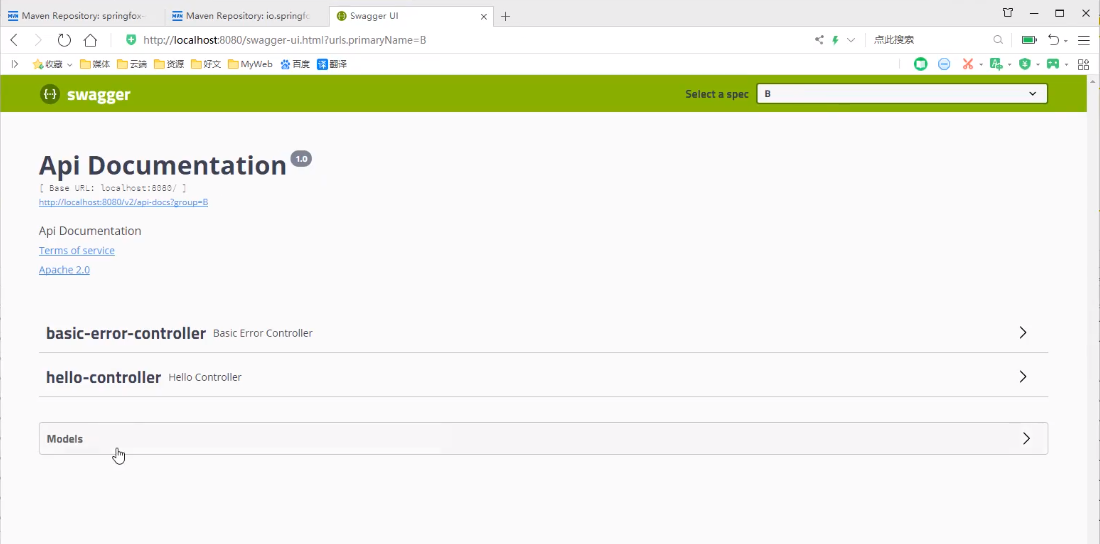
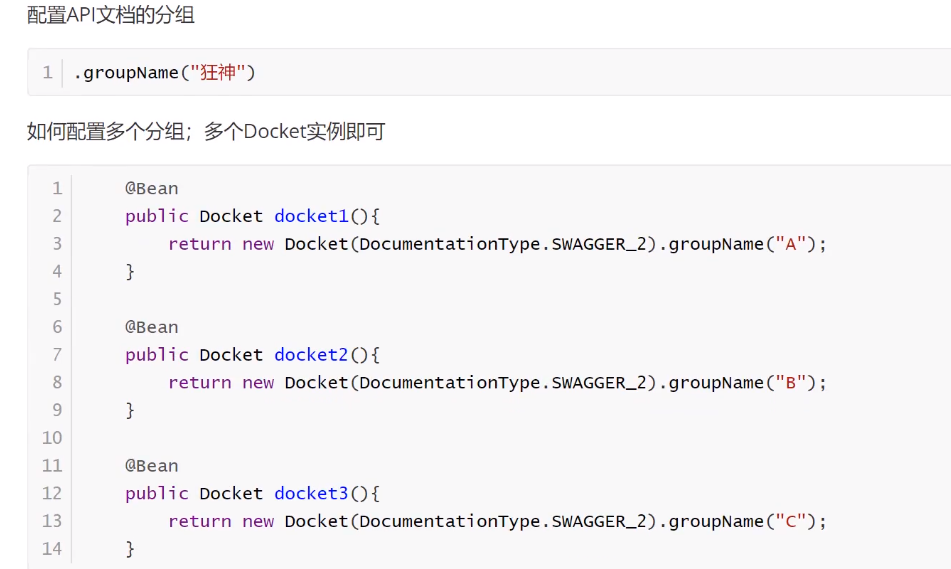
完整示例
代码结构
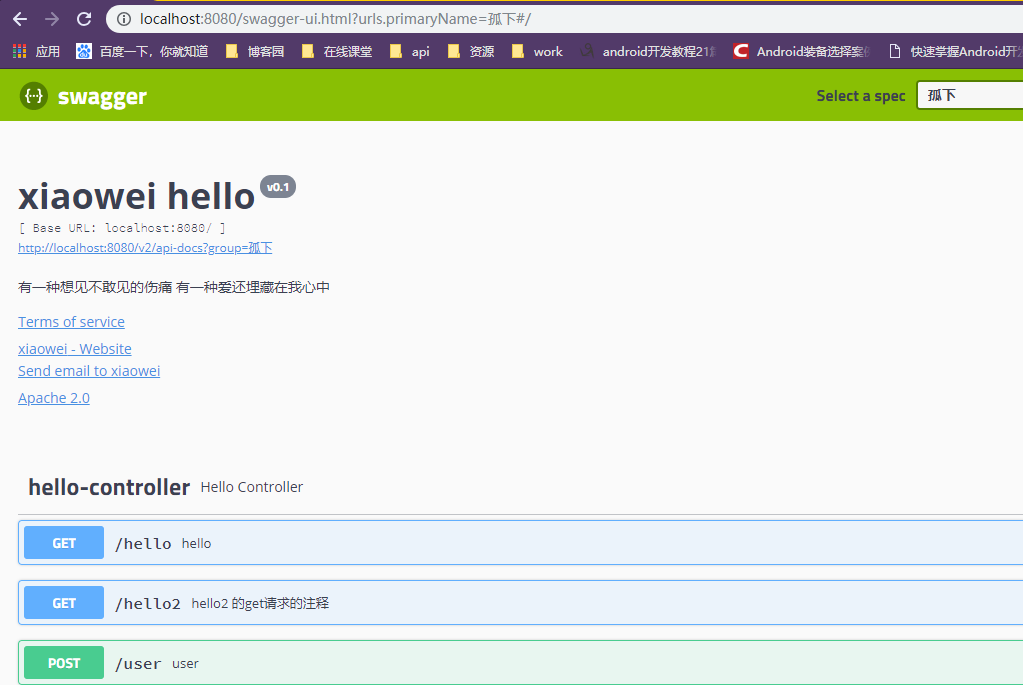
运行效果
SwaggerConfig.class
@Configuration //变成配置文件 @EnableSwagger2 //开启swagger2 public class SwaggerConfig { @Bean public Docket docket01(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .groupName("洒家"); } @Bean public Docket docket02(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .groupName("白水煮开一切"); } @Bean //配置swagger的docket的bean实例 public Docket docket(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .groupName("孤下") .enable(true) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller")) .build(); } //配置swagger信息的ApiInfo private ApiInfo apiInfo(){ //作者的联系方式 Contact contact = new Contact("xiaowei","https://www.baidu.com","[email protected]"); return new ApiInfo( "xiaowei hello", "有一种想见不敢见的伤痛 有一种爱还埋藏在我心中", "v0.1", "ttps://www.baidu.com", contact, "Apache 2.0", "http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0", new ArrayList() ); } }
HelloController.class
@RestController public class HelloController { @GetMapping(value = "/hello") public String hello(){ return "hello swagger"; } @ApiOperation("hello2 的get请求的注释") @GetMapping(value = "/hello2") public String hello2(String username){ return "hello"+username; } //只要我们的接口中,返回值中存在实体类,他就会被扫描到swagger中 @PostMapping(value = "/user") public User user(){ int i=5/0; return new User(); } @ApiOperation("user2 的post请求的注释") @PostMapping(value = "/user2") public User user2(@ApiParam("用户名") User user){ return user; } }
User.class
@ApiModel("用户实体类")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
public String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
public String password;
}