文章目录
- 一:nginx动静分离介绍
- 1.1 nginx的静态处理能力很强,但是动态处理能力不足,因此,在企业中常用动静分离技术
- 1.2 针对PHP的动静分离
- 1.3 在nginx的配置中,是通过location配置段配合正则匹配实现静态与动态页面的不同处理方式
- 二:反向代理原理
- 2.1 nginx不仅能作为web服务器,还具有反向代理、负载均衡和缓存的功能
- 2.2 nginx通过proxy模块实现将客户端的请求代理至上服务器,此时nginx与上游服务器的链接是通过http协议进行的
- 2.3 nginx在实现反向代理功能时的最重要指令为proxy_pass,它能够并根据URI、客户端参数或其它的处理逻辑将用户请求调度至上游服务器
- 三:配置nginx实现动静分离
- 四:演示
前言:
部署nginx+apache动静分离
一:nginx动静分离介绍
1.1 nginx的静态处理能力很强,但是动态处理能力不足,因此,在企业中常用动静分离技术
1.2 针对PHP的动静分离
- 静态页面交给nginx处理
- 动态页面交给PHP-FPM模块或apache处理
1.3 在nginx的配置中,是通过location配置段配合正则匹配实现静态与动态页面的不同处理方式
二:反向代理原理
2.1 nginx不仅能作为web服务器,还具有反向代理、负载均衡和缓存的功能
2.2 nginx通过proxy模块实现将客户端的请求代理至上服务器,此时nginx与上游服务器的链接是通过http协议进行的
2.3 nginx在实现反向代理功能时的最重要指令为proxy_pass,它能够并根据URI、客户端参数或其它的处理逻辑将用户请求调度至上游服务器
三:配置nginx实现动静分离
3.1 本案例根据企业需要,将配置nginx实现动静分离,对php页面的请求转发给LAMP处理,而静态页面交给nginx处理,以实现动静分离
3.2 架构图演示

3.3 配置步骤
- 架设并调试后端LAMP环境
- 安装配置nginx处理静态页面请求,在server{};段中加入

- 配置nginx处理动态页面请求,在server{};中加入
- 在apache工作目录新建test.php
- 重启nginx并测试

总结:
nginx动静分离方法
- 静态页面交给nginx处理
- 动态页面交给php-fpm模块或apache处理
四:演示
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname nginx
[root@localhost ~]# su
[root@nginx ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname LAMP
[root@localhost ~]# su
[root@lamp ~]#
4.1 首先先设置lamp
4.2 先安装apache
安装httpd
[root@lamp ~]# yum install httpd httpd-devel -y
已安装:
httpd.x86_64 0:2.4.6-90.el7.centos httpd-devel.x86_64 0:2.4.6-90.el7.centos
开启服务,关闭防火墙
[root@lamp ~]# systemctl start httpd.service
[root@lamp ~]# systemctl enable httpd.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.
[root@lamp ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@lamp ~]# systemctl disable firewalld.service
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service.
[root@lamp ~]# setenforce 0
[root@lamp ~]#
//如果不关闭防火墙,则进行以下操作
[root@lamp ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
FirewallD is not running
[root@lamp ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
FirewallD is not running
[root@lamp ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
FirewallD is not running
查看ip
[root@lamp ~]# ifconfig
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.247.161 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.247.255
4.3 然后安装数据库mariadb
mariadb mysql的表兄弟
[root@lamp ~]# yum install mariadb mariadb-server mariadb-libs mariadb-devel -y
[root@lamp ~]# systemctl start mariadb.service
[root@lamp ~]# systemctl enable mariadb.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service.
[root@lamp ~]# netstat -natp | grep 3306
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4378/mysqld
[root@lamp ~]#
初始化数据库,一键式设定
[root@lamp ~]# mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] n
... skipping.
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] n
... skipping.
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] n
... skipping.
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
[root@lamp ~]#
4.4 安装php
[root@lamp ~]# yum install php -y
已安装:
php.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7
安装php与mysql的组件,建立php和mysql的关联
[root@lamp ~]# yum install php-mysql -y
已安装:
php-mysql.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7
安装php的插件
[root@lamp ~]# yum install -y php-gd php-ldap php-odbc php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-mbstring php-snmp php-soap curl curl-devel php-bcmath
已安装:
libcurl-devel.x86_64 0:7.29.0-54.el7_7.1 php-bcmath.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7
php-gd.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7 php-ldap.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7
php-mbstring.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7 php-odbc.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7
php-pear.noarch 1:1.9.4-21.el7 php-snmp.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7
php-soap.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7 php-xml.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7
php-xmlrpc.x86_64 0:5.4.16-46.1.el7_7
4.5 LAMP架构结束,配置网页站点
[root@lamp ~]# cd /var/www/html/
[root@lamp html]# ls
[root@lamp html]#
[root@lamp html]# vim index.php
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
[root@lamp html]# systemctl restart httpd.service
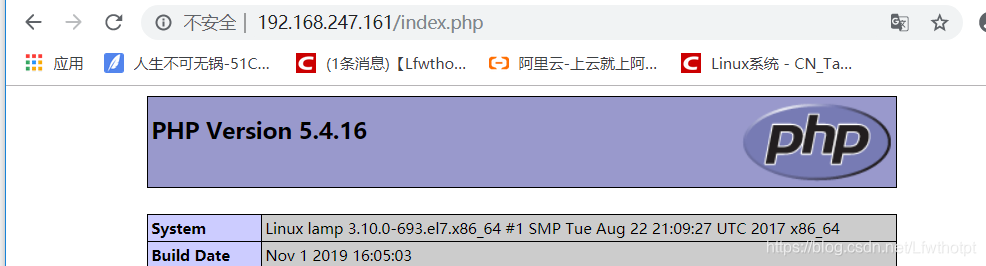
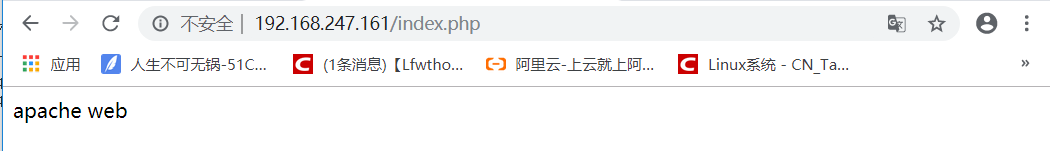
[root@lamp html]# vim index.php
<?php
echo "apache web"
?>
4.6 nginx
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /abc
[root@nginx ~]# mount.cifs //192.168.254.10/linuxs /abc
Password for root@//192.168.254.10/linuxs:
[root@nginx ~]# cd /abc/LNMP-C7/LNMP-C7/
[root@nginx LNMP-C7]# ls
Discuz_X3.4_SC_UTF8.zip php-7.1.10.tar.bz2
mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz php-7.1.20.tar.bz2
ncurses-5.6.tar.gz php-7.1.20.tar.gz
nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz zend-loader-php5.6-linux-x86_64_update1.tar.gz
php-5.6.11.tar.bz2
[root@nginx LNMP-C7]#
[root@nginx LNMP-C7]# tar zxvf nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz -C /opt
[root@nginx LNMP-C7]# cd /opt
[root@nginx opt]# ls
nginx-1.12.2 rh
[root@nginx opt]# useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
安装编译包
[root@nginx opt]# yum install pcre pcre-devel make zlib-devel gcc gcc-c++ -y
已安装:
gcc.x86_64 0:4.8.5-39.el7 gcc-c++.x86_64 0:4.8.5-39.el7
pcre-devel.x86_64 0:8.32-17.el7 zlib-devel.x86_64 0:1.2.7-18.el7
nginx配置属性
[root@nginx opt]# cd nginx-1.12.2/
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# ls
auto CHANGES.ru configure html man src
CHANGES conf contrib LICENSE README
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# ./configure \
--prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-http_stub_status_module
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# make && make install
在service中设置脚本启动程序
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# vim /etc/init.d/nginx
#!/bin/bash
# chkconfig: - 99 20
# description:Nginx Service Control Script
PROG="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
PIDF="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
case "$1" in
start)
$PROG
;;
stop)
kill -s QUIT $(cat $PIDF)
;;
restart)
$0 stop
$0 start
;;
reload)
kill -s HUP $(cat $PIDF)
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|reload}"
exit 1
esac
exit 0
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# chkconfig --add nginx
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# yum install elinks -y
开启服务
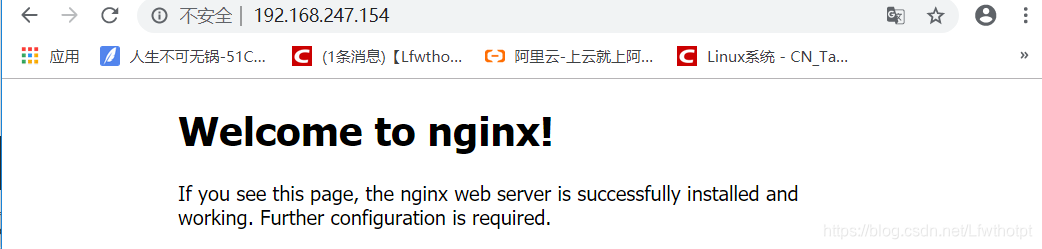
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# service nginx start
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# netstat -natp | grep 80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8875/nginx: master
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# systemctl disable firewalld.service
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service.
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# setenforce 0
查看ip
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# ifconfig
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.247.154 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.247.255

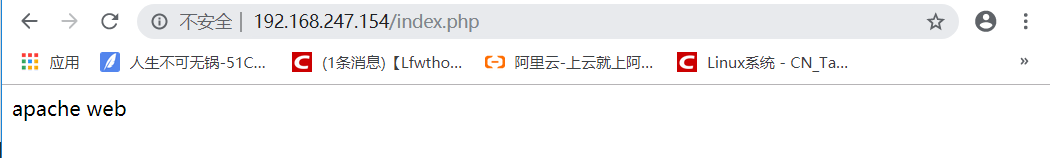
接下来开始做动静分离,把动态请求交给lamp
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
59 location ~ \.php$ {
60 proxy_pass http://192.168.247.161; //这里的ip地址指向LAMP地址
61 }
重启服务
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# service nginx stop
[root@nginx nginx-1.12.2]# service nginx start
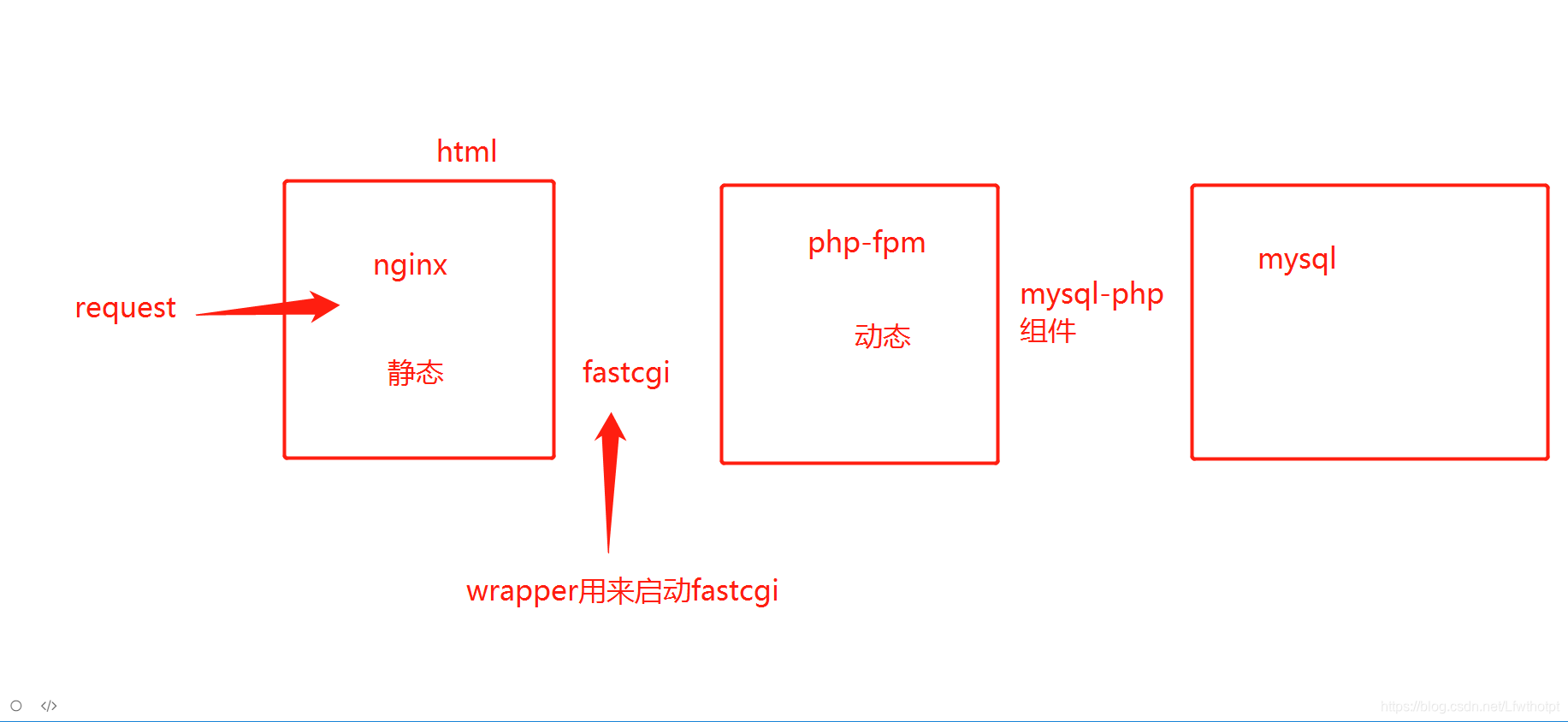
- Nginx 工作原理
Nginx 由内核和模块组成。
Nginx 本身做的工作实际很少,当它接到一个 HTTP 请求时, 它仅仅是通过查找配置文件将此次请求映射到一个 location block,而此 location 中所配 置的各个指令则会启动不同的模块去完成工作,因此模块可以看做 Nginx 真正的劳动工作者。
通常一个 location 中的指令会涉及一个 handler 模块和多个 filter 模块(当然,多个 location 可以复用同一个模块)。handler 模块负责处理请求,完成响应内容的生成,而 filter 模块对响应内容进行处理。 用户根据自己的需要所开发的模块都属于第三方模块。正是有了这么多模块的支撑, Nginx 的功能才会如此强大。
Nginx 的模块从结构上分为核心模块、基础模块和第三方模块:
核心模块:HTTP 模块、EVENT 模块和 MAIL 模块;
基础模块:HTTP Access 模块、HTTP FastCGI 模块、HTTP Proxy 模块和 HTTP Rewrite 模块;
第三方模块:HTTP Upstream Request Hash 模块、Notice 模块和 HTTP Access Key 模 块。
通用网关接口模块 fastcgi
反向代理模块 access
重写模块 rewrite
对请求进行哈希验证模块 upstream request
密钥模块 access key
handlers 核心处理模块
wrapper 是启动fastcgi 的程序
Nginx 的模块从功能上分为如下三类:
Handlers(处理器模块):此类模块直接处理请求,并进行输出内容和修改 headers 信息等操作。Handlers 处理器模块一般只能有一个;
Filters(过滤器模块):此类模块主要对其他处理器模块输出的内容进行修改操作,最后由 Nginx 输出;
Proxies(代理类模块):此类模块是 Nginx 的 HTTP Upstream 之类的模块,这些模块主要与后端一些服务比如 FastCGI 等进行交互,实现服务代理和负载均衡等功能。
- Nginx 的进程模型 在工作方式上,Nginx 分为单工作进程和多工作进程两种模式。
在单工作进程模式下,除主进程外,还有一个工作进程,工作进程是单线程的;
在多工作进程模式下,每个工作进程包含多个线程。Nginx 默认为单工作进程模式。
Nginx 在启动后,会有一个 master 进程和多个 worker 进程。
master 进程主要用来管理 worker 进程,主要包含:接收来自外界的信号,向各 worker 进程发送信号,监控 worker 进程的运行状态,当 worker 进程退出后(异常情况下),会自动 重新启动新的 worker 进程。 master 进程充当整个进程组与用户的交互接口,同时对进程进行监护。它不需要处理网络事件,不负责业务的执行,只会通过管理worker 进程来实现重启服务、平滑升级、更换日志文件、配置文件实时生效等功能。
- Nginx+FastCGI运行原理
Nginx 不支持对外部程序的直接调用或者解析,所有的外部程序(包括 PHP)必须通过FastCGI 接口来调用。FastCGI 接口在 Linux 下是 socket(这个 socket 可以是文件 socket, 也可以是 ip socket)。 wrapper 为了调用 CGI 程序,还需要一个 FastCGI 的 wrapper(wrapper 可以理解为用于启动另一个程序的程序),这个 wrapper 绑定在某个固定 socket 上,如端口或者文件 socket。当 Nginx 将 CGI 请求发送给这个 socket 的时候,通过 FastCGI 接口,wrapper 接收到请求,然后 Fork(派生)出一个新的线程,这个线程调用解释器或者外部程序处理脚本并读取返回数据;接着 wrapper 再将返回的数据通过 FastCGI 接口,沿着固定的 socket传递给 Nginx;最后 Nginx 将返回的数据(html 页面或者图片)发送给客户端。