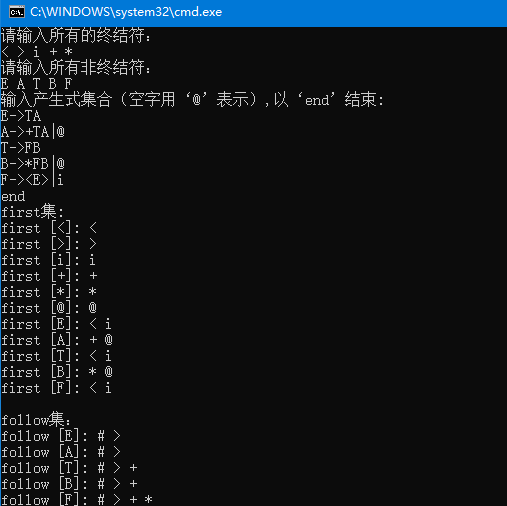
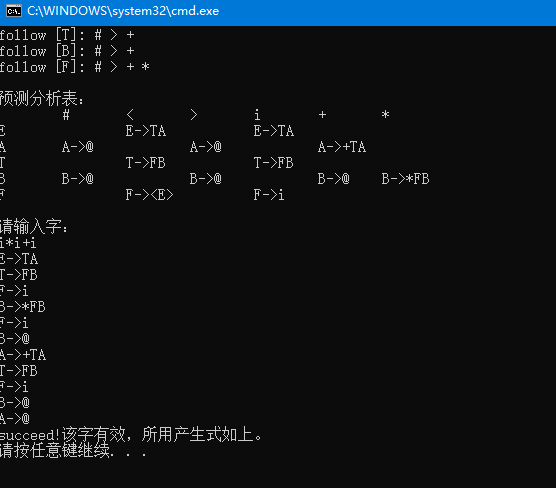
- 根据某一文法编制调试 LL ( 1 )分析程序,以便对任意输入的符号串进行分析。
- 构造预测分析表,并利用分析表和一个栈来实现对上述程序设计语言的分析程序。
- 分析法的功能是利用LL(1)控制程序根据显示栈顶内容、向前看符号以及LL(1)分析表,对输入符号串自上而下的分析过程。
【设计思想】
(1)定义部分:定义常量、变量、数据结构。
(2)初始化:设立LL(1)分析表、初始化变量空间(包括堆栈、结构体、数组、临时变量等);
(3)控制部分:从键盘输入一个表达式符号串;
(4)利用LL(1)分析算法进行表达式处理:根据LL(1)分析表对表达式符号串进行堆栈(或其他)操作,输出分析结果,如果遇到错误则显示错误信息。
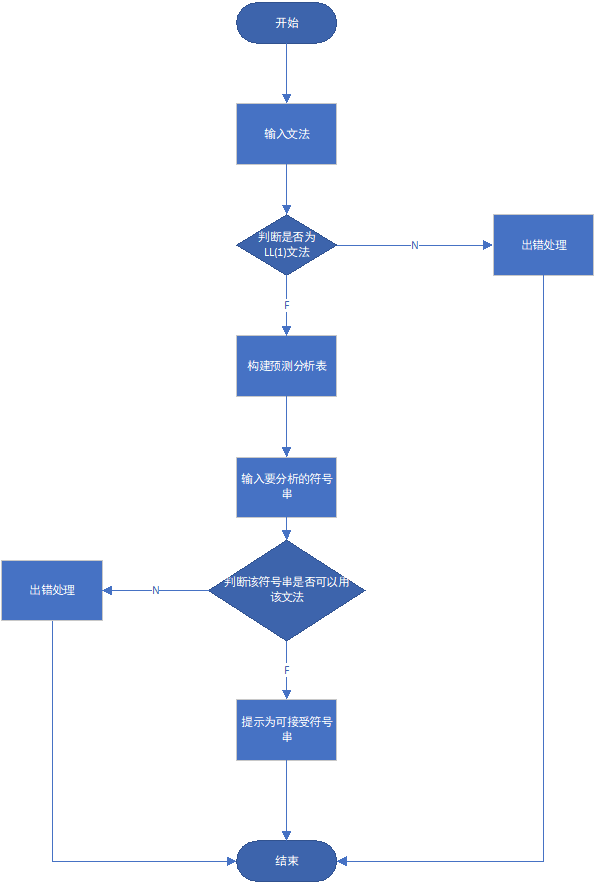
流程图
源程序
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
map<char, int>getnum;
char text[100]; //获得对应字符
vector<string>proce;
int table[100][100]; //预测分析表
int num = 0; int numvt = 0; //numvt是终结符集合,0是'#',numvt表空字
string first[100];
string follow[200];
void readin()
{
memset(table, -1, sizeof(table));
getnum['#'] = 0;
text[0] = '#';
cout << "请输入所有的终结符:" << endl;
char x;
do
{
cin >> x;
getnum[x] = ++num;
text[num] = x;
} while (cin.peek() != '\n');
numvt = ++num;
getnum['@'] = numvt; //kong zi
text[num] = ('@');
cout << "请输入所有非终结符:" << endl;
do
{
cin >> x;
getnum[x] = ++num;
text[num] = x;
} while (cin.peek() != '\n');
cout << "输入产生式集合(空字用'@'表示),以'end'结束:" << endl;
string pro;
while (cin >> pro&&pro != "end")
{
string ss;
ss += pro[0];
for (int i = 3; i<pro.size(); i++)
{
if (pro[i] == '|')
{
proce.push_back(ss);
ss.clear(); ss += pro[0];
}
else
{
ss += pro[i];
}
}
proce.push_back(ss);
}
}
void jiaoji(string &a, string b) //a=a or b 取a,b交集赋值给a
{
set<char>se;
for (int i = 0; i<a.size(); i++)
se.insert(a[i]);
for (int i = 0; i<b.size(); i++)
se.insert(b[i]);
string ans;
set<char>::iterator it;
for (it = se.begin(); it != se.end(); it++)
ans += *it;
a = ans;
}
string get_f(int vn, int & has_0) //dfs:vn能推出的不含空字的vt集合,并且判断vn能否推出空字
{
if (vn == numvt)has_0 = 1;
if (vn<numvt)return first[vn];
string ans;
for (int i = 0; i<proce.size(); i++)
{
if (getnum[proce[i][0]] == vn)
ans += get_f(getnum[proce[i][1]], has_0);
}
return ans;
}
void getfirst()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= numvt; i++) //终结符,first集是其本身。
{
first[i] += ('0' + i);
}
for (int j = 0; j<proce.size(); j++) //扫描所有产生式
{
int k = 0; int has_0 = 0; //k扫瞄该产生式
do{
has_0 = 0;
k++;
if (k == proce[j].size()) //推到最后一个了,则附加空字
{
first[getnum[proce[j][0]]] += ('0' + numvt);
break;
} //合并之
jiaoji(first[getnum[proce[j][0]]], get_f(getnum[proce[j][k]], has_0));
} while (has_0); //到无法推出空字为止
}
}
void print_first()
{
cout << "first集:" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++)
{
cout << "first [" << text[i] << "]: ";
for (int j = 0; j<first[i].size(); j++)
cout << text[first[i][j] - '0'] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void getfollow()
{
jiaoji(follow[getnum[proce[0][0]]], "0"); //先添加'#';
for (int j = 0; j<proce.size(); j++) //扫所有产生式
{
for (int jj = 1; jj<proce[j].size(); jj++) //每个非终结符的follow集
{
if (getnum[proce[j][jj]] <= numvt)continue; //vt无follow集
int k = jj; int has_0;
do
{
has_0 = 0;
k++;
if (k == proce[j].size()) //都能推出空字,follow集=产生式左边的vn,
{
jiaoji(follow[getnum[proce[j][jj]]], follow[getnum[proce[j][0]]]);
break;
}
jiaoji(follow[getnum[proce[j][jj]]], get_f(getnum[proce[j][k]], has_0));
} while (has_0);
}
}
}
void gettable() //得预测分析表
{
for (int i = 0; i<proce.size(); i++) //扫所有产生式
{
if (proce[i][1] == '@') //直接推出空字的,特判下(follow集=产生式左边的vn中元素填)
{
string flw = follow[getnum[proce[i][0]]];
for (int k = 0; k<flw.size(); k++)
{
table[getnum[proce[i][0]]][flw[k] - '0'] = i;
}
}
string temps = first[getnum[proce[i][1]]];
for (int j = 0; j<temps.size(); j++) //考察first集
{
if (temps[j] != ('0' + numvt))
{
table[getnum[proce[i][0]]][temps[j] - '0'] = i;
}
else //有空字的,考察follw集
{
string flw = follow[getnum[proce[i][1]]];
for (int k = 0; k<flw.size(); k++)
{
table[getnum[proce[i][0]]][flw[k] - '0'] = i;
}
}
}
}
}
string get_proce(int i) //由对应下标获得对应产生式。
{
if (i<0)return " "; //无该产生式
string ans;
ans += proce[i][0];
ans += "->";
//ans+=(proce[i][0]+"->"); 注意这样不行!思之即可。
for (int j = 1; j<proce[i].size(); j++)
ans += proce[i][j];
return ans;
}
void print_table()
{
cout << "预测分析表:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i<numvt; i++)
cout << '\t' << text[i];
cout << endl;
for (int i = numvt + 1; i <= num; i++)
{
cout << text[i];
for (int j = 0; j<numvt; j++)
{
cout << '\t' << get_proce(table[i][j]);
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void print_follow()
{
cout << "follow集:" << endl;
for (int i = numvt + 1; i <= num; i++)
{
cout << "follow [" << text[i] << "]: ";
for (int j = 0; j<follow[i].size(); j++)
cout << text[follow[i][j] - '0'] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
string word;
bool analyze() //总控,分析字word的合法性,若合法,输出所有产生式。
{
stack<char>sta;
sta.push('#'); sta.push(proce[0][0]);
int i = 0;
while (!sta.empty())
{
int cur = sta.top();
sta.pop();
if (cur == word[i]) //是终结符,推进
{
i++;
}
else if (cur == '#') //成功,结束
{
return 1;
}
else if (table[getnum[cur]][getnum[word[i]]] != -1) //查表
{
int k = table[getnum[cur]][getnum[word[i]]];
cout << proce[k][0] << "->";
for (int j = 1; j<proce[k].size(); j++)
cout << proce[k][j];
cout << endl;
for (int j = proce[k].size() - 1; j>0; j--) //逆序入栈
{
if (proce[k][j] != '@')
sta.push(proce[k][j]);
}
}
else //失败!
{
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main()
{
readin();
getfirst();
getfollow();
getfollow();
gettable();
print_first();
print_follow();
print_table();
cout << "请输入字:" << endl;
cin >> word;
if (analyze())
cout << "succeed!该字有效,所用产生式如上。" << endl;
else cout << "error!" << endl;
return 0;
}
结果