You are given nn arrays that can have different sizes. You also have a table with ww columns and nn rows. The ii-th array is placed horizontally in the ii-th row. You can slide each array within its row as long as it occupies several consecutive cells and lies completely inside the table.
You need to find the maximum sum of the integers in the jj-th column for each jj from 11 to ww independently.
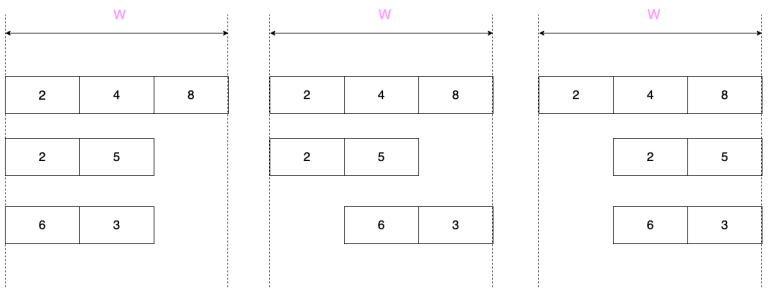 Optimal placements for columns 11, 22 and 33 are shown on the pictures from left to right.
Optimal placements for columns 11, 22 and 33 are shown on the pictures from left to right.
Note that you can exclude any array out of a column provided it remains in the window. In this case its value is considered to be zero.
The first line contains two integers nn (1≤n≤1061≤n≤106) and ww (1≤w≤1061≤w≤106) — the number of arrays and the width of the table.
Each of the next nn lines consists of an integer lili (1≤li≤w1≤li≤w), the length of the ii-th array, followed by lili integers ai1,ai2,…,ailiai1,ai2,…,aili (−109≤aij≤109−109≤aij≤109) — the elements of the array.
The total length of the arrays does no exceed 106106.
Print ww integers, the ii-th of them should be the maximum sum for column ii.
3 3 3 2 4 8 2 2 5 2 6 3
10 15 16
2 2 2 7 8 1 -8
7 8
Illustration for the first example is in the statement.
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef pair<int, int> pii; const int maxn = 1e6 + 10000; int n, w; vector<ll> e[maxn]; ll tag[maxn], tot[maxn]; int main() { //freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin); scanf("%d%d", &n, &w); for (register int i = 1, l; i <= n; ++i) { scanf("%d", &l); //e[i].resize(l + 100); e[i].emplace_back(0); ll x; for (register int j = 1; j <= l; ++j) { scanf("%lld", &x); e[i].emplace_back(x); } ll mx = max(*max_element(e[i].begin(), e[i].end()), 1ll * 0); //printf("debug mx = %d\n", mx); if (2 * l <= w) { ll head_max = 0; for (register int j = 1; j <= l; ++j) { head_max = max(head_max, e[i][j]); tot[j] += head_max; } ll tail_max = 0; for (register int j = l, cur = w; j >= 1; --j, --cur) { tail_max = max(tail_max, e[i][j]); tot[cur] += tail_max; } tag[l + 1] += mx; tag[w - l + 1] -= mx; } else { multiset<ll> cap; for (register int j = 1, k = 1; j <= w; ++j) { if (j <= l)cap.insert(e[i][j]); ll cur_max = *cap.rbegin(); if (j > l || j < w - l + 1)cur_max = max(cur_max, 1ll * 0); tot[j] += cur_max; //printf("debug k = %d\n",k); if (j - k + 1 == w - l + 1) { //printf("debug tot[%d] = %d\n",j,tot[j]); //if(cap.find(e[i][k])!=cap.end()){ cap.erase(cap.find(e[i][k])); ++k; //} } } } } ll cur = 0; for (register int i = 1; i <= w; ++i) { cur += tag[i]; printf("%lld%c", cur + tot[i], (i == w) ? '\n' : ' '); } return 0; }