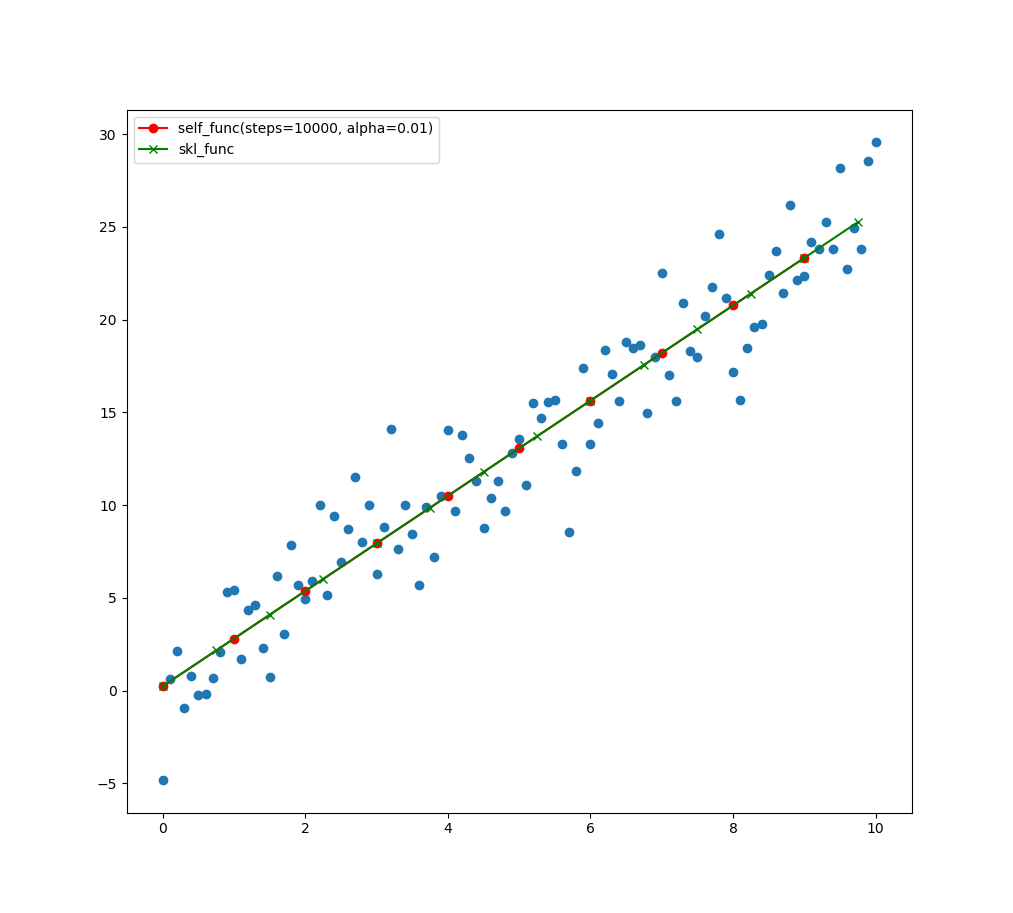
下面代码实现的是最小二乘法线性拟合,并且包含自己造的轮子与别人造的轮子的结果比较。
问题:对
y=2.5x+0.8y=2.5x+0.8直线附近的带有噪声的数据进行线性拟合,最终求出w,b的估计值。
最小二乘法基本思想是使得样本方差最小。
代码中self_func()函数为自定义拟合函数,skl_func()为调用scikit-learn中线性模块的函数。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
n = 101
x = np.linspace(0,10,n)
noise = np.random.randn(n)
y = 2.5 * x + 0.8 + 2.0 * noise
def self_func(steps=100, alpha=0.01):
w = 0.5
b = 0
alpha = 0.01
for i in range(steps):
y_hat = w*x + b
dy = 2.0*(y_hat - y)
dw = dy*x
db = dy
w = w - alpha*np.sum(dw)/n
b = b - alpha*np.sum(db)/n
e = np.sum((y_hat-y)**2)/n
#print (i,'W=',w,'\tb=',b,'\te=',e)
print ('self_func:\tW =',w,'\n\tb =',b)
plt.scatter(x,y)
plt.plot(np.arange(0,10,1), w*np.arange(0,10,1) + b, color = 'r', marker = 'o', label = 'self_func(steps='+str(steps)+', alpha='+str(alpha)+')')
def skl_func():
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(x.reshape(-1,1),y)
y_hat = lr.predict(np.arange(0,10,0.75).reshape(-1,1))
print('skl_fun:\tW = %f\n\tb = %f'%(lr.coef_,lr.intercept_))
plt.plot(np.arange(0,10,0.75), y_hat, color = 'g', marker = 'x', label = 'skl_func')
self_func(10000)
skl_func()
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
结果:
self_func: W = 2.5648753825503197 b = 0.24527830841237772
skl_fun: W = 2.564875 b = 0.245278
skl_fun: W = 2.564875 b = 0.245278