一. 测试代码
@RestController @RequestMapping("/book") public class BookController { @PostMapping("add") public JsonResponse<Integer> add(@Valid @RequestBody Book book, BindingResult errors){ //1. 对 item 数据进行验证 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); if (errors.hasErrors()) { for (ObjectError objectError : errors.getAllErrors()) { sb.append(objectError.getDefaultMessage()); } } if (sb.length() > 0) { return JsonResponse.error(sb.toString()); } int id = BookDB.add(book); return JsonResponse.success(id); } @GetMapping("getById") public JsonResponse<Book> getById(@RequestParam("id") Integer id){ Book book = BookDB.getById(id); return JsonResponse.success(book); } @GetMapping("getAll") public JsonResponse<List<Book>> getAll(){ List<Book> list = BookDB.getAll(); return JsonResponse.success(list); } }
在 BookController 中, 有三个方法可以访问.
/book/add -> add()
/book/getById -> getById()
/book/getAll -> getAll()
url 和 对应的名字, 是可以不一样的, 比如 我新写个方法:
@GetMapping("byWhat")
public JsonResponse<Book> getBy(){return JsonResponse.success(null);
}
此时的对应关系就是: /book/byWhat -> getBy() 方法.
这种映射, 就是一种路由关系. 通过地址路由到方法上.
二. 建立路由
1. 配置文件配置
DispatcherServlet.properties 文件中配置了两个路由处理类:
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.`.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
2. 配置类配置
spring-boot-autoconfigure 中, 有一块专门对 web 进行配置的类, WebMvcAutoConfiguration 是其中之一
@Bean public SimpleUrlHandlerMapping faviconHandlerMapping() { SimpleUrlHandlerMapping mapping = new SimpleUrlHandlerMapping(); mapping.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 1); mapping.setUrlMap(Collections.singletonMap("**/favicon.ico", faviconRequestHandler())); return mapping; } @Bean public ResourceHttpRequestHandler faviconRequestHandler() { ResourceHttpRequestHandler requestHandler = new ResourceHttpRequestHandler(); requestHandler.setLocations(resolveFaviconLocations()); return requestHandler; }
3. 类图
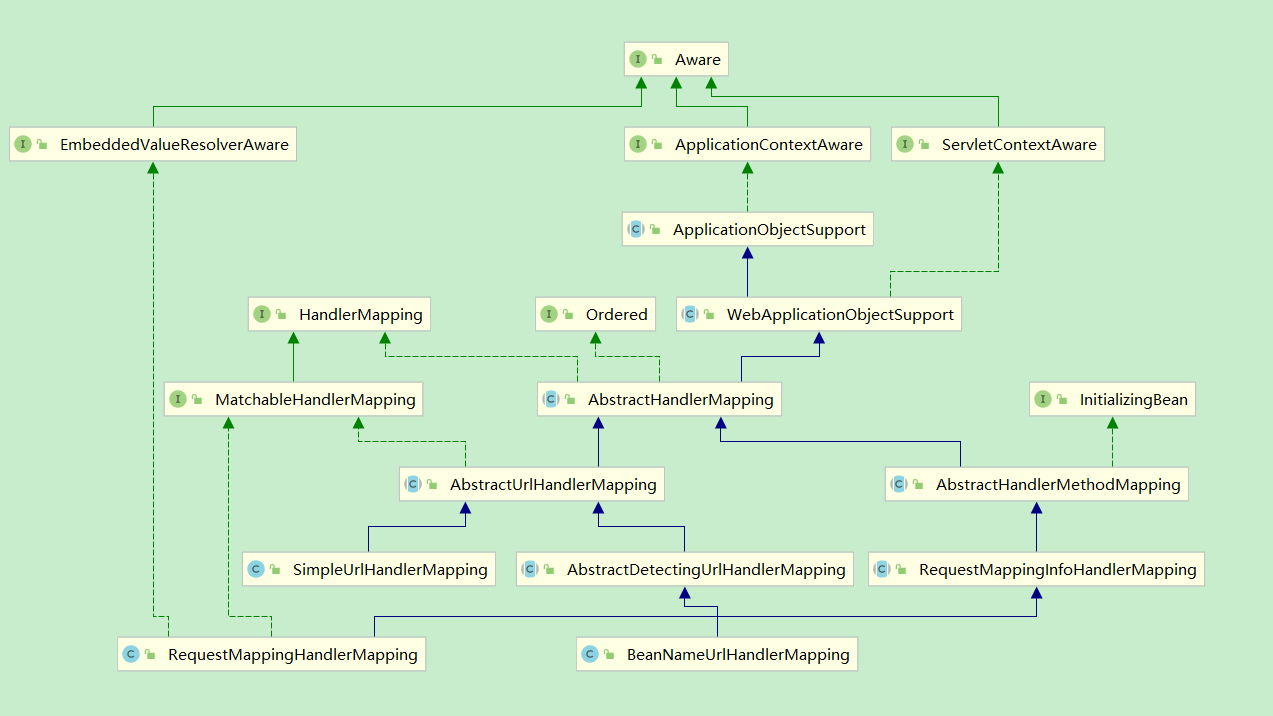
4. SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
由于 其 祖先类 ApplicationObjectSupport 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口, 所以在实例化后, 会调用 setApplicationContext() 方法:
@Override public final void setApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException { if (context == null && !isContextRequired()) { // Reset internal context state. this.applicationContext = null; this.messageSourceAccessor = null; } else if (this.applicationContext == null) { // Initialize with passed-in context. if (!requiredContextClass().isInstance(context)) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Invalid application context: needs to be of type [" + requiredContextClass().getName() + "]"); } this.applicationContext = context; this.messageSourceAccessor = new MessageSourceAccessor(context); initApplicationContext(context); } else { // Ignore reinitialization if same context passed in. if (this.applicationContext != context) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Cannot reinitialize with different application context: current one is [" + this.applicationContext + "], passed-in one is [" + context + "]"); } } } protected void initApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException { initApplicationContext(); } //空方法, 被子类重写 protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException { }
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 重写了 initApplicationContext 方法:
@Override public void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
//此处调用了 AbstractHandlerMapping 中的方法 super.initApplicationContext(); registerHandlers(this.urlMap); } protected void registerHandlers(Map<String, Object> urlMap) throws BeansException { if (urlMap.isEmpty()) { logger.warn("Neither 'urlMap' nor 'mappings' set on SimpleUrlHandlerMapping"); } else { urlMap.forEach((url, handler) -> { // Prepend with slash if not already present. if (!url.startsWith("/")) { url = "/" + url; } // Remove whitespace from handler bean name. if (handler instanceof String) { handler = ((String) handler).trim(); } registerHandler(url, handler); }); } }
在 faviconHandlerMapping() 中, 设置了 urlMap, 经过上面的方法后, 其关系为
/**/favicon.ico -> ResourceHttpRequestHandler
然后对其进行注册:
protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null"); Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null"); Object resolvedHandler = handler; // Eagerly resolve handler if referencing singleton via name. if (!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext(); if (applicationContext.isSingleton(handlerName)) { resolvedHandler = applicationContext.getBean(handlerName); } } Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath); if (mappedHandler != null) { if (mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Cannot map " + getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath + "]: There is already " + getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped."); } } else { if (urlPath.equals("/")) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Root mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler)); } setRootHandler(resolvedHandler); } else if (urlPath.equals("/*")) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Default mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler)); } setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler); } else { this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Mapped URL path [" + urlPath + "] onto " + getHandlerDescription(handler)); } } } }
5. BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
这个类并没有重写 initApplicationContext() 方法. 但是他的父类 AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping 重写了此方法:
@Override public void initApplicationContext() throws ApplicationContextException { super.initApplicationContext(); detectHandlers(); } protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException { ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Looking for URL mappings in application context: " + applicationContext); }
//拿取容器中所有的 bean String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, Object.class) : applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
//遍历容器中所有的 bean, 按照规则, 进行 urls 的生成工作 // Take any bean name that we can determine URLs for. for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//这个是一个抽象方法, 留给子类BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping实现的 String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) { // URL paths found: Let's consider it a handler. registerHandler(urls, beanName); } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Rejected bean name '" + beanName + "': no URL paths identified"); } } } }
接着看一下 BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping 里的方法:
public class BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping extends AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping { /** * Checks name and aliases of the given bean for URLs, starting with "/". */ @Override protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) { List<String> urls = new ArrayList<>(); if (beanName.startsWith("/")) { urls.add(beanName); } String[] aliases = obtainApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName); for (String alias : aliases) { if (alias.startsWith("/")) { urls.add(alias); } } return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls); } }
determineUrlsForHandler 实现了父类留的坑, 此处主要是检测 beanName 或其别名 是否是以 "/" 开头的, 如果是, 则对其执行注册方法 registerHandler(与前面4里是同一个方法).
在此例中, 并没有 beanName 是以 "/" 开头的, 所以这里并没有进行任何注册操作.
6. RequestMappingHandlerMapping
RequestMappingHandlerMapping 并不是通过 initApplicationContext() 来进行扫描触发的.
其祖先类 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 实现了 InitializingBean 接口, 也就是说, 在属性设置后, 会调用其 afterPropertiesSet() 方法.
但是 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 重写了 afterPropertiesSet() 方法:
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() { this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration(); this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper()); this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher()); this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(this.useSuffixPatternMatch); this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(this.useTrailingSlashMatch); this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch); this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager()); super.afterPropertiesSet(); }
super.afterPropertiesSet() 调用的就是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的方法了.
@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { initHandlerMethods(); } private static final String SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX = "scopedTarget."; protected void initHandlerMethods() { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext()); }
//获取容器中所有的 beanName String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class) : obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
//遍历 beanName for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//判断 beanName是否以 scopedTarget. 开头 if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { Class<?> beanType = null; try { beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { // An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex); } } if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
//进一步处理 detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); }
isHandler() 是一个过滤方法, 判断 bean 是否有 Controller 或 RequestMapping 注解:
@Override protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) { return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) || AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class)); }
detectHandlerMethods() 能进来的, 此例中就 bookController 了.
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) { Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); if (handlerType != null) { final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> { try { return getMappingForMethod(method, userType); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" + userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex); } }); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(methods.size() + " request handler methods found on " + userType + ": " + methods); } methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> { Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType); registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); }); } }
methods 就是 BookController 里面的那三个方法: add , getById, getAll
查找的基本思路:
1. 拿到spring容器中所有的 beanNames
2. 遍历beanNames, 进行过滤, 过滤依据: bean上是否有 Controller 或 RequestMapping 注解修饰
3. 对 bean 进行处理, 拿到他和他所有父类中的方法
4. 对这些方法进行过滤, 过滤依据为: 方法上是否有 RequestMapping 注解修饰, 并创建 RequestMappingInfo 对象 - A.
5. 为 bean 也创建 RequestMappingInfo 对象 - B.
如果 B 为空(bean上没有 RequestMappingInfo注解修饰), 则跳过合并操作
如果B不为空, 则对 A 和 B 进行合并操作. 路径 "/book/add"也就组合出来了.
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) { this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method); } public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) { this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock(); try { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method); assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + handlerMethod); } this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod); List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping); for (String url : directUrls) { this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping); } String name = null; if (getNamingStrategy() != null) { name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping); addMappingName(name, handlerMethod); } CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping); if (corsConfig != null) {
//如果配置了跨域, 此处还会对跨域进行记录 this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig); } this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name)); } finally { this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock(); } }
这里的 mappingLookup 存放的是 RequestMappingInfo -> HandlerMethod
而 urlLookup 存放的是 url -> RequestMappingInfo
private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap<>(); private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();