pcl 官网该教程
本教程旨在解释如何基于pcl_recognition模块执行3D对象识别。 具体来说,它解释了如何使用对应分组算法,以便将在3D描述符匹配阶段之后获得的点对点对应集合聚类到当前场景中存在的模型实例中。 对于表示场景中可能的模型实例的每个聚类,对应分组算法还输出识别当前场景中该模型的6DOF姿态估计的变换矩阵。
关于输入一个具体的物体的点云,从场景中找出与该物体点云相匹配的,这种方法可以用来抓取指定的物体等等,代码说明:
-
对模型点云、场景点云分别进行下采样,得到稀疏关键点;
-
对模型点云、场景点云关键点,分别计算描述子;
-
利用KdTreeFLANN搜索对应点对;
-
使用【对应点聚类算法】将【对应点对】聚类为待识别模型;
-
返回识别到的每一个模型的变换矩阵(旋转矩阵+平移矩阵),以及对应点对聚类结果
具体代码:
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/correspondence.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d_omp.h>
#include <pcl/features/shot_omp.h>
#include <pcl/features/board.h>
#include <pcl/keypoints/uniform_sampling.h>
#include <pcl/recognition/cg/hough_3d.h>
#include <pcl/recognition/cg/geometric_consistency.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/impl/kdtree_flann.hpp>
#include <pcl/common/transforms.h>
#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZRGBA PointType;
typedef pcl::Normal NormalType;
typedef pcl::ReferenceFrame RFType;
typedef pcl::SHOT352 DescriptorType;
std::string model_filename_;
std::string scene_filename_;
//Algorithm params
bool show_keypoints_ (false);
bool show_correspondences_ (false);
bool use_cloud_resolution_ (false);
bool use_hough_ (true);
float model_ss_ (0.01f);
float scene_ss_ (0.03f);
float rf_rad_ (0.015f);
float descr_rad_ (0.02f);
float cg_size_ (0.01f);
float cg_thresh_ (5.0f);
void
showHelp (char *filename)
{
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "***************************************************************************" << std::endl;
std::cout << "* *" << std::endl;
std::cout << "* Correspondence Grouping Tutorial - Usage Guide *" << std::endl;
std::cout << "* *" << std::endl;
std::cout << "***************************************************************************" << std::endl << std::endl;
std::cout << "Usage: " << filename << " model_filename.pcd scene_filename.pcd [Options]" << std::endl << std::endl;
std::cout << "Options:" << std::endl;
std::cout << " -h: Show this help." << std::endl;
std::cout << " -k: Show used keypoints." << std::endl;
std::cout << " -c: Show used correspondences." << std::endl;
std::cout << " -r: Compute the model cloud resolution and multiply" << std::endl;
std::cout << " each radius given by that value." << std::endl;
std::cout << " --algorithm (Hough|GC): Clustering algorithm used (default Hough)." << std::endl;
std::cout << " --model_ss val: Model uniform sampling radius (default 0.01)" << std::endl;
std::cout << " --scene_ss val: Scene uniform sampling radius (default 0.03)" << std::endl;
std::cout << " --rf_rad val: Reference frame radius (default 0.015)" << std::endl;
std::cout << " --descr_rad val: Descriptor radius (default 0.02)" << std::endl;
std::cout << " --cg_size val: Cluster size (default 0.01)" << std::endl;
std::cout << " --cg_thresh val: Clustering threshold (default 5)" << std::endl << std::endl;
}
void
parseCommandLine (int argc, char *argv[])
{
//Show help
if (pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-h"))
{
showHelp (argv[0]);
exit (0);
}
//Model & scene filenames
std::vector<int> filenames;
filenames = pcl::console::parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".pcd");
if (filenames.size () != 2)
{
std::cout << "Filenames missing.\n";
showHelp (argv[0]);
exit (-1);
}
model_filename_ = argv[filenames[0]];
scene_filename_ = argv[filenames[1]];
//Program behavior
if (pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-k"))//可视化构造对应点时用到的关键点
{
show_keypoints_ = true;
}
if (pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-c"))//可视化支持实例假设的对应点对
{
show_correspondences_ = true;
}
if (pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-r"))//计算点云的分辨率和多样性
{
use_cloud_resolution_ = true;
}
std::string used_algorithm;
if (pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--algorithm", used_algorithm) != -1)
{
if (used_algorithm.compare ("Hough") == 0)
{
use_hough_ = true;
}else if (used_algorithm.compare ("GC") == 0)
{
use_hough_ = false;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Wrong algorithm name.\n";
showHelp (argv[0]);
exit (-1);
}
}
//General parameters
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--model_ss", model_ss_);
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--scene_ss", scene_ss_);
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--rf_rad", rf_rad_);
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--descr_rad", descr_rad_);
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--cg_size", cg_size_);
pcl::console::parse_argument (argc, argv, "--cg_thresh", cg_thresh_);
}
double
computeCloudResolution (const pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::ConstPtr &cloud)
{
double res = 0.0;
int n_points = 0;
int nres;
std::vector<int> indices (2);
std::vector<float> sqr_distances (2);
pcl::search::KdTree<PointType> tree;
tree.setInputCloud (cloud);
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->size (); ++i)
{
if (! pcl_isfinite ((*cloud)[i].x))
{
continue;
}
//Considering the second neighbor since the first is the point itself.
nres = tree.nearestKSearch (i, 2, indices, sqr_distances);
if (nres == 2)
{
res += sqrt (sqr_distances[1]);
++n_points;
}
}
if (n_points != 0)
{
res /= n_points;
}
return res;
}
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
parseCommandLine (argc, argv);
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr model (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType> ()); //模型点云
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr model_keypoints (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType> ()); //模型角点
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr scene (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType> ()); //目标点云
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr scene_keypoints (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType> ()); //目标角点
pcl::PointCloud<NormalType>::Ptr model_normals (new pcl::PointCloud<NormalType> ()); //法线
pcl::PointCloud<NormalType>::Ptr scene_normals (new pcl::PointCloud<NormalType> ()); //
pcl::PointCloud<DescriptorType>::Ptr model_descriptors (new pcl::PointCloud<DescriptorType> ()); //描述子
pcl::PointCloud<DescriptorType>::Ptr scene_descriptors (new pcl::PointCloud<DescriptorType> ());
//
// Load clouds
//
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile (model_filename_, *model) < 0)
{
std::cout << "Error loading model cloud." << std::endl;
showHelp (argv[0]);
return (-1);
}
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile (scene_filename_, *scene) < 0)
{
std::cout << "Error loading scene cloud." << std::endl;
showHelp (argv[0]);
return (-1);
}
//
// Set up resolution invariance
//
if (use_cloud_resolution_)
{
float resolution = static_cast<float> (computeCloudResolution (model));
if (resolution != 0.0f)
{
model_ss_ *= resolution;
scene_ss_ *= resolution;
rf_rad_ *= resolution;
descr_rad_ *= resolution;
cg_size_ *= resolution;
}
std::cout << "Model resolution: " << resolution << std::endl;
std::cout << "Model sampling size: " << model_ss_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "Scene sampling size: " << scene_ss_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "LRF support radius: " << rf_rad_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "SHOT descriptor radius: " << descr_rad_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "Clustering bin size: " << cg_size_ << std::endl << std::endl;
}
//
// Compute Normals:计算法线
//
pcl::NormalEstimationOMP<PointType, NormalType> norm_est;
norm_est.setNumberOfThreads(4); //手动设置线程数
norm_est.setKSearch (10); //设置k邻域搜索阈值为10个点
norm_est.setInputCloud (model); //设置输入模型点云
norm_est.compute (*model_normals);//计算点云法线
norm_est.setInputCloud (scene);
norm_est.compute (*scene_normals);
//
// Downsample Clouds to Extract keypoints:均匀采样点云并提取关键点
// 类UniformSampling实现对点云的统一重采样,具体通过建立点云的空间体素栅格,然后在此基础上实现下采样并且过滤一些数据。
// 所有采样后得到的点用每个体素内点集的重心近似,而不是用每个体素的中心点近似,前者速度较后者慢,但其估计的点更接近实际的采样面。
//
//pcl::PointCloud<int> sampled_indices;
pcl::UniformSampling<PointType> uniform_sampling;
uniform_sampling.setInputCloud (model); //输入点云
uniform_sampling.setRadiusSearch (model_ss_); //输入半径
//uniform_sampling.compute (sampled_indices);
//pcl::copyPointCloud (*model, sampled_indices.points, *model_keypoints);
uniform_sampling.filter(*model_keypoints); //滤波
std::cout << "Model total points: " << model->size () << "; Selected Keypoints: " << model_keypoints->size () << std::endl;
uniform_sampling.setInputCloud (scene);
uniform_sampling.setRadiusSearch (scene_ss_);
//uniform_sampling.compute (sampled_indices);
//pcl::copyPointCloud (*scene, sampled_indices.points, *scene_keypoints);
uniform_sampling.filter(*scene_keypoints);
std::cout << "Scene total points: " << scene->size () << "; Selected Keypoints: " << scene_keypoints->size () << std::endl;
//
// Compute Descriptor for keypoints:为关键点计算描述子
//
pcl::SHOTEstimationOMP<PointType, NormalType, DescriptorType> descr_est;
descr_est.setNumberOfThreads(4);
descr_est.setRadiusSearch (descr_rad_); //设置搜索半径
descr_est.setInputCloud (model_keypoints); //模型点云的关键点
descr_est.setInputNormals (model_normals); //模型点云的法线
descr_est.setSearchSurface (model); //模型点云
descr_est.compute (*model_descriptors); //计算描述子
descr_est.setInputCloud (scene_keypoints);
descr_est.setInputNormals (scene_normals);
descr_est.setSearchSurface (scene);
descr_est.compute (*scene_descriptors);
//
// Find Model-Scene Correspondences with KdTree:使用Kdtree找出 Model-Scene 匹配点
//
pcl::CorrespondencesPtr model_scene_corrs (new pcl::Correspondences ());
pcl::KdTreeFLANN<DescriptorType> match_search; //设置配准方式
match_search.setInputCloud (model_descriptors);//模型点云的描述子
//每一个场景的关键点描述子都要找到模板中匹配的关键点描述子并将其添加到对应的匹配向量中。
for (size_t i = 0; i < scene_descriptors->size (); ++i)
{
std::vector<int> neigh_indices (1); //设置最近邻点的索引
std::vector<float> neigh_sqr_dists (1);//设置最近邻平方距离值
if (!pcl_isfinite (scene_descriptors->at (i).descriptor[0])) //忽略 NaNs点
{
continue;
}
int found_neighs = match_search.nearestKSearch (scene_descriptors->at (i), 1, neigh_indices, neigh_sqr_dists);
if(found_neighs == 1 && neigh_sqr_dists[0] < 0.25f) //仅当描述子与临近点的平方距离小于0.25(描述子与临近的距离在一般在0到1之间)才添加匹配
{
//neigh_indices[0]给定点,i是配准数neigh_sqr_dists[0]与临近点的平方距离
pcl::Correspondence corr (neigh_indices[0], static_cast<int> (i), neigh_sqr_dists[0]);
model_scene_corrs->push_back (corr);//把配准的点存储在容器中
}
}
std::cout << "Correspondences found: " << model_scene_corrs->size () << std::endl;
//
// Actual Clustering:实际的配准方法的实现
//
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4f, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4f> > rototranslations;
std::vector<pcl::Correspondences> clustered_corrs;
// 使用 Hough3D算法寻找匹配点
if (use_hough_)
{
//
// Compute (Keypoints) Reference Frames only for Hough
//
//利用hough算法时,需要计算关键点的局部参考坐标系(LRF)
pcl::PointCloud<RFType>::Ptr model_rf (new pcl::PointCloud<RFType> ());
pcl::PointCloud<RFType>::Ptr scene_rf (new pcl::PointCloud<RFType> ());
pcl::BOARDLocalReferenceFrameEstimation<PointType, NormalType, RFType> rf_est;
rf_est.setFindHoles (true);
rf_est.setRadiusSearch (rf_rad_);//估计局部参考坐标系时当前点的邻域搜索半径
rf_est.setInputCloud (model_keypoints);
rf_est.setInputNormals (model_normals);
rf_est.setSearchSurface (model);
rf_est.compute (*model_rf);
rf_est.setInputCloud (scene_keypoints);
rf_est.setInputNormals (scene_normals);
rf_est.setSearchSurface (scene);
rf_est.compute (*scene_rf);
// Clustering
pcl::Hough3DGrouping<PointType, PointType, RFType, RFType> clusterer;
clusterer.setHoughBinSize (cg_size_); //hough空间的采样间隔:0.01
clusterer.setHoughThreshold (cg_thresh_); //在hough空间确定是否有实例存在的最少票数阈值:5
clusterer.setUseInterpolation (true); //设置是否对投票在hough空间进行插值计算
clusterer.setUseDistanceWeight (false); //设置在投票时是否将对应点之间的距离作为权重参与计算
clusterer.setInputCloud (model_keypoints); //设置模型点云的关键点
clusterer.setInputRf (model_rf); //设置模型对应的局部坐标系
clusterer.setSceneCloud (scene_keypoints);
clusterer.setSceneRf (scene_rf);
clusterer.setModelSceneCorrespondences (model_scene_corrs);//设置模型与场景的对应点的集合
//clusterer.cluster (clustered_corrs);
clusterer.recognize (rototranslations, clustered_corrs); //结果包含变换矩阵和对应点聚类结果
}
else // Using GeometricConsistency:使用几何一致性性质
{
pcl::GeometricConsistencyGrouping<PointType, PointType> gc_clusterer;
gc_clusterer.setGCSize (cg_size_); //设置几何一致性的大小
gc_clusterer.setGCThreshold (cg_thresh_); //阈值
gc_clusterer.setInputCloud (model_keypoints);
gc_clusterer.setSceneCloud (scene_keypoints);
gc_clusterer.setModelSceneCorrespondences (model_scene_corrs);
//gc_clusterer.cluster (clustered_corrs);
gc_clusterer.recognize (rototranslations, clustered_corrs);
}
//
// Output results:找出输入模型是否在场景中出现
//
std::cout << "Model instances found: " << rototranslations.size () << std::endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < rototranslations.size (); ++i)
{
std::cout << "\n Instance " << i + 1 << ":" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Correspondences belonging to this instance: " << clustered_corrs[i].size () << std::endl;
//打印处相对于输入模型的旋转矩阵与平移矩阵
Eigen::Matrix3f rotation = rototranslations[i].block<3,3>(0, 0);
Eigen::Vector3f translation = rototranslations[i].block<3,1>(0, 3);
printf ("\n");
printf (" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", rotation (0,0), rotation (0,1), rotation (0,2));
printf (" R = | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", rotation (1,0), rotation (1,1), rotation (1,2));
printf (" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", rotation (2,0), rotation (2,1), rotation (2,2));
printf ("\n");
printf (" t = < %0.3f, %0.3f, %0.3f >\n", translation (0), translation (1), translation (2));
}
//
// Visualization
//
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer ("点云库PCL学习教程第二版-基于对应点聚类的3D模型识别");
viewer.addPointCloud (scene, "scene_cloud");//可视化场景点云
viewer.setBackgroundColor(255,255,255);
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr off_scene_model (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType> ());
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr off_scene_model_keypoints (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType> ());
if (show_correspondences_ || show_keypoints_)//可视化配准点
{
//We are translating the model so that it doesn't end in the middle of the scene representation
//对输入的模型进行旋转与平移,使其在可视化界面的中间位置
pcl::transformPointCloud (*model, *off_scene_model, Eigen::Vector3f (0,0,0), Eigen::Quaternionf (1, 0, 0, 0));
pcl::transformPointCloud (*model_keypoints, *off_scene_model_keypoints, Eigen::Vector3f (-1,0,0), Eigen::Quaternionf (1, 0, 0, 0));
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointType> off_scene_model_color_handler (off_scene_model, 0, 255, 0);
viewer.addPointCloud (off_scene_model, off_scene_model_color_handler, "off_scene_model");
}
if (show_keypoints_)//可视化关键点:蓝色
{
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointType> scene_keypoints_color_handler (scene_keypoints, 0, 0, 255);
viewer.addPointCloud (scene_keypoints, scene_keypoints_color_handler, "scene_keypoints");
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 5, "scene_keypoints");
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointType> off_scene_model_keypoints_color_handler (off_scene_model_keypoints, 0, 0, 255);
viewer.addPointCloud (off_scene_model_keypoints, off_scene_model_keypoints_color_handler, "off_scene_model_keypoints");
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 5, "off_scene_model_keypoints");
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < rototranslations.size (); ++i)
{
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr rotated_model (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType> ());
pcl::transformPointCloud (*model, *rotated_model, rototranslations[i]);//把model转化为rotated_model
std::stringstream ss_cloud;
ss_cloud << "instance" << i;
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointType> rotated_model_color_handler (rotated_model, 255, 0, 0);
viewer.addPointCloud (rotated_model, rotated_model_color_handler, ss_cloud.str ());
if (show_correspondences_)//显示配准连接线
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < clustered_corrs[i].size (); ++j)
{
std::stringstream ss_line;
ss_line << "correspondence_line" << i << "_" << j;
PointType& model_point = off_scene_model_keypoints->at (clustered_corrs[i][j].index_query);
PointType& scene_point = scene_keypoints->at (clustered_corrs[i][j].index_match);
// We are drawing a line for each pair of clustered correspondences found between the model and the scene
viewer.addLine<PointType, PointType> (model_point, scene_point, 0, 255, 0, ss_line.str ());
}
}
}
while (!viewer.wasStopped ())
{
viewer.spinOnce ();
}
return (0);
}
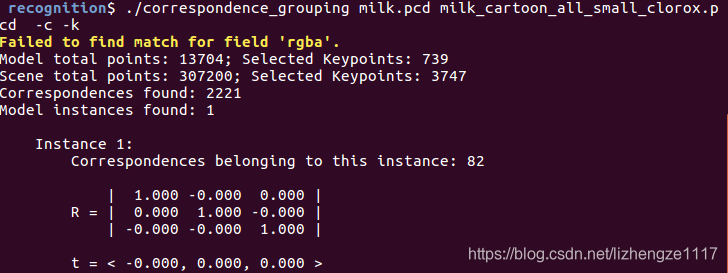
如果用书中带的pcd,加载milk_pose_changed.pcd时,会报“Failed to find match for field ‘rgba’.”因为这个文件中不包括rgba信息;可从官网下载原始文件:源文件github地址
命令行输入指令说明:
-k: 在源点云和场景点云中 显示关键点
-c: 显示对应点连线
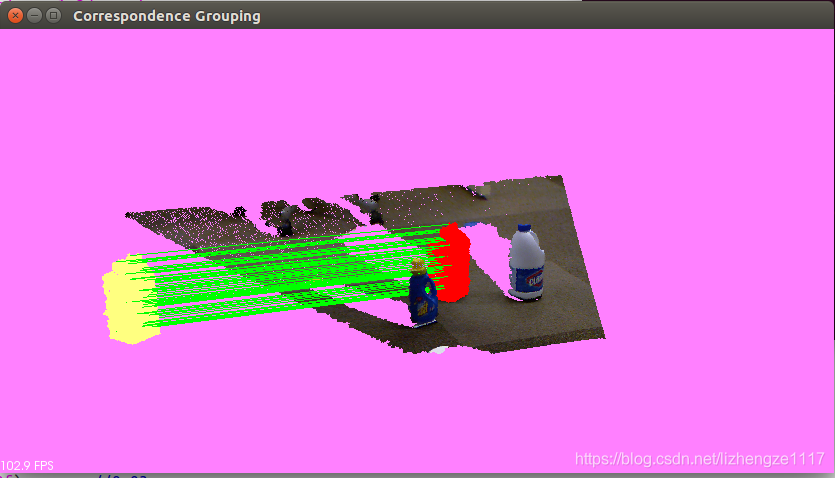
./correspondence_grouping milk.pcd milk_cartoon_all_small_clorox.pcd -c
效果显示如下
./correspondence_grouping milk.pcd milk_cartoon_all_small_clorox.pcd -c -k效果显示如下
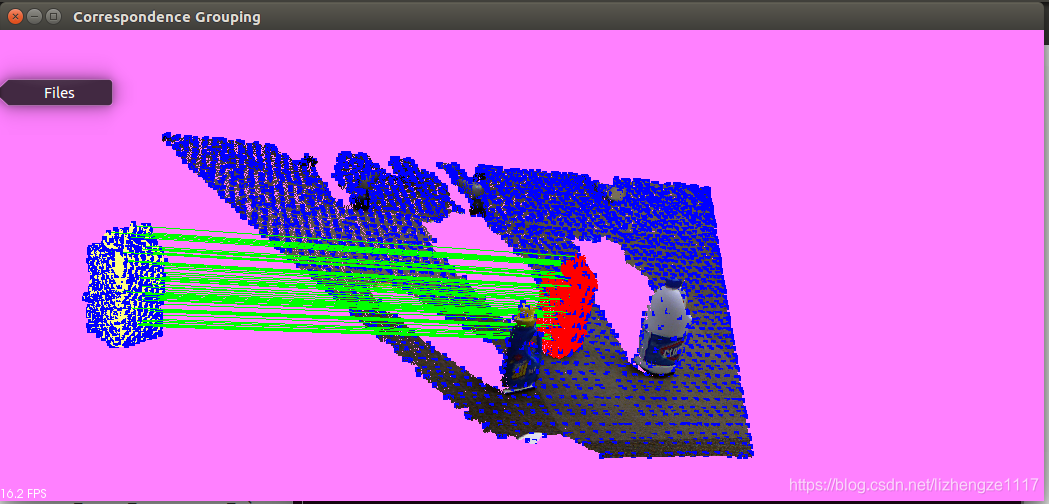
结果显示:关键点(蓝色),识别出的模型实例(红色),对应点对连接线(绿色) 源点云(黄色)
重点:为什么R和T的值都是原始值:因为 源点云和目标点云完全重合
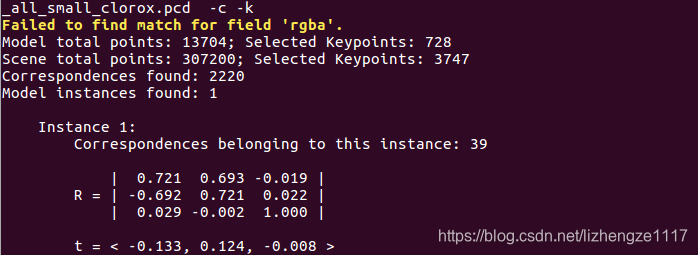
我们将源点云进行旋转平移后再匹配,结果如下
[pcl::SHOTEstimation::computeFeature] The local reference frame is not valid! Aborting description of point with index 3045
这个错误是由于正常半径较小的事实,一些法线是NaN(在设置半径的球体内它们的邻域中没有点),导致SHOT出现问题。
只需要把代码中的, 搜索半径改大点。
搜索半径改大点。
之后我尝试将源点云与多个相同点云进行 匹配,结果如下
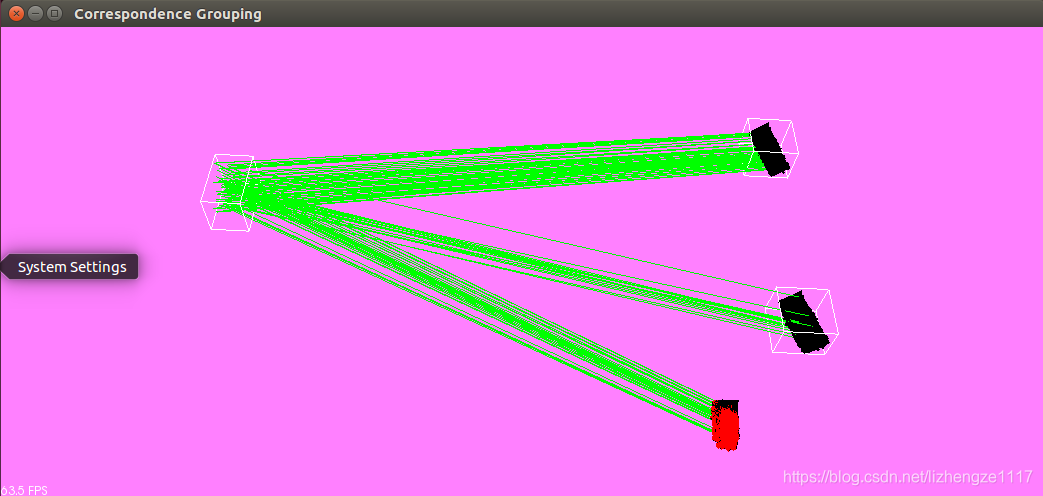

但是我用自己的数据集并没有实现点云匹配 正在修改参数中 ,哪位可以指点一下,谢谢
