版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/lyf52010/article/details/80464962
1.需要在会话中完成op
2.初始化操作
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
3.fetch run多个op
print(sess.run([mul,add]))
4.placeholder + feed_dict
input1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[1,2])
input2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
output = tf.multiply(input1,input2)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(output,feed_dict={input1:[[1,2]],input2:3}))
小练习
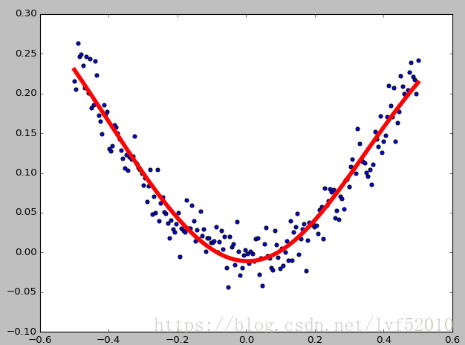
下面贴一个非线性回归练习:
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x_data = np.linspace(-0.5,0.5,200).reshape(-1,1) noise = np.random.normal(0,0.02,x_data.shape) y_data= np.square(x_data )+noise #定义两个placeholder x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1]) y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None,1]) #定义神经网络 Weights_L1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1,10])) bias_L1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,10])) Wx_plus_b_L1 = tf.matmul(x,Weights_L1) + bias_L1 L1 = tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L1) #定义输出层 Weight_L2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10,1])) bias_L2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,1])) Wx_plus_b_L2 = tf.matmul(L1,Weight_L2) + bias_L2 presiction = tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L2) #loss loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(presiction-y_data)) optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2) train = optimizer.minimize(loss) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) for step in range(2000): sess.run(train, feed_dict={x:x_data,y:y_data}) if step % 20 ==0: print(step, sess.run(Weight_L2)) prediction_value = sess.run(presiction,feed_dict={x:x_data,y:y_data}) plt.figure() plt.scatter(x_data,y_data) plt.plot(x_data,prediction_value,'r-',lw=5) plt.show()