在本章, 我们会把验证平台的结构跟功能进行分离。我们要添加另外一个用于搭建验证平台的类 uvm_env。然后我们会看到测试用例怎么跟这个类通过 factory来通信
tinyalu_pkg.sv
package tinyalu_pkg; import uvm_pkg::*; `include "uvm_macros.svh" typedef enum bit[2:0] {no_op = 3'b000, add_op = 3'b001, and_op = 3'b010, xor_op = 3'b011, mul_op = 3'b100, rst_op = 3'b111} operation_t; `include "coverage.svh" `include "base_tester.svh" `include "random_tester.svh" `include "add_tester.svh" `include "scoreboard.svh" `include "env.svh" `include "random_test.svh" `include "add_test.svh" endpackage : tinyalu_pkg
tinyalu_bfm.sv
interface tinyalu_bfm; import tinyalu_pkg::*; byte unsigned A; byte unsigned B; bit clk; bit reset_n; wire [2:0] op; bit start; wire done; wire [15:0] result; operation_t op_set; assign op = op_set; task reset_alu(); reset_n = 1'b0; @(negedge clk); @(negedge clk); reset_n = 1'b1; start = 1'b0; endtask : reset_alu task send_op(input byte iA, input byte iB, input operation_t iop, shortint alu_result); if (iop == rst_op) begin @(negedge clk); op_set = iop; @(posedge clk); reset_n = 1'b0; start = 1'b0; @(posedge clk); #1; reset_n = 1'b1; end else begin @(negedge clk); op_set = iop; A = iA; B = iB; start = 1'b1; if (iop == no_op) begin @(posedge clk); #1; start = 1'b0; end else begin do @(negedge clk); while (done == 0); alu_result = result; start = 1'b0; end end // else: !if(iop == rst_op) endtask : send_op initial begin clk = 0; forever begin #10; clk = ~clk; end end endinterface : tinyalu_bfm
coverage.svh
class coverage extends uvm_component; `uvm_component_utils(coverage) virtual tinyalu_bfm bfm; byte unsigned A; byte unsigned B; operation_t op_set; covergroup op_cov; coverpoint op_set { bins single_cycle[] = {[add_op : xor_op], rst_op,no_op}; bins multi_cycle = {mul_op}; bins opn_rst[] = ([add_op:no_op] => rst_op); bins rst_opn[] = (rst_op => [add_op:no_op]); bins sngl_mul[] = ([add_op:xor_op],no_op => mul_op); bins mul_sngl[] = (mul_op => [add_op:xor_op], no_op); bins twoops[] = ([add_op:no_op] [* 2]); bins manymult = (mul_op [* 3:5]); } endgroup covergroup zeros_or_ones_on_ops; all_ops : coverpoint op_set { ignore_bins null_ops = {rst_op, no_op};} a_leg: coverpoint A { bins zeros = {'h00}; bins others= {['h01:'hFE]}; bins ones = {'hFF}; } b_leg: coverpoint B { bins zeros = {'h00}; bins others= {['h01:'hFE]}; bins ones = {'hFF}; } op_00_FF: cross a_leg, b_leg, all_ops { bins add_00 = binsof (all_ops) intersect {add_op} && (binsof (a_leg.zeros) || binsof (b_leg.zeros)); bins add_FF = binsof (all_ops) intersect {add_op} && (binsof (a_leg.ones) || binsof (b_leg.ones)); bins and_00 = binsof (all_ops) intersect {and_op} && (binsof (a_leg.zeros) || binsof (b_leg.zeros)); bins and_FF = binsof (all_ops) intersect {and_op} && (binsof (a_leg.ones) || binsof (b_leg.ones)); bins xor_00 = binsof (all_ops) intersect {xor_op} && (binsof (a_leg.zeros) || binsof (b_leg.zeros)); bins xor_FF = binsof (all_ops) intersect {xor_op} && (binsof (a_leg.ones) || binsof (b_leg.ones)); bins mul_00 = binsof (all_ops) intersect {mul_op} && (binsof (a_leg.zeros) || binsof (b_leg.zeros)); bins mul_FF = binsof (all_ops) intersect {mul_op} && (binsof (a_leg.ones) || binsof (b_leg.ones)); bins mul_max = binsof (all_ops) intersect {mul_op} && (binsof (a_leg.ones) && binsof (b_leg.ones)); ignore_bins others_only = binsof(a_leg.others) && binsof(b_leg.others); } endgroup function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); op_cov = new(); zeros_or_ones_on_ops = new(); endfunction : new function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); if(!uvm_config_db #(virtual tinyalu_bfm)::get(null, "*","bfm", bfm)) $fatal("Failed to get BFM"); endfunction : build_phase task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); forever begin : sampling_block @(negedge bfm.clk); A = bfm.A; B = bfm.B; op_set = bfm.op_set; op_cov.sample(); zeros_or_ones_on_ops.sample(); end : sampling_block endtask : run_phase endclass : coverage
scoreboard.svh
class scoreboard extends uvm_component; `uvm_component_utils(scoreboard); virtual tinyalu_bfm bfm; function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); if(!uvm_config_db #(virtual tinyalu_bfm)::get(null, "*","bfm", bfm)) $fatal("Failed to get BFM"); endfunction : build_phase task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); shortint predicted_result; ; forever begin : self_checker @(posedge bfm.done) case (bfm.op_set) add_op: predicted_result = bfm.A + bfm.B; and_op: predicted_result = bfm.A & bfm.B; xor_op: predicted_result = bfm.A ^ bfm.B; mul_op: predicted_result = bfm.A * bfm.B; endcase // case (op_set) if ((bfm.op_set != no_op) && (bfm.op_set != rst_op)) if (predicted_result != bfm.result) $error ("FAILED: A: %0h B: %0h op: %s result: %0h", bfm.A, bfm.B, bfm.op_set.name(), bfm.result); end : self_checker endtask : run_phase endclass : scoreboard
base_tester.svh
我们创建了base_tester 类,它提供了run_phase()方法。这个run_phase()方法用get_op()和get_data()方法进行1000次指令。base_tester是一个虚类,不能例化,不过可以继承base_tester来创建其他Test类
run_phase()方法假定所有的base_tester子类都重载get_op()和get_data()方法,用pure virtual关键字来强制random_tester和add_tester来完成
virtual class base_tester extends uvm_component; `uvm_component_utils(base_tester) virtual tinyalu_bfm bfm; function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); if(!uvm_config_db #(virtual tinyalu_bfm)::get(null, "*","bfm", bfm)) $fatal("Failed to get BFM"); endfunction : build_phase pure virtual function operation_t get_op(); pure virtual function byte get_data(); task run_phase(uvm_phase phase); byte unsigned iA; byte unsigned iB; operation_t op_set; shortint result; phase.raise_objection(this); bfm.reset_alu(); repeat (1000) begin : random_loop op_set = get_op(); iA = get_data(); iB = get_data(); bfm.send_op(iA, iB, op_set, result); end : random_loop #500; phase.drop_objection(this); endtask : run_phase function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new endclass : base_tester
random_tester.svh继承自base_tester并重载了get_op()和get_data()方法
class random_tester extends base_tester; `uvm_component_utils (random_tester) function byte get_data(); bit [1:0] zero_ones; zero_ones = $random; if (zero_ones == 2'b00) return 8'h00; else if (zero_ones == 2'b11) return 8'hFF; else return $random; endfunction : get_data function operation_t get_op(); bit [2:0] op_choice; op_choice = $random; case (op_choice) 3'b000 : return no_op; 3'b001 : return add_op; 3'b010 : return and_op; 3'b011 : return xor_op; 3'b100 : return mul_op; 3'b101 : return no_op; 3'b110 : return rst_op; 3'b111 : return rst_op; endcase // case (op_choice) endfunction : get_op function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new endclass : random_tester
add_tester.svh继承自random_tester并重载了get_op()函数
class add_tester extends random_tester; `uvm_component_utils(add_tester) function operation_t get_op(); bit [2:0] op_choice; return add_op; endfunction : get_op function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); endfunction : new endclass : add_tester
Separating Structure from stimulus
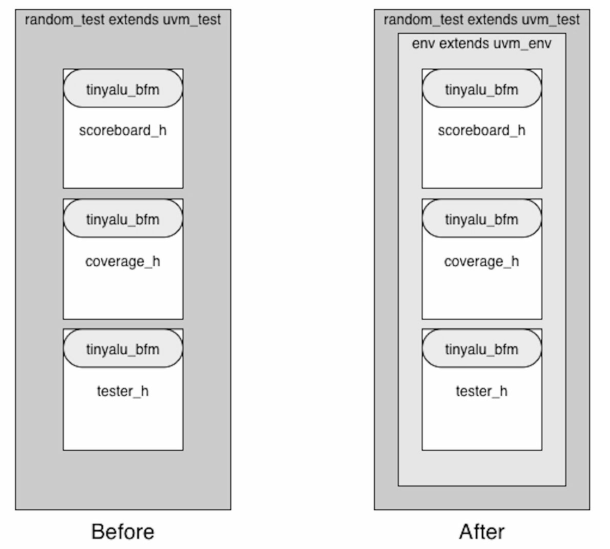
- base_tester是测试平台架构中关键的一环,通过base_tester可以派生出一系列的tester,然后我么可以像前两节所述,在uvm_test中例化这些tester开始仿真,这样可以正常工作但是却不利于代码维护。
- 原因: testbench中的stimulus和structure都被封装在uvm_test中,每一个扩展自uvm_tester的都包含了,tester,coverage,scoreboard的对象,如果我们需要修改测试平台的结构,此时工作就会变得相当复杂。
- 这样的测试平台,违背了“每个类只做一件事情”的原则,因此我们需要将平台中的structure(uvm_componnet及其子类组件)和stimulus(uvm_test及其子类)分成两个不同的功能类。UVM定义了uvm_env(扩展自uvm_component),用于存放测试平台的各个组件,uvm_env通常只包含build_phase和connect_phase两个方法。
- 使用uvm_component将测试平台的各个组件封装起来,然后使用uvm_test将各个组件填充起来。我们首先在uvm_env中例化各个uvm_component,然后在uvm_test中例化uvm_env,此时测试平台的结构如下所示:
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「我不是悍跳狼丶」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39556143/article/details/88377144
env.svh
env类定义了验证平台的结构。它例化了验证平台中的对象
class env extends uvm_env; `uvm_component_utils(env); base_tester tester_h; coverage coverage_h; scoreboard scoreboard_h;
//下面的代码用Factory格式创建三个对象 function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase); tester_h = base_tester::type_id::create("tester_h",this); //创建了base_tester类(抽象类)的对象,需要重载Factory coverage_h = coverage::type_id::create ("coverage_h",this); scoreboard_h = scoreboard::type_id::create("scoreboard_h",this); endfunction : build_phase function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name,parent); endfunction : new endclass
random_test.svh
class random_test extends uvm_test;
`uvm_component_utils(random_test);
env env_h;
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
base_tester::type_id::set_type_override(random_tester::get_type()); //重载Factory,静态方法set_type_override()告诉Factory,在看到base_class_name的请求时,返回child_class_name类型的对象
env_h = env::type_id::create("env_h",this); //例化env类
endfunction : build_phase
function new (string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction : new endclass
add_test.svh
class add_test extends uvm_test;
`uvm_component_utils(add_test);
env env_h;
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
base_tester::type_id::set_type_override(add_tester::get_type()); //重载Factory,静态方法set_type_override()告诉Factory,在看到base_class_name的请求时,返回child_class_name类型的对象
env_h = env::type_id::create("env_h",this);
endfunction : build_phase
function new (string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction : new endclass
这一节我们介绍了uvm_env,env将测试平台分割成structure和stimulus两个功能模块;
通过定义虚类base_tester和factory override使得uvm_env (stucture)和uvm_test (stimulus) 可以通信;
top.sv
module top; import uvm_pkg::*; import tinyalu_pkg::*; `include "tinyalu_macros.svh" `include "uvm_macros.svh" tinyalu_bfm bfm(); tinyalu DUT (.A(bfm.A), .B(bfm.B), .op(bfm.op), .clk(bfm.clk), .reset_n(bfm.reset_n), .start(bfm.start), .done(bfm.done), .result(bfm.result)); initial begin uvm_config_db #(virtual tinyalu_bfm)::set(null, "*", "bfm", bfm); run_test(); end endmodule : top