【题解】Digit Tree
呵呵以为是数据结构题然后是淀粉质还行...
题目就是给你一颗有边权的树,问你有多少路径,把路径上的数字顺次写出来,是\(m\)的倍数。
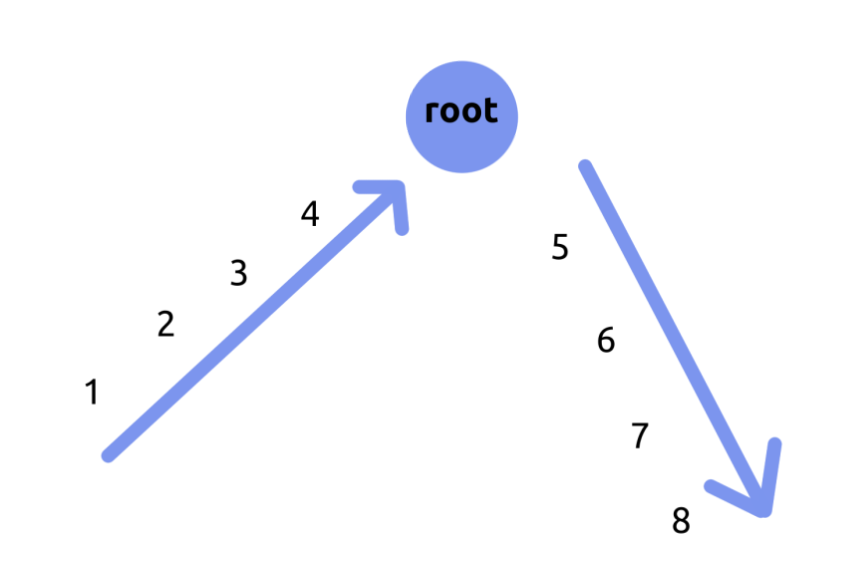
很明显可以点分治嘛,我们可以按照图上的样子,把一条路径本来是\(12345678\)的路径,变成\(1234|5678\),我们记录图中左边的那种路径为\(f\)(往根),右边的那种路径为\(g\)(从根),记右边的那种到分治中心的深度为\(d\),那么这条路径就可以被表示成\(f\times 10^d+g\),条件就变成了
\[ f \times 10^d +g\equiv 0 \\ f \times 10^d \equiv -g \\ f \equiv -g \times 10^{-d} \]
我们把坐边压到一个\(map\)里面,每次分治时拿右边直接枚举就好了,然后还要用第二个\(map\)去掉同一颗子树内的非法情况,具体实现看代码。
由于处理这个\(f,g\)真的很难(博主搞了好久,自己都晕了),所以代码里的\(f,g\)可能是反的...
不觉得难的可以自己去试试,如果你真的没晕的话..收下我的膝盖orz
咱们把\(map\)看做一个\(log\),时间复杂度就是\(O(n \log^2n)\)的
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; typedef long long ll;
template < class ccf > inline ccf qr(ccf ret){ ret=0;
register char c=getchar();
while(not isdigit(c)) c=getchar();
while(isdigit(c)) ret=ret*10+c-48,c=getchar();
return ret;
}
const int maxn=1e5+5;
typedef pair < int , ll > P;
vector < P > e[maxn];
vector < int > ve;
#define pb push_back
#define st first
#define nd second
#define mk make_pair
inline void add(int fr,int to,int w){
e[fr].pb(mk(to,w));
e[to].pb(mk(fr,w));
}
int sum;
int siz[maxn];
int d0[maxn];//深度
int f[maxn];
int g[maxn];
int rt;
int spc[maxn];
int inv[maxn];
int ten[maxn];
bool usd[maxn];
int n,mod;
map < int , int > mp,un;
ll ans;
void dfsrt(const int&now){//重心
usd[now]=1;
siz[now]=spc[now]=1;
for(auto t:e[now])
if(not usd[t.first]){
dfsrt(t.st);
siz[now]+=siz[t.st];
if(siz[t.st]>spc[now])spc[now]=siz[t.st];
}
spc[now]=max(spc[now],sum-siz[now]);
if(spc[now]<spc[rt]|| not rt) rt=now;
usd[now]=0;
}
void dfsd(const int&now,const int& last,const int&w){//dis
usd[now]=1;
d0[now]=d0[last]+1;
g[now]=(g[last]+1ll*ten[d0[last]]*w%mod)%mod;
f[now]=(f[last]*10ll%mod+w)%mod;
//printf("now=%d d0=%d f=%d g=%d\n",now-1,d0[now],f[now],g[now]);
ans+=(f[now]==0)+(g[now]==0);
++un[g[now]];
++mp[g[now]];
ve.pb(now);
for(auto t:e[now])
if(not usd[t.st])
dfsd(t.st,now,t.nd);
usd[now]=0;
}
inline void calc(const int&now){
d0[now]=f[now]=g[now]=0;
ve.clear();mp.clear();
int k=0;
for(auto t:e[now])
if(not usd[t.st]){
un.clear();
dfsd(t.st,now,t.nd);
register int edd=ve.size();
while(k<edd){
register int it=ve[k];
register int p=1ll*(((mod-f[it])%mod+mod)%mod)*inv[d0[it]]%mod;
if(un.find(p)!=un.end())
ans-=un[p];
++k;
}
}
for(auto t:ve){
register int p=1ll*(((mod-f[t])%mod+mod)%mod)*inv[d0[t]]%mod;
if(mp.find(p)!=mp.end())
/*cout<<"?qaq="<<t-1<<' '<<p<<endl;*/
ans+=mp[p];
}
}
void divd(const int&now){
usd[now]=1;calc(now);
for(auto t:e[now])
if(not usd[t.st]){
sum=siz[t.st];rt=0;
dfsrt(t.st);
divd(rt);
}
}
void exgcd(int a,int b,int&d,int&x,int&y){
if(!b) d=a,x=1,y=0;
else exgcd(b,a%b,d,y,x),y-=x*(a/b);
}
int Inv(const int&a, const int&p){
int d,x,y;
exgcd(a,p,d,x,y);
return d==1?(x+p)%p:-1;
}
int main(){
sum=n=qr(1);mod=qr(1);
if(mod==1)return cout<<1ll*n*(n-1)<<endl,0;
inv[0]=ten[0]=1;
ten[1]=10;
inv[1]=Inv(10,mod);
if(inv[1]==-1)return -1;
for(register int t=2;t<=n+1;++t)
ten[t]=1ll*ten[t-1]*ten[1]%mod,inv[t]=1ll*inv[t-1]*inv[1]%mod;
for(register int t=1,t1,t2,t3;t< n;++t){
t1=qr(1)+1;t2=qr(1)+1;t3=qr(1);
add(t1,t2,t3);
}
dfsrt(1);
divd(rt);
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}