写在最前面,我总结出了很多互联网公司的面试题及答案,并整理成了文档,以及各种学习的进阶学习资料,免费分享给大家。扫码加微信好友进【程序员面试学习交流群】,免费领取。也欢迎各位一起在群里探讨技术。
本文有些长,贴的源码较多,请各位看官自备花生瓜子啤酒饮料矿泉水小板凳,且听我慢慢道来。
Java面试都会问集合,集合必问HashMap,CurrentHashMap,后面的套路就肯定会问多线程、线程安全等等,今天就来学习下HashMap,不对,是补习下。
1、HasMap的属性
先看下HashMap的继承体系,它继承自抽象类AbstractMap,实现了Map、Cloneable、Serializable接口,还有较常用的子类LinkedHashMap也实现了Map接口。
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable{... public abstract class AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {... public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>{...
再看看HashMap的成员变量和一些默认值:
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // 默认的初始化数组大小,16 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // HashMap的最大长度 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 负载因子的默认值 static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {}; // Entry数组默认为空 transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE; // Entry数组 transient int size; // map中key-value 键值对的数量 int threshold; // 阈值,即table.length 乘 loadFactor final float loadFactor; //负载因子,默认值为 DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75 transient int modCount; // HashMap结构被修改的次数 static final int ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD_DEFAULT = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 阈值的默认值 HashMap.Holder.trasient int hashSeed; // 翻译过来叫哈希种子,是一个随机数, //它能够减小hashCode碰撞的几率,默认为0,表示不能进行选择性哈希(我也不知道是啥意思)
所以我们用默认构造方法new 出来的HashMap(),长度默认为16,阈值为12,并且size达到threshold,就会resize为原来的2倍。
再看下HashMap的一些重要的内部类:
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key; V value; Entry<K,V> next; int hash; Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) { value = v; next = n; key = k; hash = h; } }
Entry实现了Map的内部接口Entry,它有四个属性,key、value、Entry、hash,是HashMap内数组每个位置上真正存放元素的数据结构。
private final class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> { public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() { return newEntryIterator(); } public boolean contains(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<K,V> e = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o; Entry<K,V> candidate = getEntry(e.getKey()); return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e); } public boolean remove(Object o) { return removeMapping(o) != null; } public int size() { return size; } public void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); } }
EntrySet 继承了AbstractSet,它内部有个迭代器iterator,可以获取Entry对象,方法contains用来判断所给的对象是否包含在当前EntrySet中。
2、put、get、resize方法源码分析
我们知道HashMap,在jdk1.8之前底层用数组+链表实现的,jdk1.8改成了数组+链表+红黑树实现,以避免长链表带来的遍历效率低问题。
1)jdk1.7下的源码
1.1)put()方法
public V put(K key, V value) { if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { //(1) inflateTable(threshold); } if (key == null) //(2) return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key); //(3) int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { //(4) V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i); //(5) return null; } private V putForNullKey(V value) { for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(0, null, value, 0); return null; } static int indexFor(int h, int length) { // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2"; //长度必须是2的非零幂 return h & (length-1); //table数组的下标计算:hashCode与(table数组长度减一)做与(&)运算 } &运算,即同是1才为1,否则为0 例如:h1=3 h2=20 length=16 h1: 0011 h2: 10100 length-1: 1111 h1(index): 0011 = 3 h2(index): 0100 = 4 这样运算得出的index就是舍弃了hashCode一部分高位的hash的值
(1)首先判断数组若为空,则创建一个新的数组;
(2)如果key为null,遍历table数组,如果找出key=null的位置,将value覆盖,并返回旧的value,否则调用addEntry()将它保存到table[0]位置;
(3)若key!=null,则计算出hashCode,算出下标 index,遍历table
(4)若找到hashCode与当前key的hashCode相等,并且key值也相同,那就覆盖value的值,并且放回oldValue;
(5)若没满足(4)中的条件,则调用方法addEntry(...),下面仔细看下这个方法
若indexFor计算出来的下标在数组中不为空并且size达到阈值,则扩容,然后在index位置创建一个Entry,将key-value放进去。
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { resize(2 * table.length); hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; // null的hashCode为0 bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); } void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; }
1.2)get() 方法
public V get(Object key) { if (key == null) //(1) return getForNullKey(); Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key); return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue(); //(4) } private V getForNullKey() { //(2) if (size == 0) { return null; } for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) return e.value; } return null; } final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { //(3) if (size == 0) { return null; } int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } return null; }
get() 方法就比较简单啦:
(1) 如果key为null,则判断HashMap中是否有值,若没有直接返回null;
(2) 若有就遍历table数组,找到null对应的value并返回;
(3) 若key不为null,则获取Entry,也就是一个遍历table数组命中的过程;
(4) 最后获取Entry的value,并返回。
1.3)resize() 方法
void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { //(1) threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; //(2) transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); //(3) table = newTable; threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); }
(1)首先将当前对象的一些属性保存起来,如果当前HashMap的容量达到最大值,那就无法扩容了,将阈值设置为Integer的最大值并结束方法;
(2)否则创建新的Entry数组,长度为newCapacity,在addEntry()方法中,我们知道newCapacity = 2 * table.length;
(3)然后调用transfer()方法,此方法的作用是将当前数组中的Entry转移到新数组中;
在存入key-value时会调用initHashSeedAsNeeded()方法判断是否需要rehash,该方法的过程见注释,好吧,我也不知道为什么这样处理得出的结果就能 判断是否需要rehash,后面就是根据rehash重新计算下标,并将key-value存入新的table中。
/** * Transfers all entries from current table to newTable. */ void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } } } /** * Initialize the hashing mask value. We defer initialization until we really need it. */ final boolean initHashSeedAsNeeded(int capacity) { boolean currentAltHashing = hashSeed != 0; // 当前哈希种子是否为0 boolean useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() && (capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD); // 虚拟机是否启动,当前数组容量是否大于阈值 boolean switching = currentAltHashing ^ useAltHashing; // 做异或运算 if (switching) { hashSeed = useAltHashing ? sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this) : 0; // 重置哈希种子 } return switching; // 返回异或运算的结果,作为是否rehash的标准 }
2)jdk1.8下的源码
jdk1.8中将Entry改为Node节点来实现的,属性都是一样的。
2.1)put()方法
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); } final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) // 如果数组是null或者数组为空,就调用resize()进行初始化 n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) //(n-1)&hash 算出下表,这个和1.7是一样的 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); // 如果当前计算出来的位置为null,就新建一个节点 else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) // 若计算出来的位置上不为null,它和传入的key相比,hashCode相等并且key也相等 e = p; // 那么将p赋给e else if (p instanceof TreeNode) // 如果p是树类型 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); // 则按照红黑树的结构存入进去 else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { // 遍历p,p是链表 if ((e = p.next) == null) { // 如果p的下一个节点是尾节点(尾节点.next=null) p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); // 在p的后面创建一个节点,存放key/value(尾插法,多线程并发不会形成循环链表) if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8,即当binCount达到7时转换成红黑树数据结构, // 因为binCount是从0开始的,达到7时p链表上就有8个节点了,所以是链表上达到8个节点时会转变成红黑树。 treeifyBin(tab, hash); // 这里先就不展开了,红黑树不会,有时间再研究 break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; // 若上面两个条件都不满足,此时e = p.next,也就是将p的下一个节点赋给p,进入下一次循环 } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key,jdk这段注释意思是存在key的映射,我的理解是传入的key在p位置找到它自己的坑被别人占了 V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) // 下面就是将value存入被占的位置,并将旧的value返回 e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; // 修改次数加一 if (++size > threshold) // 若已有的键值对数大于阈值,就扩容 resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
下面盗个图,嘿嘿,那老哥画的太好了,图片来源:http://www.importnew.com/20386.html,我自己又画了下,加深点印象。
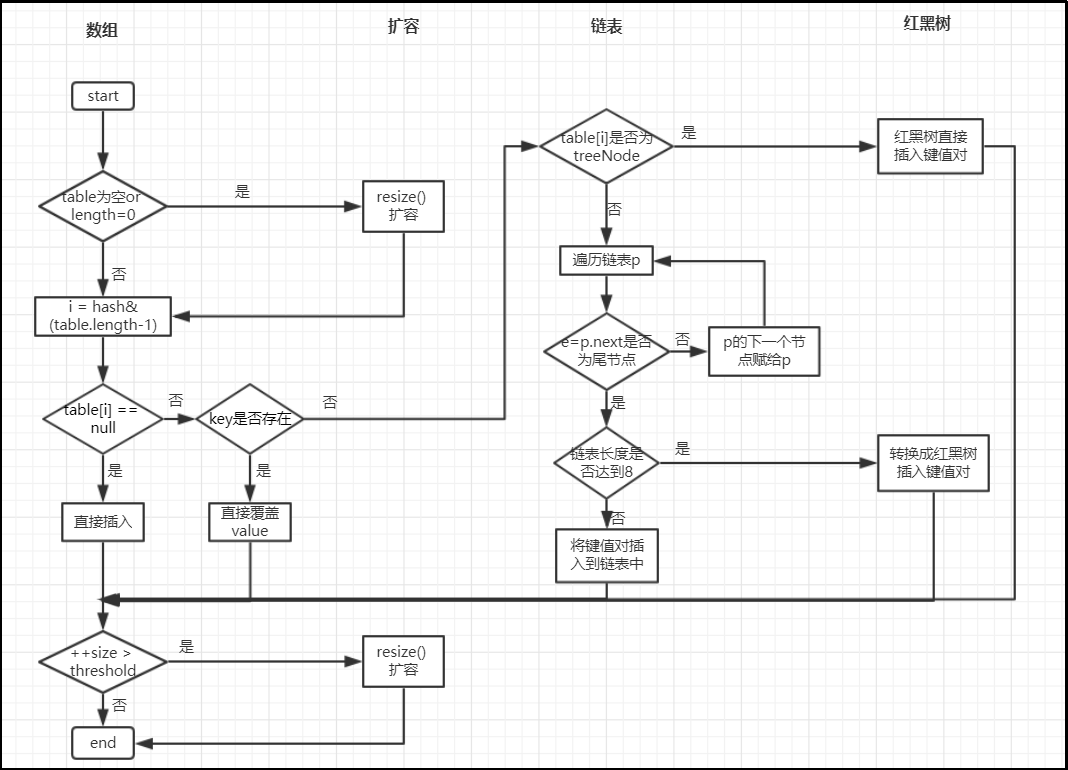
2.2)get()方法
public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; } final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } return null; }
get()方法也没什么,就是根据key的hashCode算出下标,找到对应位置上key与参数key是否相等,hash是否相等,如果是树就获取树的节点,如果是链表就遍历直到找到为止,找不到就返回null。
2.3)resize()方法
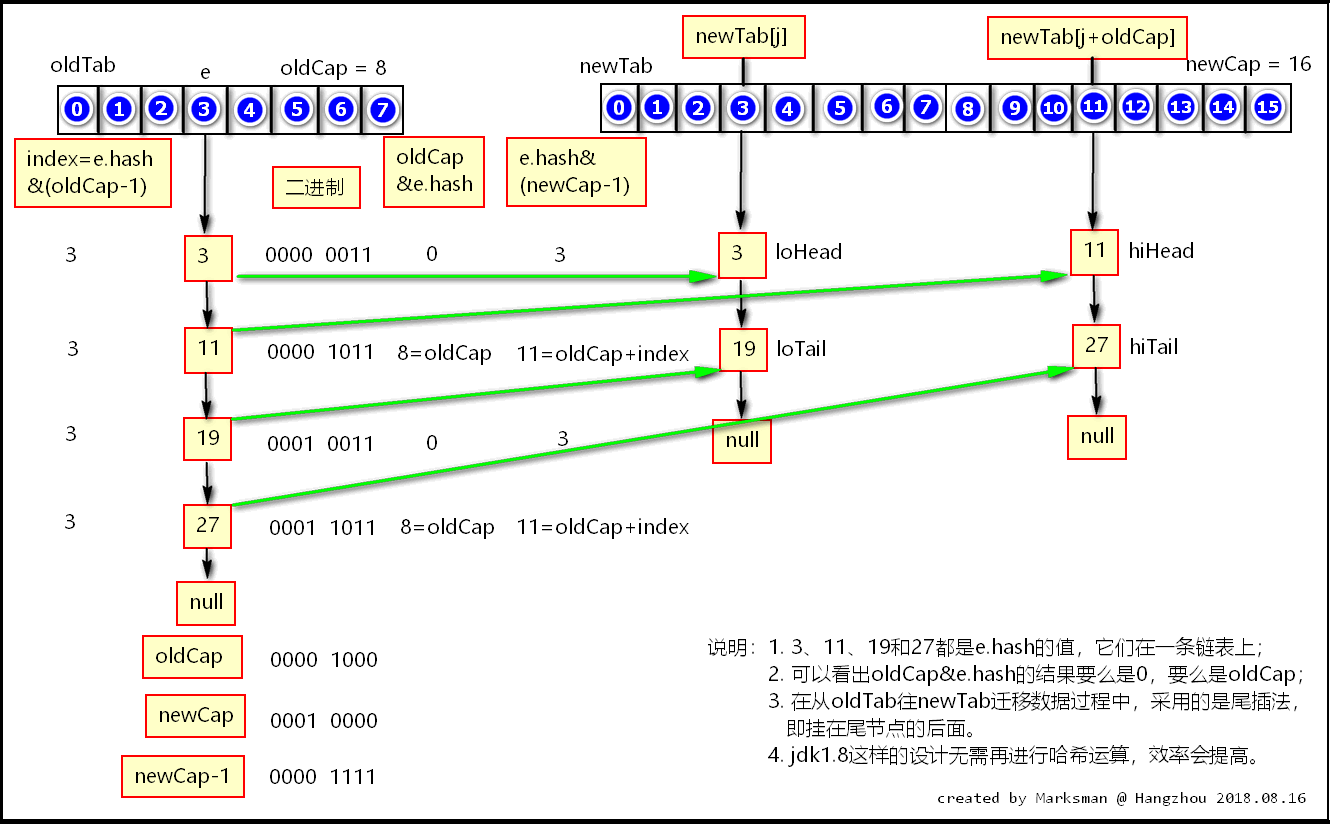
final Node<K,V>[] resize() { Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; // oldCap就是原数组的长度 int oldThr = threshold; //原阈值 int newCap, newThr = 0; if (oldCap > 0) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold 扩容成两倍 } else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold newCap = oldThr; else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults,这里表示初始化resize的另一个作用 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0) { float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; //创建新数组,容量为原数组的两倍 table = newTab; //将它指向table变量 if (oldTab != null) { for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { //遍历原数组 Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { //将不为null的j位置的元素指向e节点 oldTab[j] = null; if (e.next == null) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; //若e是尾节点,或者说e后面没有节点了,就将e指向新数组的e.hash&(newCap-1)位置 else if (e instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); //如果是树节点,就按红黑树处理,这里不展开 else { // preserve order Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; // 存放新数组中原位置的节点,这里后面展开说 Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; //存放新数组中原位置+原数组长度的节点 Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { //e.hash&oldCap 的值要么是0要么是oldCap ### if (loTail == null) loHead = e; // 第一次进来,先确定头节点,以后都走else,loHead指向e else loTail.next = e; // 第二次进来时loTail的next指向e(e=e.next), // 注意此时loHead的地址和loTail还是一样的,所以loHead也指向e, // 也就是说e被挂在了loHead的后面(尾插法,不会形成循环链表), // 以此类推,后面遍历的e都会被挂在loHead的后面。 loTail = e; // loTail指向e,第一次进来时头和尾在内存中的指向是一样的都是e, // 第二次进来时,loTail指向了e(e=e.next),这时和loHead.next指向的对象是一样的, // 所以下一次进来的时候loHead可以找到loTail.next,并将e挂在后面。 // 这段不明白的可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u013494765/article/details/77837338 } else { // 和if里面的原理是一样的 if (hiTail == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null); if (loTail != null) { loTail.next = null; newTab[j] = loHead; // 将loHead节点存到新数组中原下标位置 } if (hiTail != null) { hiTail.next = null; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; // 将hiHead节点存到新数组中 [原下标+原数组长度] 的位置 } } } } } return newTab; }
这里争对 ### 标注的右岸代码详细讲下:
为什么(e.hash&oldCap) == 0为true或false就能判断存放的位置是newTab[原下标],还是newTab[原下标+原数组长度],而不用像jdk1.7那样每次都要rehash?
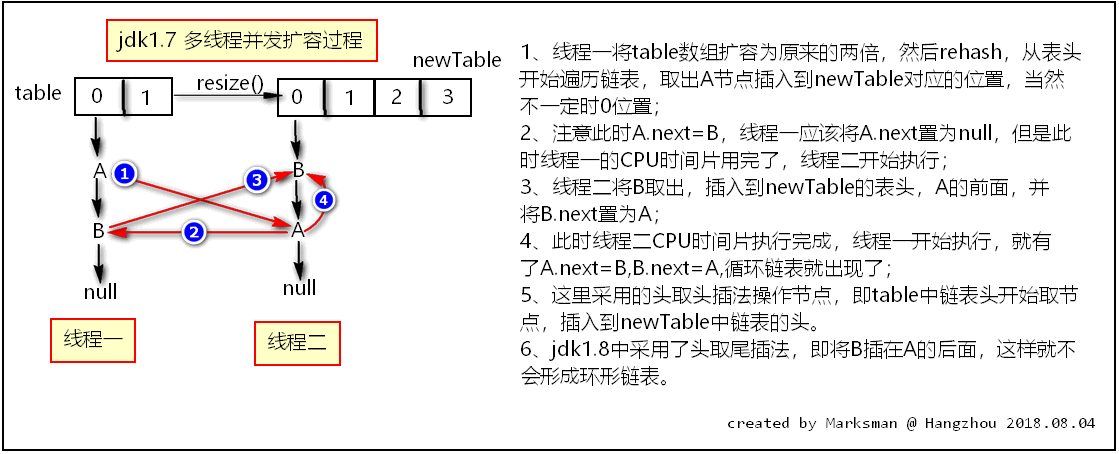
3、jdk1.7多线程并发形成循环链表问题
4、并发访问HashMap会出现哪些问题,如何解决呢
经过上面分析,我们知道jdk1.8已经不会在多线程下出现循环链表问题了,那还会出现哪些问题呢?
如:数据丢失、结果不一致......
解决方案:
(1)HashTable
用synchronized锁住整个table,效率太低,不好。
(2)Collections.SynchronizedMap()
它是对put等方法用synchronized加锁的,效率一般是不如ConcurrentHashMap的,用的不多。
(3)ConcurrentHashMap
采用锁分段,segment,每次对要操作的那部分数据加锁,并且get()是不用加锁的,这效率就高多了。具体实现原理,且听下回分解。
最后:文中若有写的不对或者不好的地方,请各位看官指出,谢谢。
参考资料:1、https://juejin.im/post/5b551e8df265da0f84562403
2、http://www.importnew.com/20386.html
3、https://blog.csdn.net/u013494765/article/details/77837338#comments
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/-Marksman/p/9441688.html