核心代码:链接
范例:

package com.jdbc; import java.sql.*; public class Jdbc1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; Statement stmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; try {// 加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("建立连接失败"); } try {// 创建连接对象 conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello", "root", "123456"); stmt = conn.createStatement();// 创建sql操作对象 String name = "佩奇"; int health = 40; int love = 90; String strain = "哈士奇"; StringBuffer sbSql = new StringBuffer("insert into dog (name,health,love,strain) values ( '"); sbSql.append(name + "',"); sbSql.append(health + ","); sbSql.append(love + ",'"); sbSql.append(strain + "')"); // 打印拼接后的sql System.out.println(sbSql.toString()); stmt.execute(sbSql.toString()); // System.out.println("插入成功"); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("建立连接失败"); } finally { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
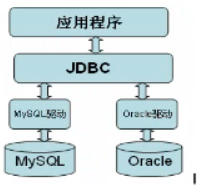
java database connectivity
回顾:
第一个标准代码:

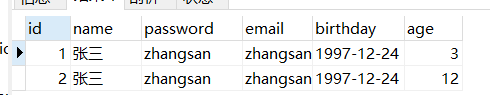
package com.test; //先在mysql里面执行 import java.sql.*; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import com.mysql.jdbc.Statement; public class TestJdbc { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection ct=null; Statement st=null; try { //1.加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.得到连接 ct=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello","root","123456"); //3.创建sql对象 st=(Statement) ct.createStatement(); //通过Statement发sql指令 //通过Statement向数据库发送指令 //n代表影响了几条 int n=st.executeUpdate("insert into user values(1,'张三','zhangsan','[email protected]','1997-12-24',12)");//update insert delete } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(st!=null){ try{ st.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } st=null; if(ct!=null){ try{ ct.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } ct=null; } }}//finally } }
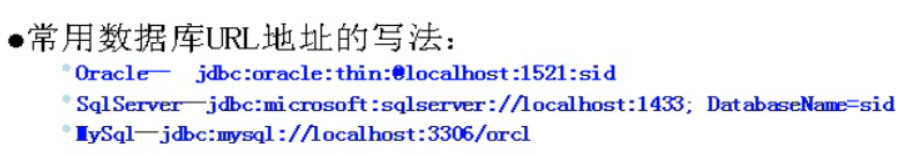
DriverManager用于加载驱动
Connection接口代表数据库的连接,客户端与数据库所有的交互

抛出异常的代码:

package com.test; //先在mysql里面执行 import java.sql.*; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import com.mysql.jdbc.Statement; public class TestJdbc { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection ct=null; Statement st=null; try { //1.加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.得到连接 ct=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello","root","123456"); //3.创建sql对象 st=(Statement) ct.createStatement(); //通过Statement发sql指令 //通过Statement向数据库发送指令 //n代表影响了几条 int n=st.executeUpdate("insert into user values(2,'张三','zhangsan','[email protected]','1997-12-24',12)");//update insert delete int t=1/0; st.executeUpdate("update user set age=8 where id=1;"); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(st!=null){ try{ st.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } st=null; if(ct!=null){ try{ ct.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } ct=null; } }}//finally } }
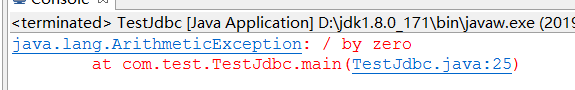
解决方法:将事务设置成不自动提交(未解决)
Connection ct=null;
输出连接ct 接口类的类型
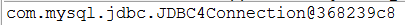
RsultSet表示sql语句执行的结果:
指向结果的前一行
st.executeQuery(sql) 查询功能
st.executeUpdate(sql) update insert delete功能
实现简单的查询功能

package com.test; //先在mysql里面执行 为啥回滚不行 import java.sql.*; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import com.mysql.jdbc.Statement; public class Jdbc1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection ct=null; Statement st=null; ResultSet rs=null; try { //1.加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.得到连接 ct=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello","root","123456"); //把事务设置成不自动提交 ct.setAutoCommit(false); System.out.println(ct); //3.创建sql对象 st=(Statement) ct.createStatement(); rs=st.executeQuery("select*from user"); while(rs.next()){ System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)+" "+rs.getString(2)); } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block //sql语句任何一行语句出错,可以整体回滚 e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(st!=null){ try{ st.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } st=null; if(ct!=null){ try{ ct.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } ct=null; } }}//finally } }
ResultSet详解:
复用:rs.beforeFirst();

package com.test; //先在mysql里面执行 为啥回滚不行 import java.sql.*; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import com.mysql.jdbc.Statement; public class Jdbc1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection ct=null; Statement st=null; ResultSet rs=null; try { //1.加载驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.得到连接 ct=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello","root","123456"); //把事务设置成不自动提交 ct.setAutoCommit(false); System.out.println(ct); //3.创建sql对象 st=(Statement) ct.createStatement(); rs=st.executeQuery("select*from user"); while(rs.next()){ System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)+" "+rs.getString(2)); } rs.beforeFirst(); System.out.println("复用"); while(rs.next()){ System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)+" "+rs.getString(2)); } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block //sql语句任何一行语句出错,可以整体回滚 e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(st!=null){ try{ st.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } st=null; if(ct!=null){ try{ ct.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } ct=null; } }}//finally } }
SqlHelper的书写:
1.访问数据库很频繁,Connection的话不要设置为static
2.
