原论文地址:https://openreview.net/forum?id=B1VWyySKx
CHAR2WAV: END-TO-END SPEECH SYNTHESIS
Jose Sotelo, Soroush Mehri, Kundan Kumar, Joao Felipe Santos, Kyle Kastner,
Aaron Courville , Yoshua Bengio
Universite de Montreal
IIT Kanpur
INRS-EMT
CIFAR Fellow
Senior CIFAR Fellow
摘要
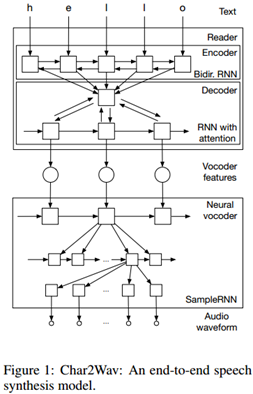
我们提出一种端到端的用于语音合成的模型 Char2Wav,其有两个组成部分:一个读取器(reader)和一个神经声码器。该读取器是一个带有注意力(attention)的编码器-解码器模型。其中编码器是一个以文本或音素作为输入的双向循环神经网络(RNN),而解码器则是一个带有注意力的循环神经网络,其会产出声码器声学特征。神经声码器是指 SampleRNN 的一种条件式的扩展,其可以根据中间表征(intermediate representations)生成原始的声波样本。与用于语音合成的传统模型不同,Char2Wav 可以学习直接根据文本生成音频。
1 介绍
语音合成的主要任务包括将文本映射为音频信号。语音合成有两个主要目标:可理解性和自然度。可理解性是指合成音频的清晰度,特别是听话人能够在多大程度上提取出原信息。自然度则描述了无法被可理解性直接获取的信息,比如听的整体容易程度、全局的风格一致性、地域或语言层面的微妙差异等等。
传统的语音合成方法是将这个任务分成两个阶段来完成的。第一个阶段被称为前端(frontend)是将文本转换为语言特征,这些特征通常包括音素、音节、词、短语和句子层面的特征(Zen, 2006; Zen et al., 2013; van den Oord et al., 2016)。第二个阶段被称为后端(backend),以前端所生成的语言特征为输入来生成对应的声音。WaveNet(van den Oord et al., 2016)就是一种可实现高质量的「神经后端(neural backend)」的方法。要更加详细地了解传统的语音合成模型,我们推荐参阅 Taylor ( 2009 ) 。
定义好的语言特征通常需要耗费大量时间,而且不同的语言也各有不同。在本论文中,我们将前端和后端整合到了一起,可以通过端到端的方式学习整个过程。这个流程消除了对专业语言学知识的需求,这就移除了在为新语言创建合成器时所面临的一个主要瓶颈。我们使用了一个强大的模型来从数据中学习这种信息。
2 相关研究
基于注意力的模型之前已经在机器翻译(Cho et al., 2014; Bahdanau et al., 2015)、语音识别(Chorowski et al., 2015; Chan et al., 2016)和计算机视觉(Xu et al. 2015)等领域得到了应用。我们的工作受到了 Alex Graves ( Graves, 2013; 2015 ) 的工作很大的影响。在一个客座讲座中,Graves 展示了一个使用了一种注意机制的语音合成模型,这是他之前在手写生成方面的研究成果的延伸。不幸的是,这个延伸工作没有被发表出来,所以我们不能将我们的方法和他的成果进行直接的比较。但是,他的结果给了我们关键的启发,我们也希望我们的成果能有助于端到端语音合成的进一步发展。
3 模型描述
3.1 读取器
我们采用了 Chorowski et al.( 2015 ) 的标记法。一个基于注意力的循环序列生成器(ARSG/attention-based recurrent sequence generator)是指一种基于一个输入序列 X 生成一个序列 Y= ( y1, . . . , yT ) 的循环神经网络。X 被一个编码器预处理输出一个序列 h = ( h1, . . . , hL ) 。在本研究中,输出 Y 是一个声学特征的序列,而 X 则是文本或要被生成的音素序列。此外,该编码器是一个双向循环网络。
在第 i 步,ARSG 重点关注 h 并生成 yi:
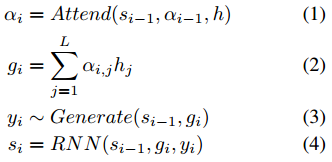
其中 si-1 是该生成器循环神经网络的第 i-1 个状态,而
是注意权重(attention weight)或对齐(alignment)。
在这项成果中,我们使用了由 Graves ( 2013 ) 开发的基于位置的注意机制(location-based attention mechanism)。我们有
![]()
而给定一个调节序列 h 的长度 L,我们有:
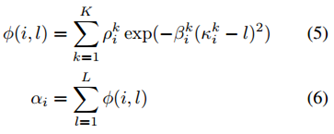
其中 κi、βi 和 ρi 分别表示该窗口的位置、宽度和重要程度。
3.2 神经声码器
使用声码器进行语音合成受到特定声码器重建质量的限制。为了获得高质量的输出,我们使用一个学习到的参数神经模块(parametric neural module)替代了该声码器。为了该目标,我们使用 SampleRNN ( Mehri et al., 2016)作为增强的函数逼近器(function approximator)。SampleRNN 最近被提出用于在音频信号这样的序列数据中建模极其长期的依存关系。SampleRNN 中的层级结构被设计来捕捉不同时间尺度中序列的动态。这对捕捉远距音频时间步骤(例如,语音信号中的词层面关系)之间的长距关联以及近距音频时间步骤的动态都是有必要的。
我们使用同一模型的条件式版本学习把来自声码器特征序列映射到相应的音频样本。每个声码器的特征帧(feature frame)被加了进来用作相应状态的最好的额外输入。这使得该模块能使用过去的音频样本和声码器特征帧来生成当前的音频样本。
4. 训练细节
首先,我们分别预训练读取器和神经声码器然后使用标准的 WORLD 声码器特征(Morise et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2016)作为读取器的目标和神经声码器的输入。最终,我们端到端的微调整个模型。代码已经在网上公开。
GitHub 开源地址:http://github.com/sotelo/parrot
合成语音样本地址:http://josesotelo.com/speechsynthesis
5 结果
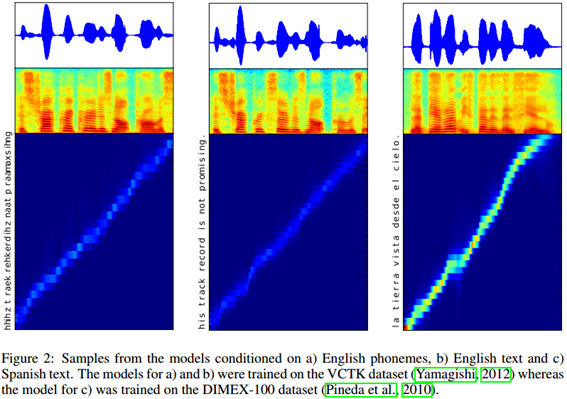
此次我们并未提供对结果的综合的定量分析。相反,我们提供了来自模型生成的语音样本。在图 2 中,我们演示了模型生成的语音样本以及相应的文本对齐结果。
REFERENCES
Dzmitry Bahdanau, Kyunghyun Cho, and Yoshua Bengio. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2015.
Jacob Benesty, M Mohan Sondhi, and Yiteng Huang. Springer handbook of speech processing. Springer Science & Business Media, 2007.
Samy Bengio, Oriol Vinyals, Navdeep Jaitly, and Noam Shazeer. Scheduled sampling for sequence prediction with recurrent neural networks. In C. Cortes, N. D. Lawrence, D. D. Lee, M. Sugiyama, and R. Garnett (eds.), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28, pp. 1171–1179. Curran Associates, Inc., 2015.
Yoshua Bengio, Rejean Ducharme, Pascal Vincent, and Christian Janvin. A neural probabilistic ´ language model. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 3:1137–1155, March 2003. ISSN 1532-4435.
William Chan, Navdeep Jaitly, Quoc Le, and Oriol Vinyals. Listen, attend and spell: A neural network for large vocabulary conversational speech recognition. In 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 4960–4964, March 2016.
Kyunghyun Cho, Bart Van Merrienboer, Caglar Gulcehre, Dzmitry Bahdanau, Fethi Bougares, Hol- ¨ ger Schwenk, and Yoshua Bengio. Learning phrase representations using rnn encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2014.
Jan K Chorowski, Dzmitry Bahdanau, Dmitriy Serdyuk, Kyunghyun Cho, and Yoshua Bengio.
Attention-based models for speech recognition. In C. Cortes, N. D. Lawrence, D. D. Lee, M. Sugiyama, and R. Garnett (eds.), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28, pp. 577–585. Curran Associates, Inc., 2015.
Yuchen Fan, Yao Qian, Frank K. Soong, and Lei He. Multi-speaker modeling and speaker adaptation for dnn-based tts synthesis. In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 4475–4479, April 2015.
Alex Graves. Practical variational inference for neural networks. In J. Shawe-taylor, R.s. Zemel, P. Bartlett, F.c.n. Pereira, and K.q. Weinberger (eds.), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 24, pp. 2348–2356. 2011.
Alex Graves. Generating sequences with recurrent neural networks. 08 2013. URL https:
//arxiv.org/abs/1308.0850.
Alex Graves. Hallucination with recurrent neural networks, 2015. URL https://www.
youtube.com/watch?v=-yX1SYeDHbg.
Alex Graves and Navdeep Jaitly. Towards end-to-end speech recognition with recurrent neural networks. In Tony Jebara and Eric P. Xing (eds.), Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-14), pp. 1764–1772. JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings,2014.
Alex Graves, Greg Wayne, and Ivo Danihelka. Neural turing machines. 10 2014. URL https:
//arxiv.org/abs/1410.5401.
Andrew J Hunt and Alan W Black. Unit selection in a concatenative speech synthesis system using a large speech database. In Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1996. ICASSP-96. Conference Proceedings., 1996 IEEE International Conference on, volume 1, pp. 373–376. IEEE,1996.
Zeyu Jin, Adam Finkelstein, Stephen DiVerdi, Jingwan Lu, and Gautham J Mysore. Cute: A concatenative method for voice conversion using exemplar-based unit selection. In Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2016 IEEE International Conference on, pp. 5660–5664. IEEE,2016.
Alexander Rosenberg Johansen, Jonas Meinertz Hansen, Elias Khazen Obeid, Casper Kaae
Sønderby, and Ole Winther. Neural machine translation with characters and hierarchical encoding. 10 2016. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.06550.
Geoffrey Zweig Kaisheng Yao. Sequence-to-sequence neural net models for grapheme-to-phoneme conversion. ISCA - International Speech Communication Association, May 2015.
Simon King. Measuring a decade of progress in text-to-speech. Loquens, 1(1), 1 2014. ISSN 2386-2637.
Diederik P. Kingma and Jimmy Ba. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2015.
Bo Li and Heiga Zen. Multi-language multi-speaker acoustic modeling for lstm-rnn based statistical parametric speech synthesis. 2016.
Zhen-Hua Ling, Shiyin Kang, Heiga Zen, Andrew Senior, Mike Schuster, Xiao-Jun Qian, Helen Meng, and Li Deng. Deep learning for acoustic modeling in parametric speech generation: A systematic review of existing techniques and future trends. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 32:35–52, 2015.
Soroush Mehri, Kundan Kumar, Ishaan Gulrajani, Rithesh Kumar, Shubham Jain, Jose Sotelo, Aaron Courville, and Yoshua Bengio. Samplernn: An unconditional end-to-end neural audio generation model. 12 2016. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.07837.
Volodymyr Mnih, Nicolas Heess, Alex Graves, and Koray Kavukcuoglu. Recurrent models of visual attention. In Z. Ghahramani, M. Welling, C. Cortes, N.d. Lawrence, and K.q. Weinberger (eds.), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27, pp. 2204–2212. Curran Associates, Inc., 2014.
Masanori Morise, Fumiya Yokomori, and Kenji Ozawa. World: A vocoder-based high-quality speech synthesis system for real-time applications. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, E99.D(7):1877–1884, 2016.
Luis A. Pineda, Hayde Castellanos, Javier Cuetara, Lucian Galescu, Janet Ju ´ arez, Joaquim Llisterri, ´Patricia Perez, and Luis Villase ´ nor. The corpus dimex100: Transcription and evaluation. ˜ Lang. Resour. Eval., 44(4):347–370, December 2010.
Kanishka Rao, Fuchun Peng, Hasim Sak, and Francoise Beaufays. Grapheme-to-phoneme conversion using long short-term memory recurrent neural networks. In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 4225–4229, April 2015. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2015.7178767.
Ilya Sutskever, Oriol Vinyals, and Quoc Le. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In Z. Ghahramani, M. Welling, C. Cortes, N.d. Lawrence, and K.q. Weinberger (eds.), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27, pp. 3104–3112. Curran Associates, Inc., 2014.
Paul Taylor. Text-to-Speech Synthesis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2009.
Theano Development Team. Theano: A Python framework for fast computation of mathematical expressions. arXiv e-prints, abs/1605.02688, May 2016. URL http://arxiv.org/abs/ 1605.02688.
Keiichi Tokuda and Heiga Zen. Directly modeling speech waveforms by neural networks for statistical parametric speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 4215–4219, 2015.
Keiichi Tokuda and Heiga Zen. Directly modeling voiced and unvoiced components in speech waveforms by neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 5640–5644, 2016.
Keiichi Tokuda, Yoshihiko Nankaku, Tomoki Toda, Heiga Zen, Junichi Yamagishi, and Keiichiro Oura. Speech synthesis based on hidden markov models. Proceedings of the IEEE, 101(5): 1234–1252, May 2013. ISSN 0018-9219.
Aaron van den Oord, Sander Dieleman, Heiga Zen, Karen Simonyan, Oriol Vinyals, Alex Graves, Nal Kalchbrenner, Andrew Senior, and Koray Kavukcuoglu. Wavenet: A generative model for raw audio. 09 2016. URL https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.03499.
Bart van Merrienboer, Dzmitry Bahdanau, Vincent Dumoulin, Dmitriy Serdyuk, David Warde- ¨Farley, Jan Chorowski, and Yoshua Bengio. Blocks and fuel: Frameworks for deep learning. CoRR, abs/1506.00619, 2015. URL http://arxiv.org/abs/1506.00619.
Zhizheng Wu, Pawel Swietojanski, Christophe Veaux, Steve Renals, and Simon King. A study of speaker adaptation for dnn-based speech synthesis. In INTERSPEECH, pp. 879–883. ISCA, 2015.
Zhizheng Wu, Oliver Watts, and Simon King. Merlin: An Open Source Neural Network Speech
Synthesis System. 7 2016.
Kelvin Xu, Jimmy Ba, Ryan Kiros, Kyunghyun Cho, Aaron Courville, Ruslan Salakhudinov, Rich Zemel, and Yoshua Bengio. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In David Blei and Francis Bach (eds.), Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-15), pp. 2048–2057. JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, 2015.
Junichi Yamagishi. English multi-speaker corpus for cstr voice cloning toolkit, 2012. URL http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/jyamagis/page3/page58/page58.html.
Heiga Zen. An example of context-dependent label format for hmm-based speech synthesis in english, 2006. URL http://hts.sp.nitech.ac.jp/?Download.
Heiga Zen. Acoustic modeling in statistical parametric speech synthesis - from hmm to lstm-rnn. In Proc. MLSLP, 2015. Invited paper.
Heiga Zen, Keiichi Tokuda, and Alan W Black. Statistical parametric speech synthesis. Speech Communication, 51(11):1039–1064, 2009.
Heiga Zen, Andrew Senior, and Mike Schuster. Statistical parametric speech synthesis using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 7962–7966, 2013.
Heiga Zen, Yannis Agiomyrgiannakis, Niels Egberts, Fergus Henderson, and Przemysław Szczepaniak. Fast, compact, and high quality lstm-rnn based statistical parametric speech synthesizers for mobile devices. In Proc. Interspeech, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016.