3. 对上一篇博客的堆进行改造,使用户可以控制创建大堆还是小堆
typedef int (*PCOM)(HPDataType, HPDataType);
// 堆中元素进行小于比较
int Less(HPDataType left, HPDataType right);
// 堆中元素进行大于比较
int Greater(HPDataType left, HPDataType right);
typedef struct Heap
{
HPDataType* _array;
int _capacity;
int _size;
PCOM Compare; // 函数指针变量,保存用户传递的比较中堆中元素方法
}Heap;
void InitHeap(Heap* hp, HPDataType* array, int size, PCOM compare);
void InitEmptyHeap(Heap* hp, int capacity, PCOM compare);
void InsertHeap(Heap* hp, HPDataType data);
void EraseHeap(Heap* hp);
int HeapSize(Heap* hp);
int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp);
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp);
void DestroyHeap(Heap* hp);
4. 堆的应用
(1)用堆的思想进行排序,即堆排序,并分析其时间复杂度
(2)TOP K 问题
- 对上一篇博客的堆进行改造,使用户可以控制创建大堆还是小堆
直接上代码,注释及总结
Heap1.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#pragma once
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef int(*PCOM)(HPDataType, HPDataType);
// 堆中元素进行小于比较
int Less(HPDataType left, HPDataType right);
// 堆中元素进行大于比较
int Greater(HPDataType left, HPDataType right);
typedef struct Heap
{
HPDataType* _array;
int _size;
int _capacity;
PCOM Compare;
}Heap, *pHeap;
// 用数组初始化堆
void InitHeap(Heap* hp, HPDataType* array, int size, PCOM compare);
// 初始化一个空堆
void InitEmptyHeap(Heap* hp, int capacity, PCOM compare);
// 在堆中插入值为data的元素
void InsertHeap(Heap* hp, HPDataType data);
// 删除堆顶元素
void EraseHeap(Heap* hp);
// 获取堆中有效元素个数
int HeapSize(Heap* hp);
// 检测堆是否为空堆
int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp);
// 获取堆顶元素
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp);
// 销毁堆
void DestroyHeap(Heap* hp);
Heap1.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Heap1.h"
//建大堆/小堆
void Swap(HPDataType* pleft, HPDataType* pright)
{
HPDataType tmp = *pleft;
*pleft = *pright;
*pright = tmp;
}
// 堆中元素进行小于比较
int Less(HPDataType left, HPDataType right)
{
return left < right;
}
// 堆中元素进行大于比较
int Greater(HPDataType left, HPDataType right)
{
return left > right;
}
void adjustDown(HPDataType* array, int size, int parent, PCOM compare)//向下调整将所传节点(这次传的是根节点)排到相应位置
{
// 默认让child标记parent的左孩子,因为:完全二叉树某个节点如果只有一个孩子,该孩子一定是其双亲的左孩子
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < size)
{
//if (child + 1 < size && array[child + 1] > array[child])//要用同一个函数来表示大小关系,所以大小于号必须统一
if (child + 1 < size && compare(array[child + 1],array[child]))//建大堆向下调整时找两个孩子中较大的,小堆找较小的(牢记呀兄dei)
{
child += 1;
}
//if (array[child] > array[parent])
if (compare(array[child],array[parent]))
{
Swap(&array[child], &array[parent]);
parent = child;//parent 这一次是要调整根节点,根节点从上往下依次走,再去和下一个子节点进行比较进而判断是否调整
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
return;
}
}
void adjustUp(HPDataType* array, int size, int child, PCOM compare)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
//对比向下调整,不需要判断寻找较小的节点,因为根节点唯一
while (child)
{
//if (child < size && array[child] > array[parent])//注意:向上调整时child不需要和他的兄弟节点来比较
//重要:向上调整时,建大堆,child比parent根节点大的的话,向上调整交换,
//反之,建小堆的话,child比parent根节点小的的话,向上调整交换
if (child < size && compare(array[child], array[parent]))
{
Swap(&array[child], &array[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
return;
}
}
void checkCapacity(pHeap hp)
{
assert(hp);
if (hp->_size == hp->_capacity)
{
int newcapacity = hp->_capacity * 2;
// 申请新空间
HPDataType* ptmp = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType)* newcapacity);
if (NULL == ptmp)
{
assert(0);
return;
}
// 拷贝元素
for (int i = 0; i < hp->_size; ++i)
ptmp[i] = hp->_array[i];
// 释放旧空间
free(hp->_array);
hp->_array = ptmp;
hp->_capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
// 用数组初始化堆
void InitHeap(Heap* hp, HPDataType* array, int size, PCOM compare)//是要把array数组(大小是size)放进堆hp中使其初始化
//用数组初始化堆,传的是数组的大小size
{
assert(hp);
hp->_array = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType)* size);//牢记,初始化需要给堆里面的数组malloc
if (NULL == hp->_array)
{
assert(0);
return;
}
hp->_capacity = size;//数组直接就放满了
//需不需要循环?需要的
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
hp->_array[i] = array[i];
}
hp->_size = size;//数组直接就放满了
hp->Compare = compare;///////////////////////重点记忆,初始化需要给对中传递比较函数
//调整为堆
int root = (size - 2) >> 1;// 找完全二叉数中倒数第一个非叶子节点
for (; root >= 0; --root)
{
adjustDown(hp->_array, hp->_size, root, hp->Compare);//这里是向下调整
}
}
// 初始化一个空堆
void InitEmptyHeap(Heap* hp, int capacity, PCOM compare)//初始化空堆,传的是capacity,并不是size
{
assert(hp);
hp->_array = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType)* capacity);//只要初始化就需要开辟空间malloc
if (NULL == hp->_array)
{
assert(0);
return;
}
hp->_capacity = capacity;
hp->_size = 0;
hp->Compare = compare;
}
// 在堆中插入值为data的元素
void InsertHeap(Heap* hp, HPDataType data)
{
assert(hp);
checkCapacity(hp);
hp->_array[hp->_size] = data;
hp->_size++;
adjustUp(hp->_array, hp->_size, hp->_size - 1,hp->Compare);//什么时候向上调整,什么时候向下,向上向下的区别
//size是堆的大小,size-1是要调整的元素下标(这里是最后一个)
}
// 删除堆顶元素
void EraseHeap(Heap* hp)//为什么不直接删除最后一个元素?只能删除堆顶元素
{
assert(hp);
if (NULL == hp->_array)
return;
Swap(&hp->_array[0], &hp->_array[hp->_size - 1]);//交换堆顶元素和堆末尾元素
hp->_size--;//size往前走一个
adjustDown(hp->_array, hp->_size, 0,hp->Compare);//再将堆顶放的交换过去的堆末尾元素向下调整到对应位置
}
// 获取堆中有效元素个数
int HeapSize(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->_size;
}
// 检测堆是否为空堆
int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
//return NULL == hp->_array;
return 0 == hp->_size;//牢记:注意这两个的区别
//这里判空用size
}
// 获取堆顶元素
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->_array[0];
}
// 销毁堆
void DestroyHeap(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
if (hp->_array)
{
free(hp->_array);
hp->_capacity = 0;
hp->_size = 0; //是需要的,不能忘
//DestroyHeap 不需要管hp->Compare
}
}
void TestHeap()
{
Heap hp;
int array[] = { 2, 3, 8, 0, 9, 1, 7, 4, 6, 5 };
//InitHeap(&hp, array, sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]), Less);
InitHeap(&hp, array, sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]),Greater);
printf("%d\n", HeapSize(&hp));
printf("%d\n", HeapTop(&hp));
EraseHeap(&hp);
printf("%d\n", HeapTop(&hp));
InsertHeap(&hp, 0);
printf("%d\n", HeapTop(&hp));
DestroyHeap(&hp);
}
int main()
{
TestHeap();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
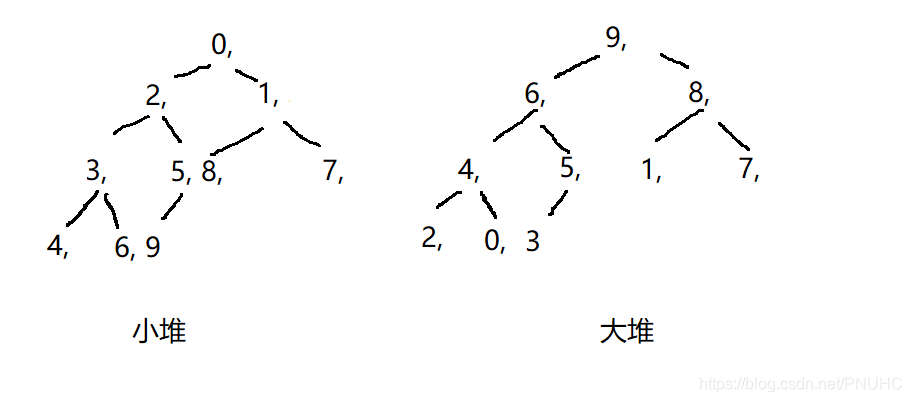
输出结果画图得到相应的大小堆:
4. 堆的应用
(1)用堆的思想进行排序,即堆排序,并分析其时间复杂度
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//建小堆降序
void Swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
//向下调整法
void adjustdown(int* arr, int size, int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
if (parent < size)
{
while (child < size)//走到child = size - 1 的位置(堆末)
{
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child + 1] < arr[child])//用child保存两个孩子节点里面较小的
child += 1; //升序建大堆找较大的;降序建小堆找较小的
if (arr[parent] > arr[child])//别再忘了,要调整的节点比较小的大的话,交换 (我的错误之处)
//反之,建大堆升序的时候,要调整的节点比较大的小的话,交换
{
Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
return;
}
}
}
//建堆:升序建大堆,降序建小堆(这个函数中不影响)
void Heapsort(int* arr,int size)//小堆
{
int nleaf = (size - 2) >> 1;//找倒数第一个非叶节点
for (int i = nleaf; i >= 0; --i)//建小堆
adjustdown(arr, size, i);
for (int j = size - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
Swap(&arr[0], &arr[j]);//交换根节点和未排序部分数组最后一个的元素
adjustdown(arr, j, 0);//将根节点出的心交换过来的节点重新调整到相应位置
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 5, 9, 3, 7, 6, 2, 4, 0, 1, 8 };
Heapsort(arr, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
输出结果:
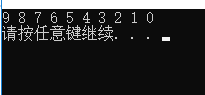
初始化建堆的时间复杂度为O(n),排序重建堆的时间复杂度为nlog(n),所以总的时间复杂度为O(n+nlogn)=O(nlogn)。
(2)TOP K 问题
建大堆找前k个最小的值
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
//建大堆找前k个最小的值
void Swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
void adjustdown(int* arr, int size, int parent)//建大堆
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
if (parent < size)
{
while (child < size)
{
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child] < arr[child + 1])//建大堆找里面较大的
child += 1;
if (arr[parent] < arr[child])//(建大堆)较大的比根节点大的话,交换 (建小堆)较小的比根节点小的话,交换
{
Swap(&arr[parent], &arr[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
return;
}
}
}
void topK(int* arr, int size, int k)
{
//int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
//取数组前k个元素建堆
int root = (k - 2) >> 1;//找倒数一个非叶节点
for (; root >= 0; --root)
adjustdown(arr, k, root);
//用剩余N-K个元素依次与堆顶元素进行比较,判断是否需要交换
for (int i = k; i < size; ++i)
{
if (arr[i] < arr[0])//滤一下
{
Swap(&arr[i], &arr[0]);
adjustdown(arr, k, 0);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 55, 99, 33, 22, 44, 88, 77, 11, 66, 5 };
topK(arr, 10, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
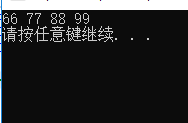
输出结果:
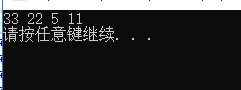
建小堆找前k个最大的值
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//建小堆找前k个最大的值
void Swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
//向下调整法
void adjustdown(int* arr, int size, int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
if (parent < size)
{
while (child < size)//走到child = size - 1 的位置(堆末)
{
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child + 1] < arr[child])//用child保存两个孩子节点里面较小的
child += 1; //升序建大堆找较大的;降序建小堆找较小的
if (arr[parent] > arr[child])//别再忘了,要调整的节点比较小的大的话,交换 (我的错误之处)
//反之,建大堆升序的时候,要调整的节点比较大的小的话,交换
{
Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
return;
}
}
}
//建堆:升序建大堆,降序建小堆(这个函数中不影响)
void Heapsort(int* arr, int size, int k)//小堆
{
int nleaf = (size - 2) >> 1;//找倒数第一个非叶节点
for (int i = nleaf; i >= 0; --i)//建小堆
adjustdown(arr, k, i);
//用剩余N-K个元素依次与堆顶元素进行比较,判断是否需要交换
for (int j = k; j < size; ++j)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[0])//滤一下
{
Swap(&arr[j], &arr[0]);
adjustdown(arr, k, 0);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 55, 99, 33, 22, 44, 88, 77, 11, 66, 5 };
//int arr[] = { 5, 9, 3, 7, 6, 2, 4, 0, 1, 8 };
Heapsort(arr, 10, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
输出结果: