详细代码可参考:github
多变量线性回归
实例:
已知房屋面积和卧室数量,预测房价 计算公式:Price = theta0*1 + theta1*square + theta2*num_houses
1.特征归一化
房间面积和卧室数量相差有2-3个数量级,如果直接利用梯度下降来计算的话,房屋面积可以让函数更快收敛,因此将两个特征进行归一化。
def featureNormalize(self):
mu = np.mean(self.x, axis=0)
sigma = np.std(self.x, axis=0, ddof=1) # 注意ddof参数,必须是1
self.x_norm = (self.x - mu)/sigma
self.x = np.hstack([np.ones((47, 1)), self.x_norm])
注意:每个特征都是一列,因此操作多是在列的基础上操作,参数axis=0, 同时注意np.std的使用,ddof参数尤其需要注意。
2. 梯度下降法计算theta
设置步长alpha = 0.01,迭代次数400次,此次损失函数使用向量形式表示:
在步长0.01的情况下,损失函数J的曲线,如下图所示。
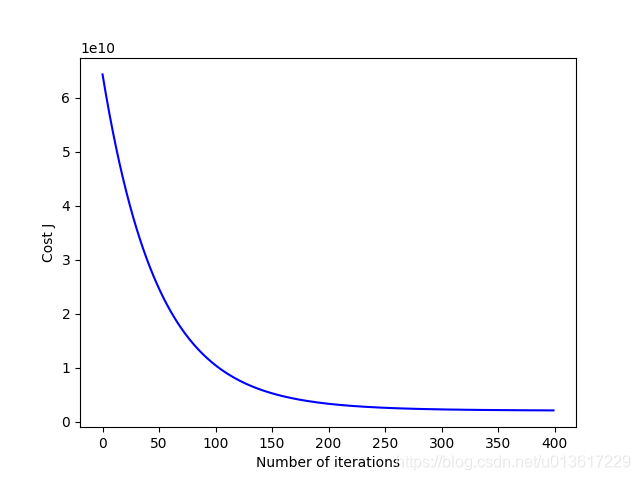
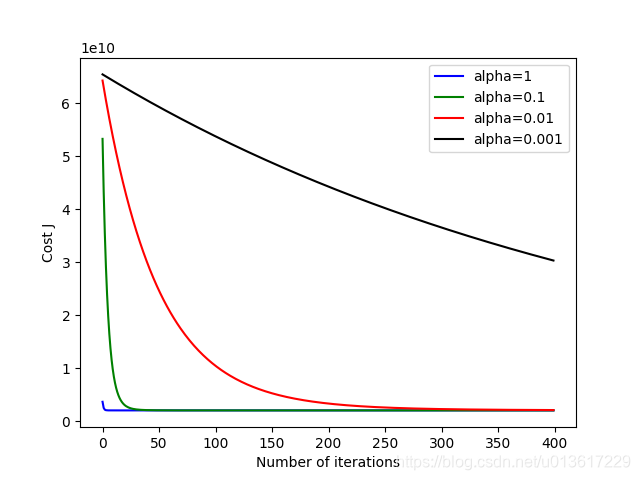
同时设置alpha = 0.001、0.01、0.1、1,见对比图,可以清晰的看出当alpha较大的时候,迅速收敛,而当alpha太小的时候,收敛速度又太慢,可以看出设置alpha=0.01最好。
参考代码:
def gradientDescentMulti(self):
m = len(self.y)
self.J_history = np.zeros((self.iters, 1))
for i in range(self.iters):
self.theta = self.theta-self.alpha/m*np.dot((np.dot(self.x, self.theta)-self.y).transpose(), self.x).transpose()
self.J_history[i] = self.computeCostMulti()
return self.theta
def convergenceGraph(self):
plt.plot([x for x in range(400)], self.J_history, 'b')
plt.xlabel('Number of iterations')
plt.ylabel('Cost J')
plt.show()
3.Normal Equations
线性回归中theta的计算也可以不使用梯度下降迭代来计算,使用Normal Equations,公式:
参考代码:
def normalEquations(self):
self.x = np.hstack([np.ones((47, 1)), self.x])
self.theta = np.dot(np.dot(np.mat(np.dot(self.x.T, self.x)).I, self.x.T), self.y)
print(self.theta)