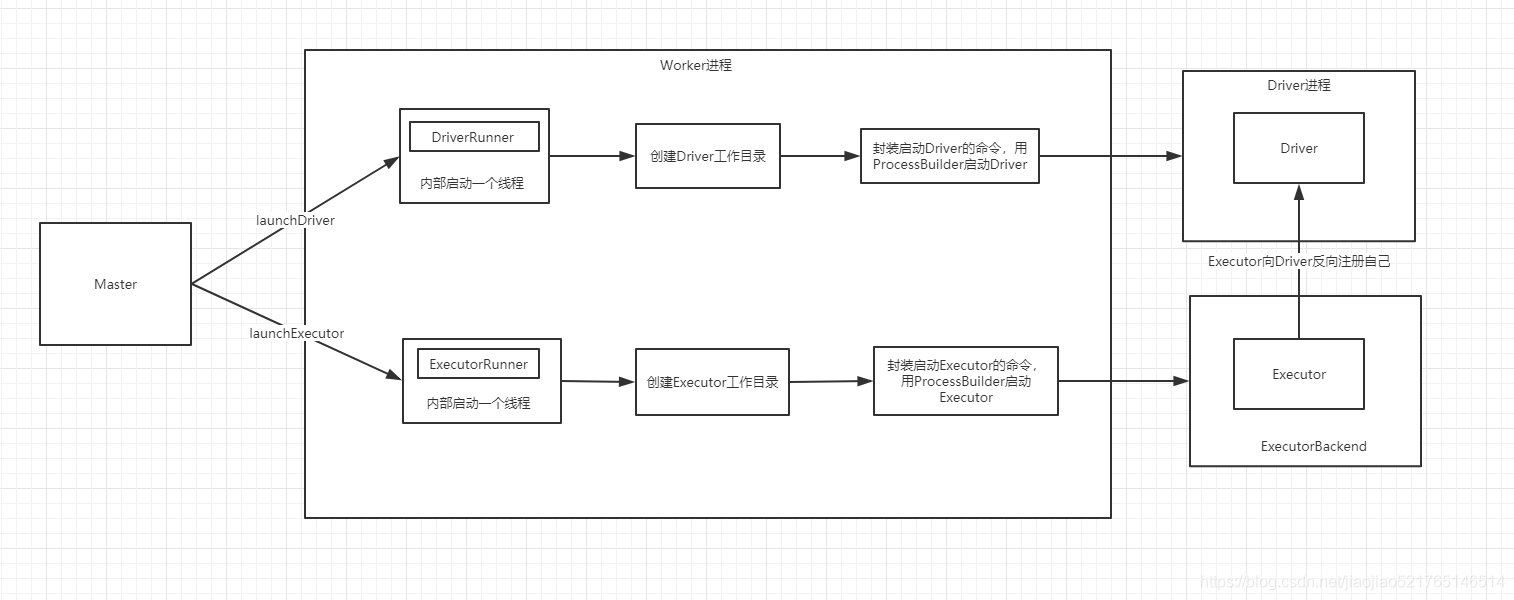
解释:
- Master要求Worker启动Driver和Executor
- Worker启动Driver的一个基本的原理,Worker会启动一个线程DriverRunner,然后DriverRunner会去负责启动Driver进程,然后在之后对Driver进程进行管理
- Worker启动Executor的一个基本的原理,Worker会启动一个线程ExecutorRunner,然后ExecutorRunner会去负责启动Executor进程,然后在之后对Executor进程进行管理
- Driver首先创建Driver的工作目录,封装启动Driver的命令,用ProcessBuilder启动Driver
- Executor首先创建Executor的工作目录,封装启动Executor的命令,用ProcessBuilder启动Executor
- Executor找到对应的Driver,去反向注册自己,然后就可以启动Executor
Worker启动并管理Driver进程源码分析:
第一步:Worker的LaunchDriver方法
源码位置:org/apache/spark/deploy/worker/Worker.scala
// 启动driver
case LaunchDriver(driverId, driverDesc) => {
logInfo(s"Asked to launch driver $driverId")
val driver = new DriverRunner(
conf,
driverId,
workDir,
sparkHome,
driverDesc.copy(command = Worker.maybeUpdateSSLSettings(driverDesc.command, conf)),
self,
workerUri,
securityMgr)
//内存缓存结构(HashMap)
drivers(driverId) = driver
driver.start()
//Worker加上driver上使用的CPU与内存
coresUsed += driverDesc.cores
memoryUsed += driverDesc.mem
}
第二步:DriverRunner方法
/**
* Manages the execution of one driver, including automatically restarting the driver on failure.
* This is currently only used in standalone cluster deploy mode.
*
* 管理一个Driver的执行,包括在Driver失败时自动重启Driver
* 目前这种方式仅仅使用于standalone集群部署模式
*/
private[deploy] class DriverRunner(
conf: SparkConf,
val driverId: String,
val workDir: File,
val sparkHome: File,
val driverDesc: DriverDescription,
val worker: RpcEndpointRef,
val workerUrl: String,
val securityManager: SecurityManager)
extends Logging {
......
/** Starts a thread to run and manage the driver. */
private[worker] def start() = {
/**
* 创建Java线程
*/
new Thread("DriverRunner for " + driverId) {
override def run() {
try {
//第一步,创建工作目录
val driverDir = createWorkingDirectory()
//第二部,下载用户上传的Jar
val localJarFilename = downloadUserJar(driverDir)
def substituteVariables(argument: String): String = argument match {
case "{{WORKER_URL}}" => workerUrl
case "{{USER_JAR}}" => localJarFilename
case other => other
}
// TODO: If we add ability to submit multiple jars they should also be added here
//构建ProcessBuilder,传入了driver的启动命令、需要的内存大小等信息
val builder = CommandUtils.buildProcessBuilder(driverDesc.command, securityManager,
driverDesc.mem, sparkHome.getAbsolutePath, substituteVariables)
// 通过ProcessBuilder启动driver
launchDriver(builder, driverDir, driverDesc.supervise)
}
catch {
case e: Exception => finalException = Some(e)
}
// 对driver的退出状态做一些处理
val state =
if (killed) {
DriverState.KILLED
} else if (finalException.isDefined) {
DriverState.ERROR
} else {
finalExitCode match {
case Some(0) => DriverState.FINISHED
case _ => DriverState.FAILED
}
}
finalState = Some(state)
//这个DriverRunner线程,向它所属的worker的actor,发送一个DriverStateChanged的事件
worker.send(DriverStateChanged(driverId, state, finalException))
}
}.start()
}
第三步:调用downloadUserJar方法
/**
* Download the user jar into the supplied directory and return its local path.
* Will throw an exception if there are errors downloading the jar.
*
* 将用户的jar包下载到提供目录中(之前创建的driver工作目录),并返回它在worker本地的路径
* 如果下载jar包的过程出现任何异常,那么会抛出Exception异常
*/
private def downloadUserJar(driverDir: File): String = {
//用Hadoop Jar里的Path
val jarPath = new Path(driverDesc.jarUrl)
//Hadoop配置
val hadoopConf = SparkHadoopUtil.get.newConfiguration(conf)
val destPath = new File(driverDir.getAbsolutePath, jarPath.getName)
val jarFileName = jarPath.getName
val localJarFile = new File(driverDir, jarFileName)
val localJarFilename = localJarFile.getAbsolutePath
//如果jar本地不存在
if (!localJarFile.exists()) { // May already exist if running multiple workers on one node
logInfo(s"Copying user jar $jarPath to $destPath")
//将jar拷贝的本地
Utils.fetchFile(
driverDesc.jarUrl,
driverDir,
conf,
securityManager,
hadoopConf,
System.currentTimeMillis(),
useCache = false)
}
//如果还是不存在,抛出异常
if (!localJarFile.exists()) { // Verify copy succeeded
throw new Exception(s"Did not see expected jar $jarFileName in $driverDir")
}
localJarFilename
}
第四步:launchDriver方法
private def launchDriver(builder: ProcessBuilder, baseDir: File, supervise: Boolean) {
builder.directory(baseDir)
def initialize(process: Process): Unit = {
// Redirect stdout and stderr to files
// 重定向stdout和stderr文件
val stdout = new File(baseDir, "stdout")
CommandUtils.redirectStream(process.getInputStream, stdout)
val stderr = new File(baseDir, "stderr")
val header = "Launch Command: %s\n%s\n\n".format(
builder.command.mkString("\"", "\" \"", "\""), "=" * 40)
Files.append(header, stderr, UTF_8)
CommandUtils.redirectStream(process.getErrorStream, stderr)
}
// 调用waitFor函数,把driver进程启动起
runCommandWithRetry(ProcessBuilderLike(builder), initialize, supervise)
}
第五步:runCommandWithRetry方法
def runCommandWithRetry(
command: ProcessBuilderLike, initialize: Process => Unit, supervise: Boolean): Unit = {
// Time to wait between submission retries.
// 在提交重试之间等待时间。
var waitSeconds = 1
// A run of this many seconds resets the exponential back-off.
val successfulRunDuration = 5
var keepTrying = !killed
while (keepTrying) {
logInfo("Launch Command: " + command.command.mkString("\"", "\" \"", "\""))
synchronized {
if (killed) { return }
process = Some(command.start())
initialize(process.get)
}
val processStart = clock.getTimeMillis()
// 启动进程
val exitCode = process.get.waitFor()
if (clock.getTimeMillis() - processStart > successfulRunDuration * 1000) {
waitSeconds = 1
}
if (supervise && exitCode != 0 && !killed) {
logInfo(s"Command exited with status $exitCode, re-launching after $waitSeconds s.")
sleeper.sleep(waitSeconds)
waitSeconds = waitSeconds * 2 // exponential back-off
}
keepTrying = supervise && exitCode != 0 && !killed
finalExitCode = Some(exitCode)
}
}
第六步:Worker收到Driver(DriverRunner线程)执行完成之后处理
源码位置:org/apache/spark/deploy/worker/Worker.scala
private[worker] def handleDriverStateChanged(driverStateChanged: DriverStateChanged): Unit = {
val driverId = driverStateChanged.driverId
val exception = driverStateChanged.exception
val state = driverStateChanged.state
state match {
case DriverState.ERROR =>
logWarning(s"Driver $driverId failed with unrecoverable exception: ${exception.get}")
case DriverState.FAILED =>
logWarning(s"Driver $driverId exited with failure")
case DriverState.FINISHED =>
logInfo(s"Driver $driverId exited successfully")
case DriverState.KILLED =>
logInfo(s"Driver $driverId was killed by user")
case _ =>
logDebug(s"Driver $driverId changed state to $state")
}
//driver执行完成之后,DriverRunner线程会发送一个状态给Worker
//然后Worker实际上会将DriverStateChanged消息发送给Master,Master会进行状态改变处理
sendToMaster(driverStateChanged)
//将driver从本地缓存移除
val driver = drivers.remove(driverId).get
//将driver加入完成队列
finishedDrivers(driverId) = driver
//将driver内存和cpu释放
trimFinishedDriversIfNecessary()
memoryUsed -= driver.driverDesc.mem
coresUsed -= driver.driverDesc.cores
}
第七步:Master收到Worker消息,实际上是DriverStateChanged消息
源码位置:org/apache/spark/deploy/master/Master.scala
/**
* Driver状态改变
*/
case DriverStateChanged(driverId, state, exception) => {
state match {
//如果Driver的状态是错误,完成,被杀掉,失败
case DriverState.ERROR | DriverState.FINISHED | DriverState.KILLED | DriverState.FAILED =>
//移除Driver
removeDriver(driverId, state, exception)
case _ =>
throw new Exception(s"Received unexpected state update for driver $driverId: $state")
}
}
Worker启动并管理executor进程源码分析:
第一步:Worker的LaunchExecutor方法
源码位置:org/apache/spark/deploy/worker/Worker.scala
case LaunchExecutor(masterUrl, appId, execId, appDesc, cores_, memory_) =>
if (masterUrl != activeMasterUrl) {
logWarning("Invalid Master (" + masterUrl + ") attempted to launch executor.")
} else {
try {
logInfo("Asked to launch executor %s/%d for %s".format(appId, execId, appDesc.name))
// Create the executor's working directory
// 创建exector的本地目录
val executorDir = new File(workDir, appId + "/" + execId)
if (!executorDir.mkdirs()) {
throw new IOException("Failed to create directory " + executorDir)
}
// Create local dirs for the executor. These are passed to the executor via the
// SPARK_EXECUTOR_DIRS environment variable, and deleted by the Worker when the
// application finishes.
val appLocalDirs = appDirectories.get(appId).getOrElse {
Utils.getOrCreateLocalRootDirs(conf).map { dir =>
val appDir = Utils.createDirectory(dir, namePrefix = "executor")
Utils.chmod700(appDir)
appDir.getAbsolutePath()
}.toSeq
}
appDirectories(appId) = appLocalDirs
// 创建exectorRunner
val manager = new ExecutorRunner(
appId,
execId,
appDesc.copy(command = Worker.maybeUpdateSSLSettings(appDesc.command, conf)),
cores_,
memory_,
self,
workerId,
host,
webUi.boundPort,
publicAddress,
sparkHome,
executorDir,
workerUri,
conf,
appLocalDirs, ExecutorState.LOADING)
// 将executorRunner加入本地缓存
executors(appId + "/" + execId) = manager
// 启动ExecutorRunner
manager.start()
// 加上executor要使用的资源
coresUsed += cores_
memoryUsed += memory_
// 向master发送ExecutorStateChanged这个事件
sendToMaster(ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, manager.state, None, None))
} catch {
case e: Exception => {
logError(s"Failed to launch executor $appId/$execId for ${appDesc.name}.", e)
if (executors.contains(appId + "/" + execId)) {
executors(appId + "/" + execId).kill()
executors -= appId + "/" + execId
}
sendToMaster(ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, ExecutorState.FAILED,
Some(e.toString), None))
}
}
}
第二步:ExecutorRunner方法
private[worker] def start() {
//创建一个Java 线程
workerThread = new Thread("ExecutorRunner for " + fullId) {
override def run() { fetchAndRunExecutor() }
}
workerThread.start()
// Shutdown hook that kills actors on shutdown.
shutdownHook = ShutdownHookManager.addShutdownHook { () =>
killProcess(Some("Worker shutting down")) }
}
第二步:fetchAndRunExecutor方法
/**
* Download and run the executor described in our ApplicationDescription
*/
private def fetchAndRunExecutor() {
try {
// Launch the process
//封装一个ProcessBuilder
val builder = CommandUtils.buildProcessBuilder(appDesc.command, new SecurityManager(conf),
memory, sparkHome.getAbsolutePath, substituteVariables)
val command = builder.command()
logInfo("Launch command: " + command.mkString("\"", "\" \"", "\""))
//工作目录
builder.directory(executorDir)
builder.environment.put("SPARK_EXECUTOR_DIRS", appLocalDirs.mkString(File.pathSeparator))
// In case we are running this from within the Spark Shell, avoid creating a "scala"
// parent process for the executor command
builder.environment.put("SPARK_LAUNCH_WITH_SCALA", "0")
// Add webUI log urls
val baseUrl =
s"http://$publicAddress:$webUiPort/logPage/?appId=$appId&executorId=$execId&logType="
builder.environment.put("SPARK_LOG_URL_STDERR", s"${baseUrl}stderr")
builder.environment.put("SPARK_LOG_URL_STDOUT", s"${baseUrl}stdout")
process = builder.start()
val header = "Spark Executor Command: %s\n%s\n\n".format(
command.mkString("\"", "\" \"", "\""), "=" * 40)
/**
* 将executor的InputStream与ErrorStream,输出的信息
* 分别重定向到本地工作目录的stdout和stderr报错文件中
*/
// Redirect its stdout and stderr to files
val stdout = new File(executorDir, "stdout")
stdoutAppender = FileAppender(process.getInputStream, stdout, conf)
val stderr = new File(executorDir, "stderr")
Files.write(header, stderr, UTF_8)
stderrAppender = FileAppender(process.getErrorStream, stderr, conf)
// Wait for it to exit; executor may exit with code 0 (when driver instructs it to shutdown)
// or with nonzero exit code
// 调用Process的waitFor()方法,启动executor进程
val exitCode = process.waitFor()
// executor执行完之后拿到返回状态
state = ExecutorState.EXITED
val message = "Command exited with code " + exitCode
// 向worker发送ExecutorStateChanged消息
worker.send(ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, state, Some(message), Some(exitCode)))
} catch {
case interrupted: InterruptedException => {
logInfo("Runner thread for executor " + fullId + " interrupted")
state = ExecutorState.KILLED
killProcess(None)
}
case e: Exception => {
logError("Error running executor", e)
state = ExecutorState.FAILED
killProcess(Some(e.toString))
}
}
}
第三步:Worker收到ExecutorStateChanged消息
private[worker] def handleExecutorStateChanged(executorStateChanged: ExecutorStateChanged):
Unit = {
//直接向Master也发送一个ExecutorStateChanged消息
sendToMaster(executorStateChanged)
val state = executorStateChanged.state
//如果Executor状态是Finished
if (ExecutorState.isFinished(state)) {
val appId = executorStateChanged.appId
val fullId = appId + "/" + executorStateChanged.execId
val message = executorStateChanged.message
val exitStatus = executorStateChanged.exitStatus
executors.get(fullId) match {
case Some(executor) =>
logInfo("Executor " + fullId + " finished with state " + state +
message.map(" message " + _).getOrElse("") +
exitStatus.map(" exitStatus " + _).getOrElse(""))
//将executors内存缓存移除
executors -= fullId
finishedExecutors(fullId) = executor
trimFinishedExecutorsIfNecessary()
//释放executors占用的内存资源与cpu资源
coresUsed -= executor.cores
memoryUsed -= executor.memory
case None =>
logInfo("Unknown Executor " + fullId + " finished with state " + state +
message.map(" message " + _).getOrElse("") +
exitStatus.map(" exitStatus " + _).getOrElse(""))
}
maybeCleanupApplication(appId)
}
}
第四步:Master收到ExecutorStateChanged消息
源码位置:org/apache/spark/deploy/master/Master.scala
/**
* Executor状态发生改变
*/
case ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, state, message, exitStatus) => {
// 找到executor对应的App,然后再反过来通过App内部的executors缓存获得executor信息
val execOption = idToApp.get(appId).flatMap(app => app.executors.get(execId))
execOption match {
// 如果有值
case Some(exec) => {
// 设置executor的当前状态为LAUNCHING状态
val appInfo = idToApp(appId)
exec.state = state
if (state == ExecutorState.RUNNING) { appInfo.resetRetryCount() }
// 向driver同步发送ExecutorUpdated消息
exec.application.driver.send(ExecutorUpdated(execId, state, message, exitStatus))
// 如果executor的状态已经发生变化
if (ExecutorState.isFinished(state)) {
// Remove this executor from the worker and app
logInfo(s"Removing executor ${exec.fullId} because it is $state")
// If an application has already finished, preserve its
// state to display its information properly on the UI
if (!appInfo.isFinished) {
// 从app缓存中移除executor
appInfo.removeExecutor(exec)
}
// 从运行executor的worker的缓存中移除executor
exec.worker.removeExecutor(exec)
// 判断,如果executor的状态是非正常的
val normalExit = exitStatus == Some(0)
// Only retry certain number of times so we don't go into an infinite loop.
if (!normalExit) {
// 判断applcation当前的重试次数,是否达到了最大值,最大值为10次
if (appInfo.incrementRetryCount() < ApplicationState.MAX_NUM_RETRY) {
//重新进行调度
schedule()
} else {
// 否则就进行removeApplication操作
// 也就是说,executor反复调度都是失败,那么就认为application失败了
val execs = appInfo.executors.values
if (!execs.exists(_.state == ExecutorState.RUNNING)) {
logError(s"Application ${appInfo.desc.name} with ID ${appInfo.id} failed " +
s"${appInfo.retryCount} times; removing it")
removeApplication(appInfo, ApplicationState.FAILED)
}
}
}
}
}
case None =>
logWarning(s"Got status update for unknown executor $appId/$execId")
}
}
Worker启动
第一步:main方法
源码位置:org/apache/spark/deploy/worker/Worker.scala
def main(argStrings: Array[String]) {
SignalLogger.register(log)
val conf = new SparkConf
val args = new WorkerArguments(argStrings, conf)
// 创建rpc环境
val rpcEnv = startRpcEnvAndEndpoint(args.host, args.port, args.webUiPort, args.cores,
args.memory, args.masters, args.workDir)
rpcEnv.awaitTermination()
}
第二步:startRpcEnvAndEndpoint方法
def startRpcEnvAndEndpoint(
host: String,
port: Int,
webUiPort: Int,
cores: Int,
memory: Int,
masterUrls: Array[String],
workDir: String,
workerNumber: Option[Int] = None,
conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf): RpcEnv = {
// The LocalSparkCluster runs multiple local sparkWorkerX RPC Environments
val systemName = SYSTEM_NAME + workerNumber.map(_.toString).getOrElse("")
val securityMgr = new SecurityManager(conf)
// 创建RpcEnv
val rpcEnv = RpcEnv.create(systemName, host, port, conf, securityMgr)
val masterAddresses = masterUrls.map(RpcAddress.fromSparkURL(_))
//通过rpcEnv 创建一个Endpoint
//new Worker 的构造器中初始化了心跳超时时间为Master端的1/4及其他变量
rpcEnv.setupEndpoint(ENDPOINT_NAME, new Worker(rpcEnv, webUiPort, cores, memory,
masterAddresses, systemName, ENDPOINT_NAME, workDir, conf, securityMgr))
rpcEnv
}
Worker向Master注册
第一步:onStart()方法
override def onStart() {
assert(!registered)
logInfo("Starting Spark worker %s:%d with %d cores, %s RAM".format(
host, port, cores, Utils.megabytesToString(memory)))
logInfo(s"Running Spark version ${org.apache.spark.SPARK_VERSION}")
logInfo("Spark home: " + sparkHome)
// 创建工作目录
createWorkDir()
shuffleService.startIfEnabled()
// web相关操作
webUi = new WorkerWebUI(this, workDir, webUiPort)
webUi.bind()
// 向master注册
registerWithMaster()
// 度量系统相关(监控)
metricsSystem.registerSource(workerSource)
metricsSystem.start()
// Attach the worker metrics servlet handler to the web ui after the metrics system is started.
metricsSystem.getServletHandlers.foreach(webUi.attachHandler)
}
第二步:registerWithMaster()方法
/**
* 向master注册
*/
private def registerWithMaster() {
// onDisconnected may be triggered multiple times, so don't attempt registration
// if there are outstanding registration attempts scheduled.
registrationRetryTimer match {
case None =>
registered = false
// 循环所有的master,给master发送RegisterWorker消息(这里是注册线程池中)
registerMasterFutures = tryRegisterAllMasters()
connectionAttemptCount = 0
// 网络或者Master故障的时候就需要重新注册自己
// 注册重试次数超过阈值则直接退出
registrationRetryTimer = Some(forwordMessageScheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(
new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
self.send(ReregisterWithMaster)
}
},
INITIAL_REGISTRATION_RETRY_INTERVAL_SECONDS,
INITIAL_REGISTRATION_RETRY_INTERVAL_SECONDS,
TimeUnit.SECONDS))
case Some(_) =>
logInfo("Not spawning another attempt to register with the master, since there is an" +
" attempt scheduled already.")
}
}
第二步:tryRegisterAllMasters()方法
private def tryRegisterAllMasters(): Array[JFuture[_]] = {
masterRpcAddresses.map { masterAddress =>
registerMasterThreadPool.submit(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = {
try {
logInfo("Connecting to master " + masterAddress + "...")
val masterEndpoint =
rpcEnv.setupEndpointRef(Master.SYSTEM_NAME, masterAddress, Master.ENDPOINT_NAME)
//给Master发送消息注册Worker
//通过RpcEndpointRef 和Master建立通信向Master发送RegisterWorker消息,并带入workerid,host,Port,cores,内存等参数信息
masterEndpoint.send(RegisterWorker(
workerId, host, port, self, cores, memory, webUi.boundPort, publicAddress))
} catch {
case ie: InterruptedException => // Cancelled
case NonFatal(e) => logWarning(s"Failed to connect to master $masterAddress", e)
}
}
})
}
}
第三步:ReregisterWithMaster方法
/**
* Re-register with the master because a network failure or a master failure has occurred.
* If the re-registration attempt threshold is exceeded, the worker exits with error.
* Note that for thread-safety this should only be called from the rpcEndpoint.
* 重注册worker到master内存中
*
*
* 1.网络失败或者master死掉,该消息会被发送
* 2.如果worker的状态是已注册状态,取消尝试注册线程
* 3.注册线程池给master发送RegisterWorker消息
* 4.定时给自己发送ReregisterWithMaster消息
*
*/
private def reregisterWithMaster(): Unit = {
Utils.tryOrExit {
connectionAttemptCount += 1
if (registered) {
// 如果worker的状态为已注册状态,取消尝试注册线程
cancelLastRegistrationRetry()
// 只要还没有达到最大尝试次数
} else if (connectionAttemptCount <= TOTAL_REGISTRATION_RETRIES) {
logInfo(s"Retrying connection to master (attempt # $connectionAttemptCount)")
/**
* Re-register with the active master this worker has been communicating with. If there
* is none, then it means this worker is still bootstrapping and hasn't established a
* connection with a master yet, in which case we should re-register with all masters.
*
* It is important to re-register only with the active master during failures. Otherwise,
* if the worker unconditionally attempts to re-register with all masters, the following
* race condition may arise and cause a "duplicate worker" error detailed in SPARK-4592:
*
* (1) Master A fails and Worker attempts to reconnect to all masters
* (2) Master B takes over and notifies Worker
* (3) Worker responds by registering with Master B
* (4) Meanwhile, Worker's previous reconnection attempt reaches Master B,
* causing the same Worker to register with Master B twice
*
* Instead, if we only register with the known active master, we can assume that the
* old master must have died because another master has taken over. Note that this is
* still not safe if the old master recovers within this interval, but this is a much
* less likely scenario.
*/
master match {
case Some(masterRef) =>
// registered == false && master != None means we lost the connection to master, so
// masterRef cannot be used and we need to recreate it again. Note: we must not set
// master to None due to the above comments.
// 如果注册线程有结果了,那么取消注册线程
if (registerMasterFutures != null) {
registerMasterFutures.foreach(_.cancel(true))
}
val masterAddress = masterRef.address
// 注册线程池去给master发送RegisterWorker消息
registerMasterFutures = Array(registerMasterThreadPool.submit(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = {
try {
logInfo("Connecting to master " + masterAddress + "...")
val masterEndpoint =
rpcEnv.setupEndpointRef(Master.SYSTEM_NAME, masterAddress, Master.ENDPOINT_NAME)
masterEndpoint.send(RegisterWorker(
workerId, host, port, self, cores, memory, webUi.boundPort, publicAddress))
} catch {
case ie: InterruptedException => // Cancelled
case NonFatal(e) => logWarning(s"Failed to connect to master $masterAddress", e)
}
}
}))
// 这里是worker还没有注册到master内存中
case None =>
if (registerMasterFutures != null) {
registerMasterFutures.foreach(_.cancel(true))
}
// We are retrying the initial registration
registerMasterFutures = tryRegisterAllMasters()
}
// We have exceeded the initial registration retry threshold
// All retries from now on should use a higher interval
if (connectionAttemptCount == INITIAL_REGISTRATION_RETRIES) {
registrationRetryTimer.foreach(_.cancel(true))
registrationRetryTimer = Some(
// 定时给master发送ReregisterWithMaster消息
forwordMessageScheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
self.send(ReregisterWithMaster)
}
}, PROLONGED_REGISTRATION_RETRY_INTERVAL_SECONDS,
PROLONGED_REGISTRATION_RETRY_INTERVAL_SECONDS,
TimeUnit.SECONDS))
}
} else {
logError("All masters are unresponsive! Giving up.")
System.exit(1)
}
}
}
第四步:worker成功注册到master内存中
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
/**
* worker成功注册到master内存中
*/
case RegisteredWorker(masterRef, masterWebUiUrl) =>
logInfo("Successfully registered with master " + masterRef.address.toSparkURL)
// 标记该worker状态为注册成功
registered = true
// 更改master url,取消注册尝试,取消给自己发送ReregisterWithMaster消息
changeMaster(masterRef, masterWebUiUrl)
// 定时给Master发送SendHeartbeat心跳信息
forwordMessageScheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
self.send(SendHeartbeat)
}
}, 0, HEARTBEAT_MILLIS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
if (CLEANUP_ENABLED) {
logInfo(s"Worker cleanup enabled; old application directories will be deleted in: $workDir")
// 定制给自己发送WorkDirCleanup清理工作目录消息(旧app工作目录)
forwordMessageScheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
self.send(WorkDirCleanup)
}
}, CLEANUP_INTERVAL_MILLIS, CLEANUP_INTERVAL_MILLIS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
case SendHeartbeat =>
if (connected) { sendToMaster(Heartbeat(workerId, self)) }
//清理工作目录消息,会有一个线程定时发送该消息
case WorkDirCleanup =>
// Spin up a separate thread (in a future) to do the dir cleanup; don't tie up worker
// rpcEndpoint.
// Copy ids so that it can be used in the cleanup thread.
val appIds = executors.values.map(_.appId).toSet
val cleanupFuture = concurrent.future {
val appDirs = workDir.listFiles()
if (appDirs == null) {
throw new IOException("ERROR: Failed to list files in " + appDirs)
}
appDirs.filter { dir =>
// the directory is used by an application - check that the application is not running
// when cleaning up
val appIdFromDir = dir.getName
val isAppStillRunning = appIds.contains(appIdFromDir)
dir.isDirectory && !isAppStillRunning &&
!Utils.doesDirectoryContainAnyNewFiles(dir, APP_DATA_RETENTION_SECONDS)
}.foreach { dir =>
logInfo(s"Removing directory: ${dir.getPath}")
Utils.deleteRecursively(dir)
}
}(cleanupThreadExecutor)
cleanupFuture.onFailure {
case e: Throwable =>
logError("App dir cleanup failed: " + e.getMessage, e)
}(cleanupThreadExecutor)
......
// 注册失败,直接退出进程
case RegisterWorkerFailed(message) =>
if (!registered) {
logError("Worker registration failed: " + message)
System.exit(1)
}
}