::pair<float, int>& rhs) {
return lhs.first > rhs.first;
}
/* Return the indices of the top N values of vector v. */
static std::vector<int> Argmax(const std::vector<float>& v, int N) {
std::vector<std::pair<float, int> > pairs;
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
pairs.push_back(std::make_pair(v[i], i));
std::partial_sort(pairs.begin(), pairs.begin() + N, pairs.end(), PairCompare);
std::vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
result.push_back(pairs[i].second);
return result;
}
/* Return the top N predictions. */
std::vector<Prediction> Classifier::Classify(const cv::Mat& img, int N) {
std::vector<float> output = Predict(img);
N = std::min<int>(labels_.size(), N);
std::vector<int> maxN = Argmax(output, N);
std::vector<Prediction> predictions;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int idx = maxN[i];
predictions.push_back(std::make_pair(labels_[idx], output[idx]));
}
return predictions;
}
/* Load the mean file in binaryproto format. */
void Classifier::SetMean(const string& mean_file) {
BlobProto blob_proto;
ReadProtoFromBinaryFileOrDie(mean_file.c_str(), &blob_proto);
/* Convert from BlobProto to Blob<float> */
Blob<float> mean_blob;
mean_blob.FromProto(blob_proto);
CHECK_EQ(mean_blob.channels(), num_channels_)
<< "Number of channels of mean file doesn't match input layer.";
/* The format of the mean file is planar 32-bit float BGR or grayscale. */
std::vector<cv::Mat> channels;
float* data = mean_blob.mutable_cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < num_channels_; ++i) {
/* Extract an individual channel. */
cv::Mat channel(mean_blob.height(), mean_blob.width(), CV_32FC1, data);
channels.push_back(channel);
data += mean_blob.height() * mean_blob.width();
}
/* Merge the separate channels into a single image. */
cv::Mat mean;
cv::merge(channels, mean);
/* Compute the global mean pixel value and create a mean image
* filled with this value. */
cv::Scalar channel_mean = cv::mean(mean);
mean_ = cv::Mat(input_geometry_, mean.type(), channel_mean);
}
std::vector<float> Classifier::Predict(const cv::Mat& img) {
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
input_layer->Reshape(1, num_channels_,
input_geometry_.height, input_geometry_.width);
/* Forward dimension change to all layers. */
net_->Reshape();
std::vector<cv::Mat> input_channels;
WrapInputLayer(&input_channels);
Preprocess(img, &input_channels);
net_->Forward();
/* Copy the output layer to a std::vector */
Blob<float>* output_layer = net_->output_blobs()[0];
const float* begin = output_layer->cpu_data();
const float* end = begin + output_layer->channels();
return std::vector<float>(begin, end);
}
/* Wrap the input layer of the network in separate cv::Mat objects
* (one per channel). This way we save one memcpy operation and we
* don't need to rely on cudaMemcpy2D. The last preprocessing
* operation will write the separate channels directly to the input
* layer. */
void Classifier::WrapInputLayer(std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels) {
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
int width = input_layer->width();
int height = input_layer->height();
float* input_data = input_layer->mutable_cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < input_layer->channels(); ++i) {
cv::Mat channel(height, width, CV_32FC1, input_data);
input_channels->push_back(channel);
input_data += width * height;
}
}
void Classifier::Preprocess(const cv::Mat& img,
std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels) {
/* Convert the input image to the input image format of the network. */
cv::Mat sample;
if (img.channels() == 3 && num_channels_ == 1)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
else if (img.channels() == 4 && num_channels_ == 1)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGRA2GRAY);
else if (img.channels() == 4 && num_channels_ == 3)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGRA2BGR);
else if (img.channels() == 1 && num_channels_ == 3)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
else
sample = img;
cv::Mat sample_resized;
if (sample.size() != input_geometry_)
cv::resize(sample, sample_resized, input_geometry_);
else
sample_resized = sample;
cv::Mat sample_float;
if (num_channels_ == 3)
sample_resized.convertTo(sample_float, CV_32FC3);
else
sample_resized.convertTo(sample_float, CV_32FC1);
cv::Mat sample_normalized;
cv::subtract(sample_float, mean_, sample_normalized);
/* This operation will write the separate BGR planes directly to the
* input layer of the network because it is wrapped by the cv::Mat
* objects in input_channels. */
cv::split(sample_normalized, *input_channels);
CHECK(reinterpret_cast<float*>(input_channels->at(0).data)
== net_->input_blobs()[0]->cpu_data())
<< "Input channels are not wrapping the input layer of the network.";
}
int main() {
string model_file = "/your_path_to_caffe/caffe/models/animal_classifier/deploy.prototxt";
string trained_file = "/your_path_to_caffe/caffe/models/animal_classifier/the_resnet_18_iter_20000.caffemodel";
string label_file = "/your_path_to_caffe/caffe/data/animal_picture/labels.txt";
string mean_file = "/your_path_to_caffe/caffe/data/animal_picture/animal_mean.binaryproto";
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::GPU);
Classifier classifier(model_file, trained_file, mean_file, label_file);
string filename;
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *entry;
string filepath = "/your_path_to_data/data/";
dir = opendir("/your_path_to_data/data/");
while((entry = readdir(dir)) != NULL){
if(strcmp(entry->d_name, ".")!=0 && strcmp(entry->d_name,"..")!=0){
filename = filepath + string(entry->d_name);
Mat img = imread(filename);
if(img.empty()){
cout<<"Unable to decode image " << filename<<endl;
break;
}
//CHECK(!img.empty()) << "Unable to decode image " << filename;
std::vector<Prediction> predictions = classifier.Classify(img, 1);
for (size_t i = 0; i < predictions.size(); ++i) {
Prediction p = predictions[i];
std::cout <<entry->d_name<<": "<< std::fixed << std::setprecision(4) << p.second << " - \""
<< p.first << "\"" << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
二、CMakeLists.txt的编写
(1)先学习一下cmake工程的建立方法 这是基础版的方法,以后得好好详细学习一下。还要搞清楚文件编译原理,头文件调用过程等等知识都需要恶补。
(2)参考了一下这篇博客,这篇博客写的很好,但是有点错误,缺了点东西,我自己在理解的基础上给自己的CMake调整一下成功编译通过。
这是我编写的:
cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 2.8)
project (classify_project)
#设定可执行二进制文件的目录
SET( EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin)
add_executable(classify classify.cpp)
include_directories ( /your_path_to_caffe/caffe/include
/your_path_to_caffe/caffe/build/include
/usr/local/include
/usr/local/cuda/include
/usr/include)
target_link_libraries(classify
/your_path_to_caffe/caffe/build/lib/libcaffe.so
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libopencv_highgui.so
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libopencv_core.so
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libopencv_imgproc.so
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libglog.so
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libboost_system.so
)
输入如下命令
mkdir bin
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
命令执行过程
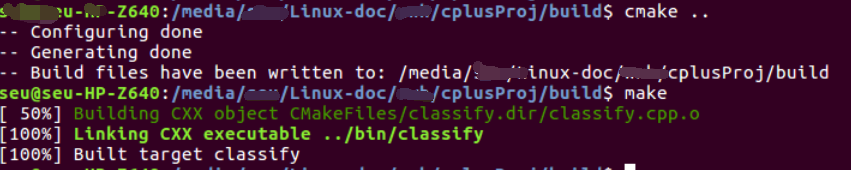
这是我建立的文件夹目录
 这是最后生成的可执行文件
这是最后生成的可执行文件
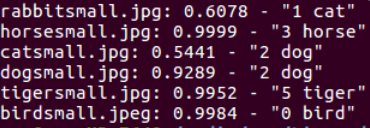
成功了,看来只要肯花时间,难题总会解决的,只要肯下功夫,小白也不会一直菜下去,现在看起来,也没什么难的,主要是自己对一些编译原理不懂,才会花了那么多功夫,不过慢慢的经验知识积累多了,以后就不会耗费那么多时间了。学无止境,怀着对知识的敬畏之心,好好学习鸭~
后续继续改进:
1.需要能够批量检测一堆图片,然后将预测结果保存到一个txt当中。
2.能够读取视频帧,每隔100ms往网络当中输送一张图片,并输出检测结果
刚才看到了个很好的博客:https://blog.csdn.net/haluoluo211/article/details/82958604 caffe c++示例(mnist 多层感知机c++训练,测试),待会可以试试学习一下。