#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score, recall_score, f1_score, fbeta_score
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_fscore_support, classification_report
if __name__ == "__main__":
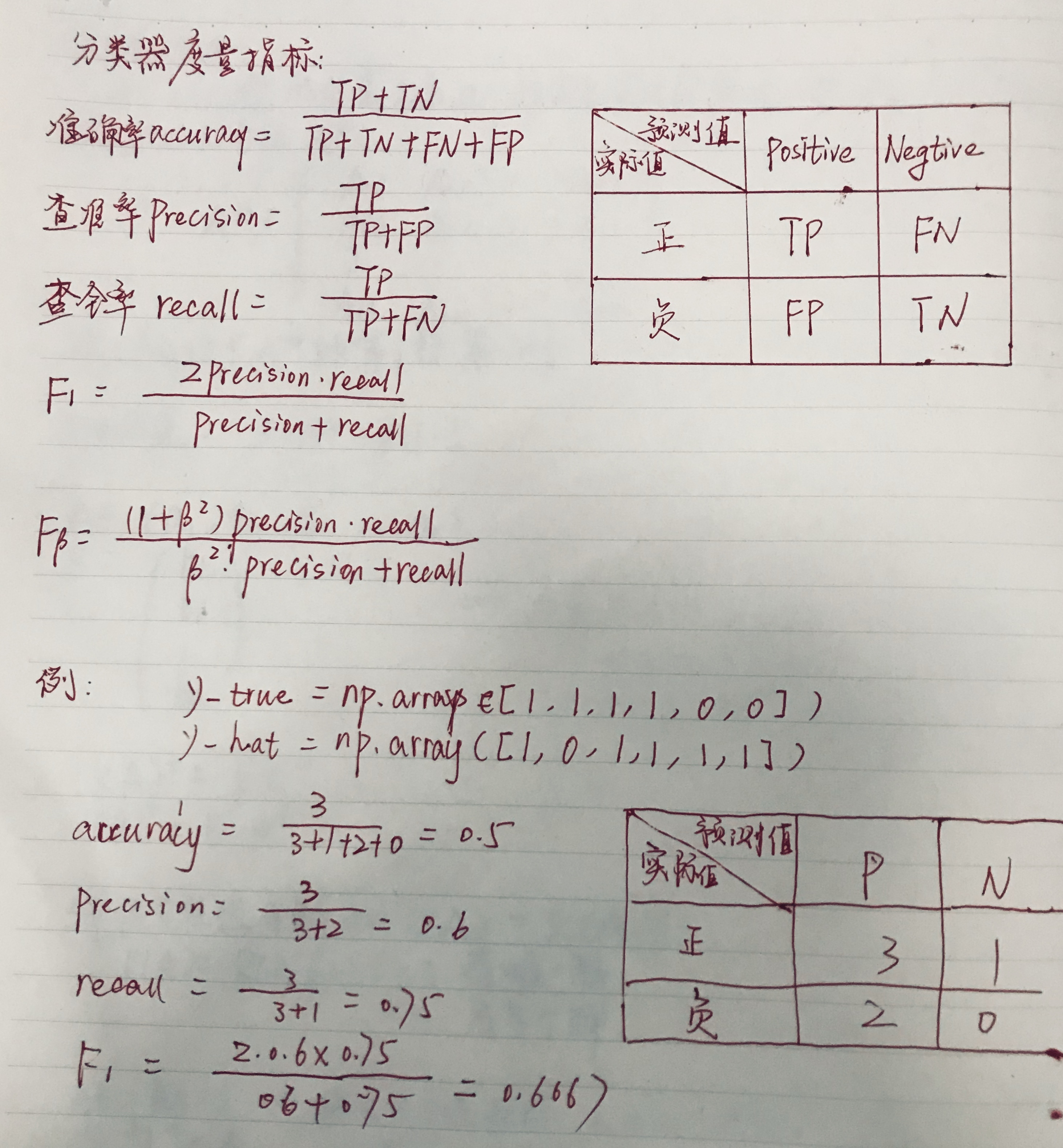
y_true = np.array([1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0])
y_hat = np.array([1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1])
print('Accuracy:\t', accuracy_score(y_true, y_hat))
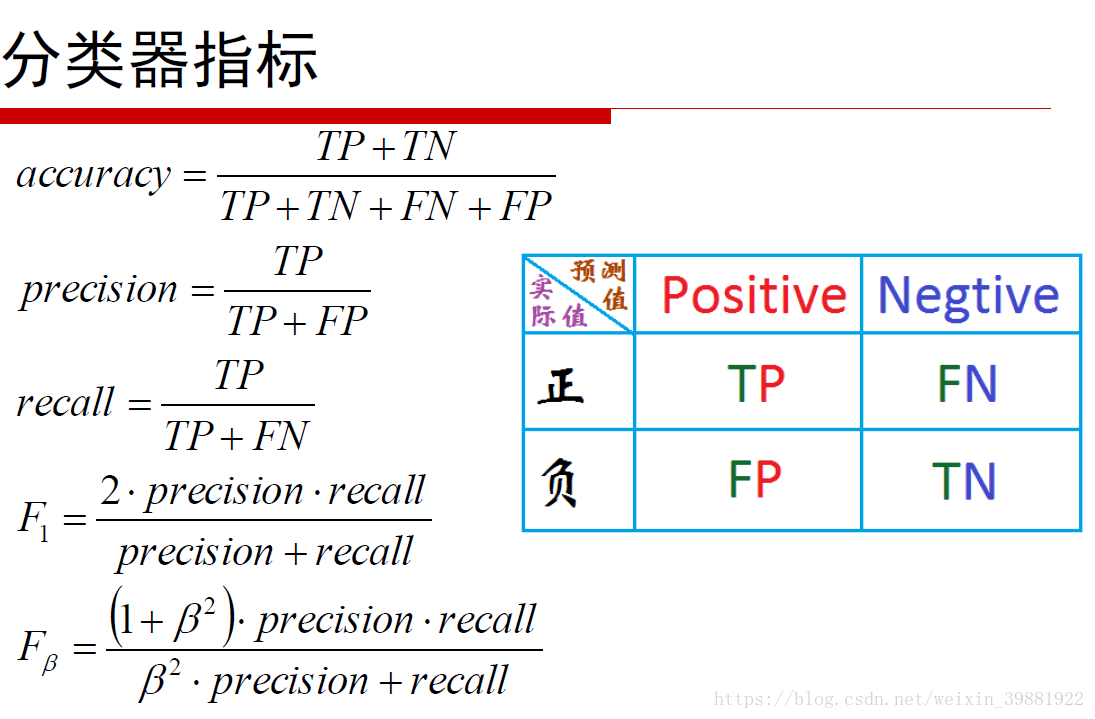
# The precision is the ratio 'tp / (tp + fp)' where 'tp' is the number of
# true positives and 'fp' the number of false positives. The precision is
# intuitively the ability of the classifier not to label as positive a sample
# that is negative.
# The best value is 1 and the worst value is 0.
precision = precision_score(y_true, y_hat)
print('Precision:\t', precision)
# The recall is the ratio 'tp / (tp + fn)' where 'tp' is the number of
# true positives and 'fn' the number of false negatives. The recall is
# intuitively the ability of the classifier to find all the positive samples.
# The best value is 1 and the worst value is 0.
recall = recall_score(y_true, y_hat)
print('Recall: \t', recall)
# F1 score, also known as balanced F-score or F-measure
# The F1 score can be interpreted as a weighted average of the precision and
# recall, where an F1 score reaches its best value at 1 and worst score at 0.
# The relative contribution of precision and recall to the F1 score are
# equal. The formula for the F1 score is:
# F1 = 2 * (precision * recall) / (precision + recall)
print('f1 score: \t', f1_score(y_true, y_hat))
print(2 * (precision * recall) / (precision + recall))
# The F-beta score is the weighted harmonic mean of precision and recall,
# reaching its optimal value at 1 and its worst value at 0.
# The 'beta' parameter determines the weight of precision in the combined
# score. 'beta < 1' lends more weight to precision, while 'beta > 1'
# favors recall ('beta -> 0' considers only precision, 'beta -> inf' only recall).
print('F-beta:')
for beta in np.logspace(-3, 3, num=7, base=10):
fbeta = fbeta_score(y_true, y_hat, beta=beta)
print('\tbeta=%9.3f\tF-beta=%.5f' % (beta, fbeta))
#print (1+beta**2)*precision*recall / (beta**2 * precision + recall)
print(precision_recall_fscore_support(y_true, y_hat, beta=1))
print(classification_report(y_true, y_hat))
Accuracy: 0.5
Precision: 0.6
Recall: 0.75
f1 score: 0.666666666667
0.666666666667
F-beta:
beta= 0.001 F-beta=0.60000
beta= 0.010 F-beta=0.60001
beta= 0.100 F-beta=0.60119
beta= 1.000 F-beta=0.66667
beta= 10.000 F-beta=0.74815
beta= 100.000 F-beta=0.74998
beta= 1000.000 F-beta=0.75000
(array([ 0. , 0.6]), array([ 0. , 0.75]), array([ 0. , 0.66666667]), array([2, 4], dtype=int64))
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.00 0.00 0.00 2
1 0.60 0.75 0.67 4
avg / total 0.40 0.50 0.44 6

