目录
一、继承是什么?
继承(inheritance)是面向对象软件技术当中的一个概念。
如果一个类别B“继承自”另一个类别A,就把这个B称为“A的子类”,而把A称为“B的父类别”也可以称“A是B的超类”
继承的优点:
1.继承可以使得子类具有父类别的各种属性和方法,而不需要再次编写相同的代码
2.在子类别继承父类别的同时,可以重新定义某些属性,并重写某些方法,即覆盖父类别的原有属性和方法,使其获得与父类别不同的功能
关于继承,可以先举一个形象的例子
汽车类作为父类,货车和轿车作为子类继承了汽车类的 一些属性和方法也可以对父类的属性和方法进行重写,也可以增加了自己的一些特有的属性和方法。
// 汽车父类
class Car {
constructor(color, type) {
this.color = color;
this.type = type;
}
getColor() {
return this.color;
}
}
// 货车子类
class Truck extends Car {
constructor(color, speed, container) {
super(color, name);
this.container = container;
}
getColor() {
return `货车的颜色为` + super.getColor();
}
}
// Suv子类
class Suv extends Car {
constructor(color, speed, quick) {
super(color, name);
this.quick = quick;
}
getColor() {
return `Suv的颜色为` + super.getColor();
}
}
let truck1 = new Truck('red', 200, 300);
console.log(truck1.getColor()); // 货车的颜色为red
let suv1 = new Suv('green', 200, 300);
console.log(suv1.getColor()); // Suv的颜色为red从这个例子中就能详细说明汽车、卡车以及suv之间的继承关系
二、继承的几种方式
1.原型链继承
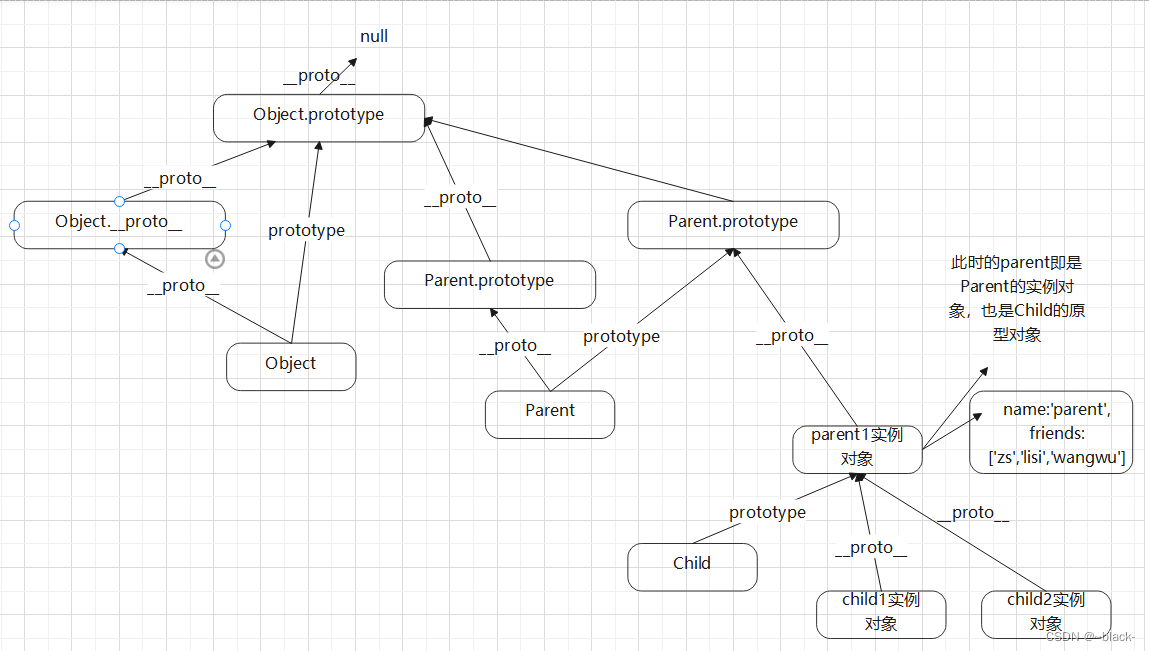
原型链继承是比较常见的继承方式之一,其中涉及的构造函数、原型和实例,三者之间存在着一定的关系,即每一个构造函数都有一个原型对象,原型对象又包含一个指向构造函数的指针,而实例则包含一个原型对象的指针
function Parent() {
this.name = 'parent';
this.friends = ['zs', 'lisi', 'wangwu '];
}
function Child() {
this.type = 'child';
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
let child1 = new Child();
let child2 = new Child();
child1.friends.push('sunqi');
console.log(child1.friends, child2.friends);
console.log(child1.__proto__);下图是上面例子的原型关系图,可以知道 Child.prototype 执行了Parent的实例对象parent1,当改变child1对象的 friends的值时,child1实例对象本身没有这个属性,就会向上查找,找到了parent1实例对象身上,而child1 和 child2 指向了同一个 parent1实例对象,内存空间是共享的
当为 parent1.friends 增加push值时,直接修改了公共的原型对象 parent1上的值。
打印输出如下

2.构造函数继承
借用call调用Parent函数, 只是调用了Parent的构造函数构造了对象,没有实现真正的原型继承,只能构造出 Parent实例的属性和方法,访问不到原型上的属性和方法
父类的引用属性不会被共享,优化了第一种继承方式的弊端,但是只能继承父类的实例属性和方法,不能继承原型属性或者方法
<script>
function Parent() {
this.name = 'parent';
}
Parent.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
function Child() {
Parent.call(this);
this.type = 'child';
}
let child = new Child();
console.log(child);
console.log(child.name);
console.log(child.getName());
</script>3.组合继承
组合继承是将前面的两种方法结合起来。
代码如下:
<script>
function Parent() {
this.name = 'parent';
this.friends = ['zs', 'lisi', 'wangwu '];
}
// 为Parent原型对象上添加方法
Parent.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
function Child() {
Parent.call(this);
this.type = 'child';
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
// 手动挂载构造器
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
let child1 = new Child();
let child2 = new Child();
child1.friends.push('sunqi');
console.log(child1.friends, child2.friends); // 不互相影响
console.log(child1.getName());
console.log(child2.getName());
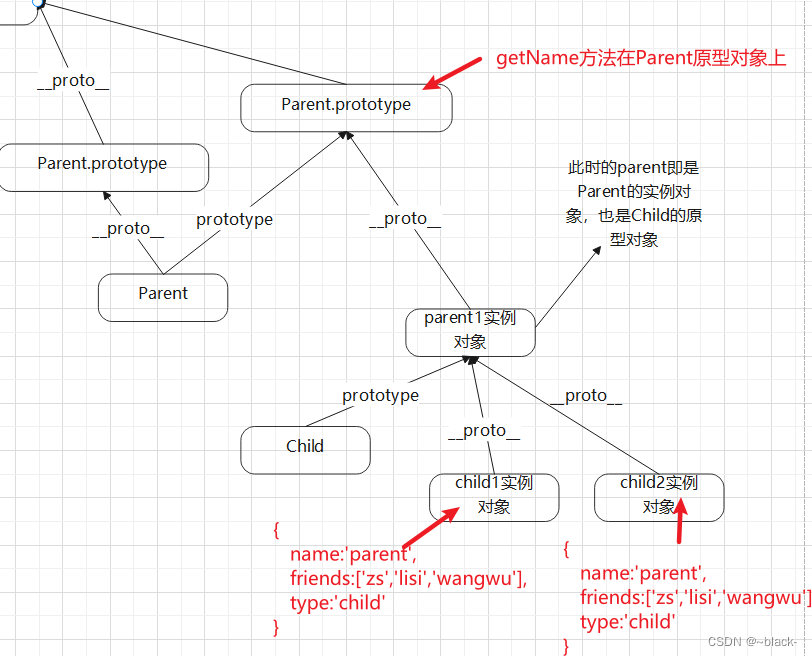
</script>组合继承 将前面两种继承方法的优点结合在一起,实例化Child时,调用了父类的构造方法,child1和child2是相互独立的,都有自己的值,所以互不影响,当调用getName方法时,child1和child2方法上并没有这个方法,向上查找,找到了Parent的原型对象上的getName方法。
打印输出结果如下:

4.原型式继承
利用了 Object.create()方法实现普通对象的继承
Object.create(proto, [propertiesObject])
该方法创建一个新对象,并指定该对象的原型对象 ------- proto
<script>
let parent = {
name: 'parent',
friends: ['zs', 'lisi', 'wangwu'],
getName() {
return this.name;
},
};
// 相当于 child.__proto__ == parent
let child1 = Object.create(parent);
console.log(child1.__proto__ == parent); // true
// 为 child1 添加属性name
child1.name = 'child1';
child1.friends.push('sunqi');
let child2 = Object.create(parent);
child2.friends.push('child2');
console.log(child1);
console.log(child2);
console.log(child1.name == child1.getName()); //true
console.log(child1.friends); // ['zs', 'lisi', 'wangwu', 'sunqi', 'child2']
console.log(child2.friends); // ['zs', 'lisi', 'wangwu', 'sunqi', 'child2']
</script>输出打印结果如下:
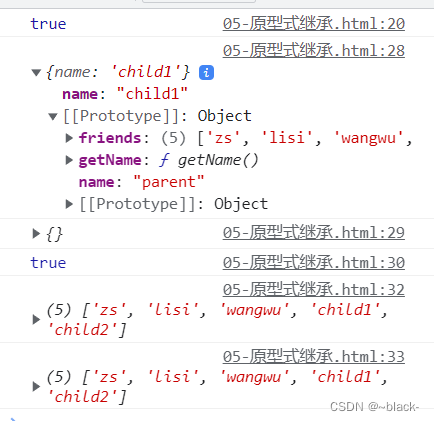
child1和child2都没有自己的friend属性,都要向上查找,找到了parent对象上的friend方法,指向的同一内存,因为Object.create方法实现的是浅拷贝,多个实例的引用类型属性指向相同的内存,存在篡改的可能
5.寄生式继承
寄生式继承在上面继承基础上进行优化,利用这个浅拷贝的能力再进行增强,添加一些方法
<script>
let parent = {
name: 'parent',
friends: ['zs', 'lisi', 'wangwu'],
getName() {
return this.name;
},
};
// 定义继承的方法,
function clone(proto) {
let clone = Object.create(proto);
// 添加自己的方法
clone.getFriends = function () {
return this.friends;
};
return clone;
}
let child = clone(parent);
console.log(child.getName()); // parent
console.log(child.getFriends()); // ['zs', 'lisi', 'wangwu']
</script>6.寄生组合式继承
结合和第五种寄生式方法和第三种组合式方法
<script>
function clone(parent, child) {
// 这里改用 Object.create 就可以减少组合继承中多进行一次构造的过程
child.prototype = Object.create(parent.prototype);
child.prototype.constructor = child;
}
function Parent() {
this.name = 'parent';
this.play = [1, 2, 3];
}
Parent.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name;
};
function Child() {
Parent.call(this);
this.friends = 'child';
}
clone(Parent, Child);
Child.prototype.getFriends = function () {
return this.friends;
};
let child = new Child();
console.log(child); //{friends:"child",name:"parent",play:[1,2,3],__proto__:Parent}
console.log(child.getName()); // parent
console.log(child.getFriends()); // child
</script>原型链继承示意图
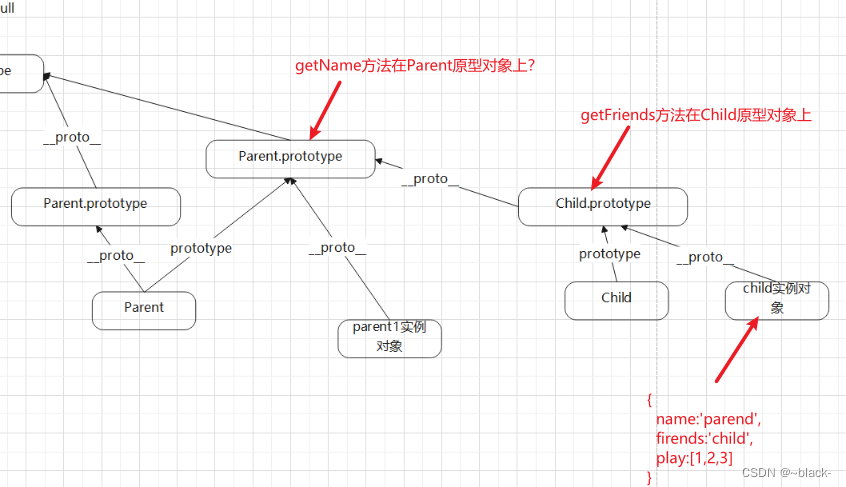
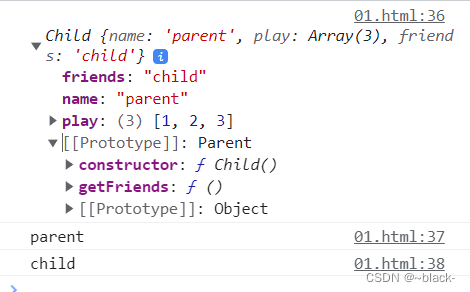
通过这种方法,我们发现,Child实例化出的实例化对象child 即能实例化出自己的属性和方法,也能继承到原型对象上的属性和方法。
三、总结
可以用一张图来总结
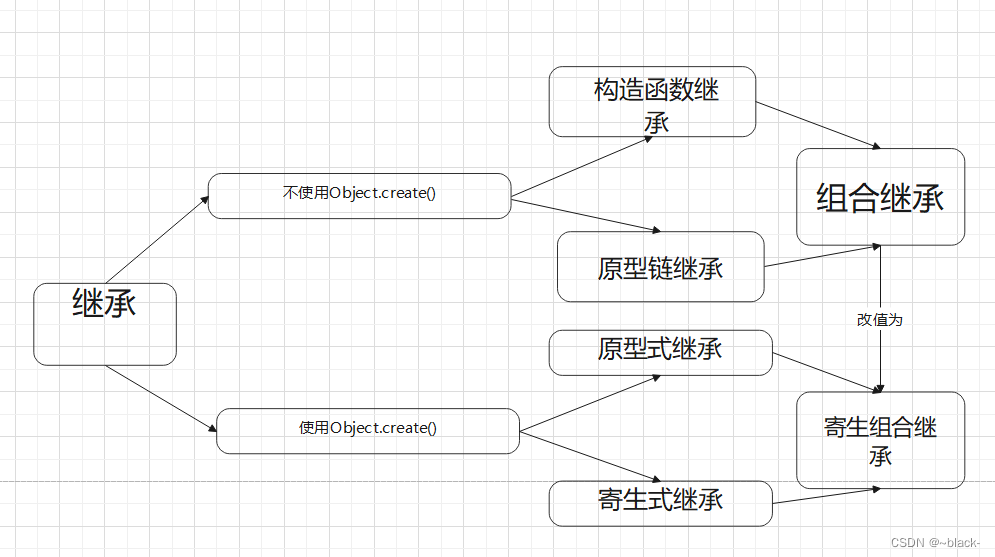
开发人员认为寄生组合式继承是最理想的继承方式
欢迎大家评论区讨论,一起学习