题面
分析
对于每一个数a[i],找到它后面第一个大于它的数a[p],由p向i连边,最终我们就会得到一个森林,且p是i的父亲。为了方便操作,我们再增加一个虚拟节点n+1,把森林变成树。
由于序列不是递增的,不能二分。维护一个单调栈,栈顶元素最小。从n到1依次对每个 数操作,弹出栈里比它小的数。如果栈为空,说明该数是森林中的根节点,向n+1连边。否则栈顶元素就是第一个大于它的数,向它的编号连边即可。
我们发现,对于每个查询区间内的所有数,它对应着树上的某些节点,记为标记节点。如果把标记节点之间的非标记节点去掉,我们就会得到一棵新树,新树上从某个节点到根的一条路径对应着一个满足条件的序列,则最大序列长度等于新树上从叶子节点到根的最长路径。这样,我们就把问题转化为了树上的最长路径。
显然不能对每一个询问建一棵新树。我们发现新树上的路径长度就是原树上的路径经过的标记节点个数,如图(加粗的节点为标记节点)。
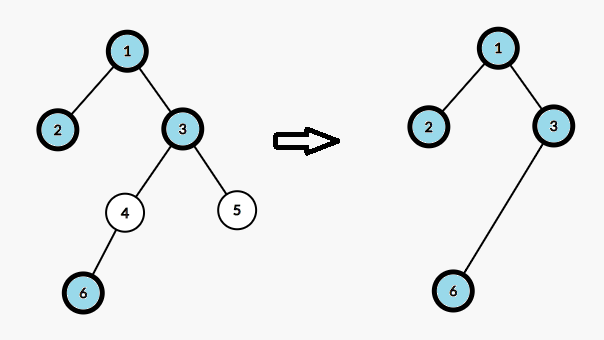
所以,我们建立一棵线段树,线段树的叶子节点存储原树上每个节点到根的路径上的标记节点个数,线段树维护最大值。
我们枚举每个长度为k的区间[i,i+k-1],显然从前一个区间转移到当前区间时,只会增加一个标记节点,减少一个标记节点。每增加一个标记节点i,我们就将i的子树内的所有节点的值+1,否则-1。答案即为整颗线段树的最大值
时间复杂度\(O(n\log n)\)
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#define maxn 1000005
using namespace std;
int n,k;
int a[maxn];
struct edge{
int from;
int to;
int next;
}E[maxn<<1];
int head[maxn];
int sz=1;
void add_edge(int u,int v){
sz++;
E[sz].from=u;
E[sz].to=v;
E[sz].next=head[u];
head[u]=sz;
}
int cnt=0;
int lb[maxn],rb[maxn];
void dfs(int x,int fa){
lb[x]=++cnt;
for(int i=head[x];i;i=E[i].next){
int y=E[i].to;
if(y!=fa){
dfs(y,x);
}
}
rb[x]=cnt;
}
struct node{
int l;
int r;
int v;
int mark;
}tree[maxn<<2];
void push_up(int pos){
tree[pos].v=max(tree[pos<<1].v,tree[pos<<1|1].v);
}
void build(int l,int r,int pos){
tree[pos].l=l;
tree[pos].r=r;
if(l==r){
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(l,mid,pos<<1);
build(mid+1,r,pos<<1|1);
push_up(pos);
}
void push_down(int pos){
if(tree[pos].mark){
tree[pos<<1].v+=tree[pos].mark;
tree[pos<<1].mark+=tree[pos].mark;
tree[pos<<1|1].v+=tree[pos].mark;
tree[pos<<1|1].mark+=tree[pos].mark;
tree[pos].mark=0;
}
}
void update(int L,int R,int v,int pos){
if(L<=tree[pos].l&&R>=tree[pos].r){
tree[pos].v+=v;
tree[pos].mark+=v;
return;
}
push_down(pos);
int mid=(tree[pos].l+tree[pos].r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) update(L,R,v,pos<<1);
if(R>mid) update(L,R,v,pos<<1|1);
push_up(pos);
}
int query(int L,int R,int pos){
if(L<=tree[pos].l&&R>=tree[pos].r){
return tree[pos].v;
}
push_down(pos);
int mid=(tree[pos].l+tree[pos].r)>>1;
int ans=0;
if(L<=mid) ans=max(ans,query(L,R,pos<<1));
if(R>mid) ans=max(ans,query(L,R,pos<<1|1));
return ans;
}
int nex[maxn];
void init(){
stack<int>s;
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){
while(!s.empty()&&a[s.top()]<=a[i]) s.pop();
if(!s.empty()){
int p=s.top();
add_edge(p,i);
add_edge(i,p);
}else{
add_edge(n+1,i);
add_edge(i,n+1);
}
s.push(i);
}
dfs(n+1,0);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
init();
build(1,n+1,1);
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){
update(lb[i],rb[i],1,1);
}
for(int i=1;i+k-1<=n;i++){
int r=i+k-1;
printf("%d ",query(1,n+1,1));
update(lb[i],rb[i],-1,1);
update(lb[r+1],rb[r+1],1,1);
}
}