线性模型的建模,运算过程,数据的展示,拟合结果的展示!
代码展示:
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def liner_regression():
#生成数据
n_object = 100
xs = np.linspace(-3,3,n_object)
ys = np.sin(xs) + np.random.uniform(-0.5,0.5,n_object)
plt.figure(figsize=[8,6])
plt.scatter(xs,ys)
plt.show()
#给数据建立placeholder
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name="X")
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name="Y")
#初始化权重和偏置
weight = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]),name="weight")
bias = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]),name="bias")
#进行求预测值
prediction = tf.add(tf.multiply(weight,X),bias)
#定义损失函数和优化器
loss = tf.square(Y-prediction)
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=1e-2).minimize(loss)
#初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
#定义session
with tf.Session() as sess:
#初始化,保存定义的运算图
sess.run(init)
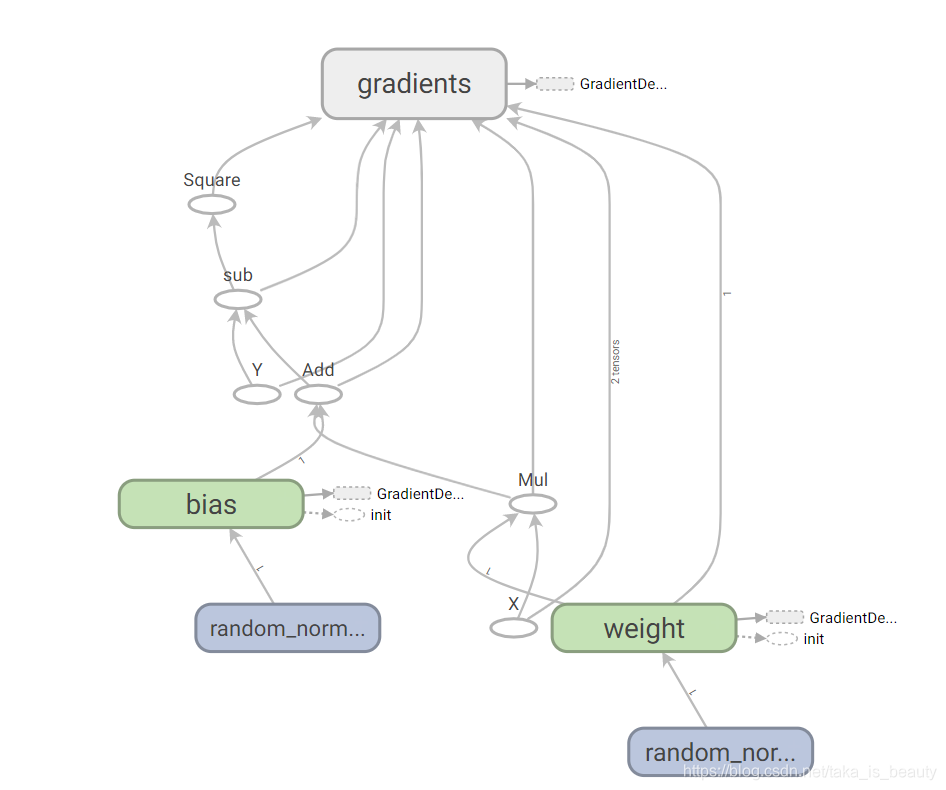
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./logs",sess.graph)
#定义迭代次数
for i in range(100):
#定义梯度下降的batch_size,SGD
loss_total = 0
for x, y in zip(xs,ys):
_,l = sess.run(fetches=[train,loss],feed_dict={X:x,Y:y})
loss_total+=l
loss_total/=xs.shape[0]
if i%5==0:
print("Iterator:{},loss:{}".format(i,loss_total))
writer.close()
w,b = sess.run([weight,bias])
print("最终的 W:{},b:{}".format(w,b))
#画图,展示结果
plt.figure(figsize=[10,8])
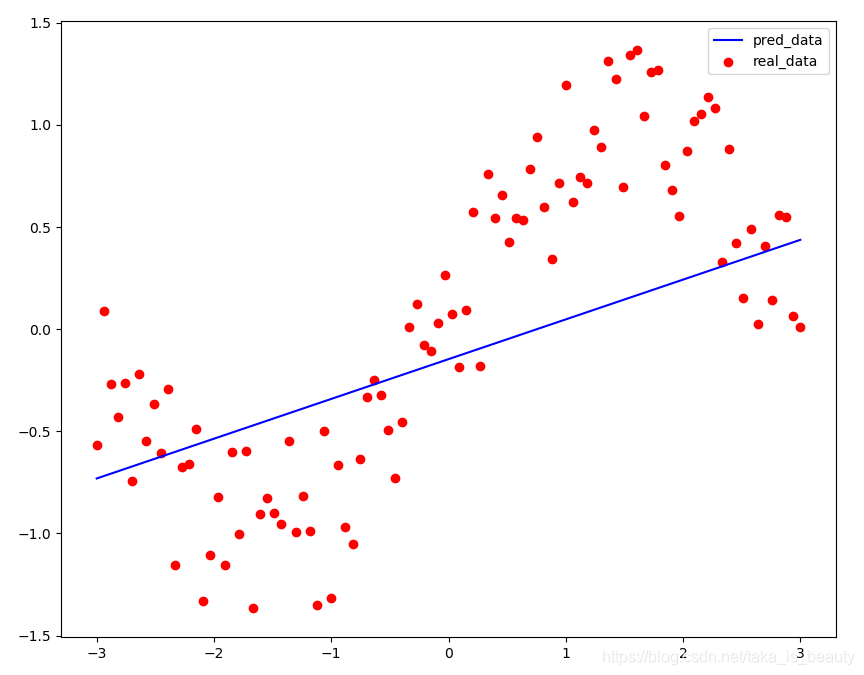
plt.scatter(xs,ys,label="real_data",c="r")
plt.plot(xs,w*xs+b,label="pred_data",c="b")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
return数据展示:(加入了噪声的结果)

效果展示:
在附上tensorboard的图模型:
上述代码使用了,梯度下降的优化方法,是因为我们的函数凹凸性特别好,可以收敛的,但是复杂一点的函数呢?
有任何问题都可指出说明,一定解答!!