| 上一篇:【目录】====== 【回到目录】====== 下一篇:【第一章课后习题参考解答】 |
|---|
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import leastsq
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 目标函数
def real_func(x):
return np.sin(2*np.pi*x)
# 多项式
def fit_func(p, x):
f = np.poly1d(p)
return f(x)
# 残差
def residuals_func(p, x, y):
ret = fit_func(p, x) - y #注意此处没有平方
return ret
regularization = 0.0001
#正则化之后的残差
def residuals_func_regularization(p, x, y):
ret = fit_func(p, x) - y
ret = np.append(ret, np.sqrt(0.5*regularization*np.square(p))) # L2范数作为正则化项
return ret
# 十个点'
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 10)
x_points = np.linspace(0, 1, 1000)
# 加上正态分布噪音的目标函数的值
y_ = real_func(x)
y = [np.random.normal(0, 0.1) + y1 for y1 in y_]
index = 0
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8))
def fitting(M=0):
"""
M 为 多项式的次数
"""
# 随机初始化多项式参数
p_init = np.random.rand(M + 1)
# 最小二乘法
p_lsq = leastsq(residuals_func, p_init, args=(x, y))
#p_lsq = leastsq(residuals_func_regularization, p_init, args=(x, y)) #加入正则化
print('Fitting Parameters:', p_lsq[0])
# 可视化
plt.subplot(141 + index)
plt.plot(x_points, real_func(x_points), label='real')
plt.plot(x_points, fit_func(p_lsq[0], x_points), label='fitted curve')
plt.plot(x, y, 'bo', label='noise')
plt.legend()
return p_lsq
for i in [0, 1, 3, 9]:
lsq_0 = fitting(i)
index += 1
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.92, bottom=0.08, left=0.10, right=0.95, hspace=0.25,
wspace=0.35) #调整子图间距
plt.savefig("demo.jpg")
plt.show()
正则化前
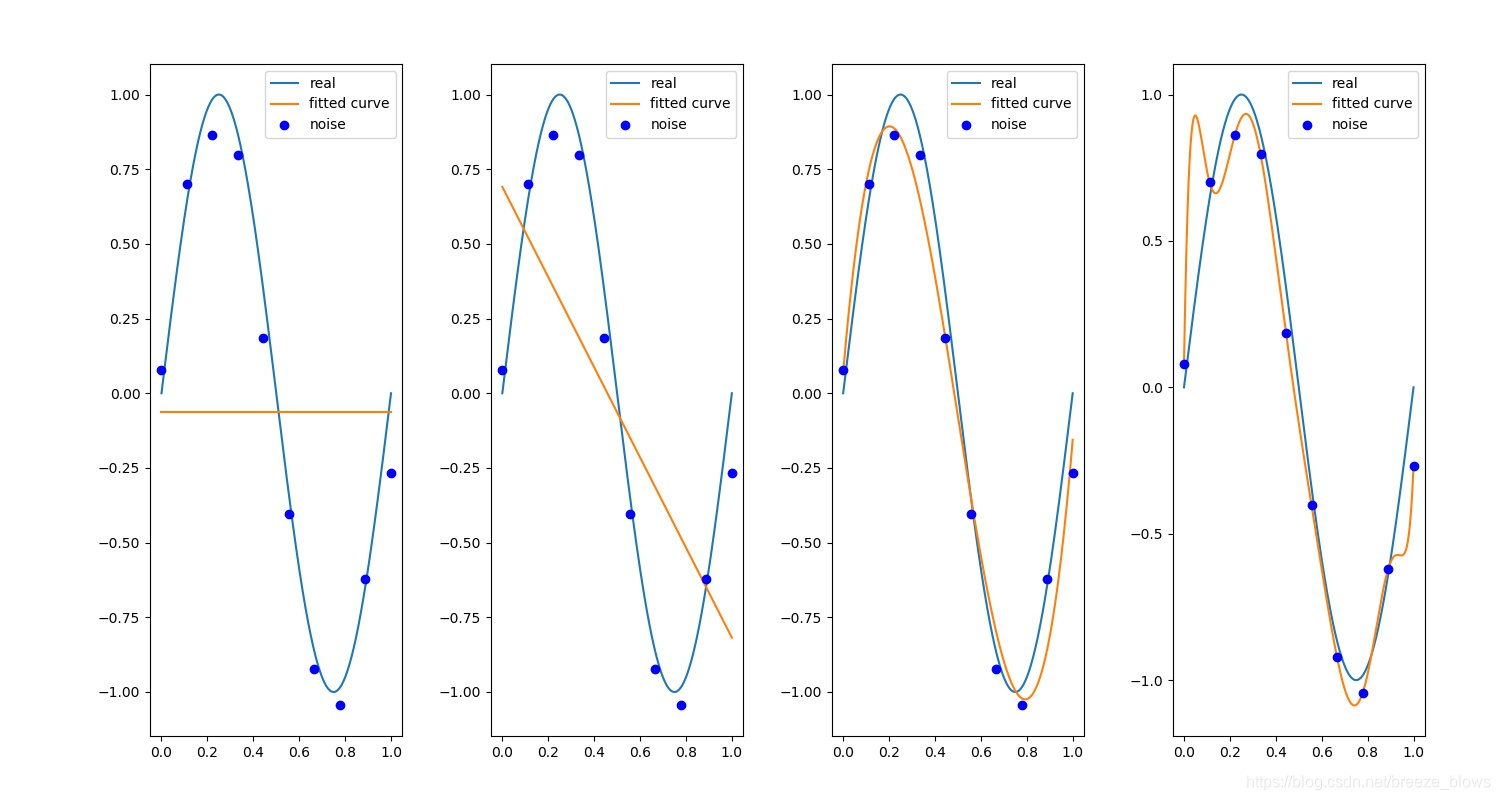
正则化后
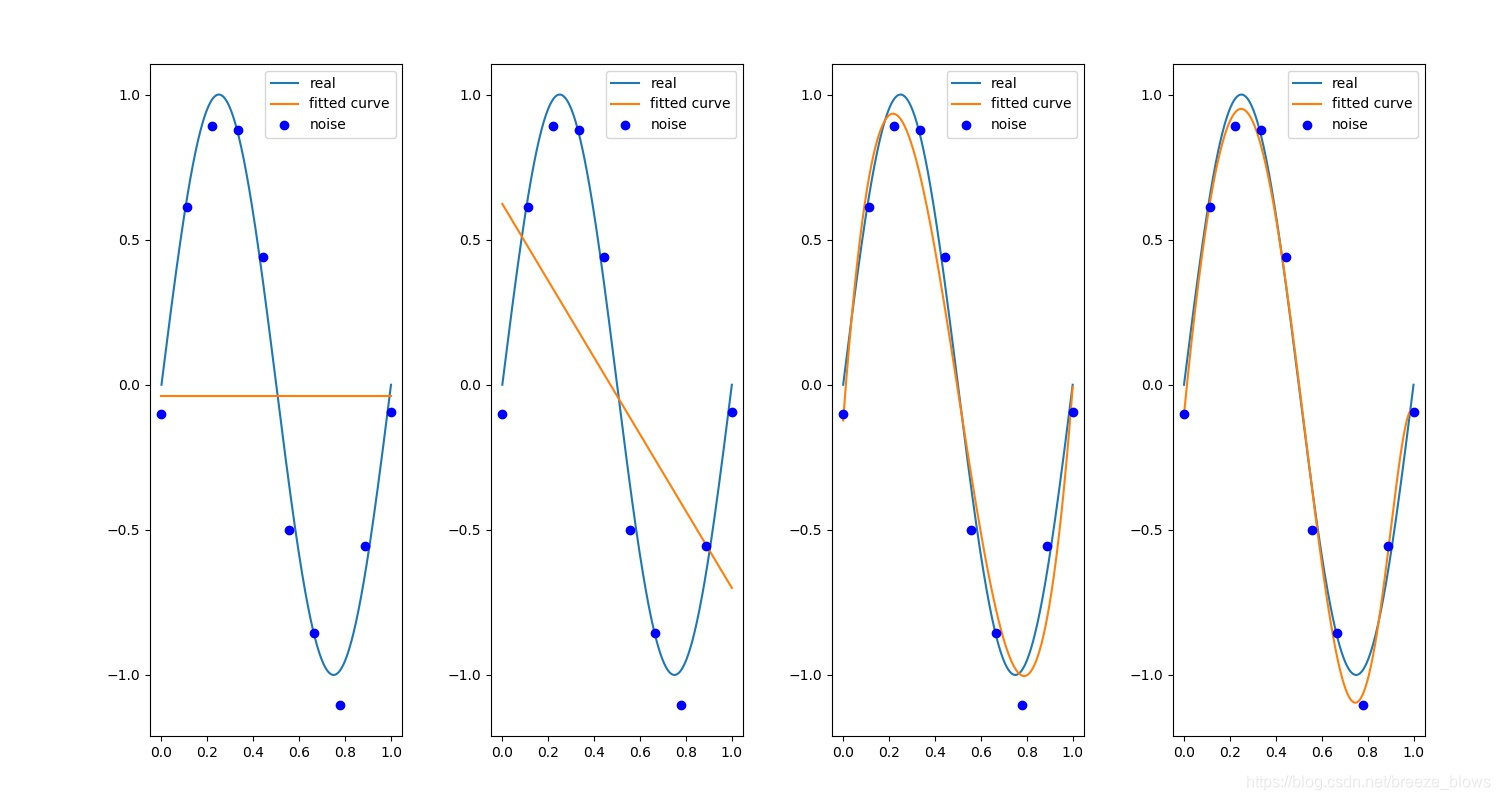
可以明显看出正则化的作用